标签:
1.首先我们编写一个生成4种模式的文件的程序案例:
(1)首先是activity_main.xml文件:
1 <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 2 xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" 3 android:layout_width="match_parent" 4 android:layout_height="match_parent" 5 tools:context=".MainActivity" > 6 7 <Button 8 android:onClick="click" 9 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 10 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 11 android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" 12 android:layout_centerVertical="true" 13 android:text="生成文件" /> 14 15 <RadioGroup 16 android:id="@+id/rg_mode" 17 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 18 android:layout_height="wrap_content" > 19 20 <RadioButton 21 android:id="@+id/rb_private" 22 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 23 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 24 android:checked="true" 25 android:text="私有 private" /> 26 27 <RadioButton 28 android:id="@+id/rb_readble" 29 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 30 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 31 android:text="全局可读 world readable" /> 32 33 <RadioButton 34 android:id="@+id/rb_writeable" 35 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 36 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 37 android:text="全局可写world writeable" /> 38 39 <RadioButton 40 android:id="@+id/rb_public" 41 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 42 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 43 android:text="全局可读可写public" /> 44 </RadioGroup> 45 46 </RelativeLayout>
布局效果如下图:

(2)接下来是代码逻辑部分如下:MainActivity.java:
1 package com.itheima.filemode; 2 3 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 4 5 import android.app.Activity; 6 import android.os.Bundle; 7 import android.view.View; 8 import android.widget.RadioGroup; 9 10 public class MainActivity extends Activity { 11 private RadioGroup rg_mode; 12 13 @Override 14 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 15 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 16 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); 17 rg_mode = (RadioGroup) findViewById(R.id.rg_mode); 18 } 19 20 /** 21 * 按钮的点击事件 22 * 23 * @param view 24 */ 25 public void click(View view) { 26 try { 27 int id = rg_mode.getCheckedRadioButtonId(); 28 FileOutputStream fos = null; 29 switch (id) { 30 case R.id.rb_private:// 私有文件 31 fos = openFileOutput("private.txt", MODE_PRIVATE); 32 break; 33 case R.id.rb_public:// 可读可写文件 34 fos = openFileOutput("public.txt", MODE_WORLD_READABLE+MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE); 35 break; 36 case R.id.rb_readble:// 全局可读文件 37 fos = openFileOutput("readble.txt", MODE_WORLD_READABLE); 38 break; 39 case R.id.rb_writeable:// 全局可写文件 40 fos = openFileOutput("/sdcard/files/writeable.txt", MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE); 41 break; 42 } 43 fos.write("dfafda".getBytes()); 44 fos.close(); 45 } catch (Exception e) { 46 e.printStackTrace(); 47 } 48 } 49 }
openFileOutput()方法的第一参数用于指定文件名称,不能包含路径分隔符“/” ,如果文件不存在,Android 会自动创建它。创建的文件保存在/data/data/<package name>/files目录,如: /data/data/cn.itcast.action/files/itcast.txt ,通过点击Eclipse菜单“Window”-“Show View”-“Other”,在对话窗口中展开android文件夹,选择下面的File Explorer视图,然后在File Explorer视图中展开/data/data/<package name>/files目录就可以看到该文件。
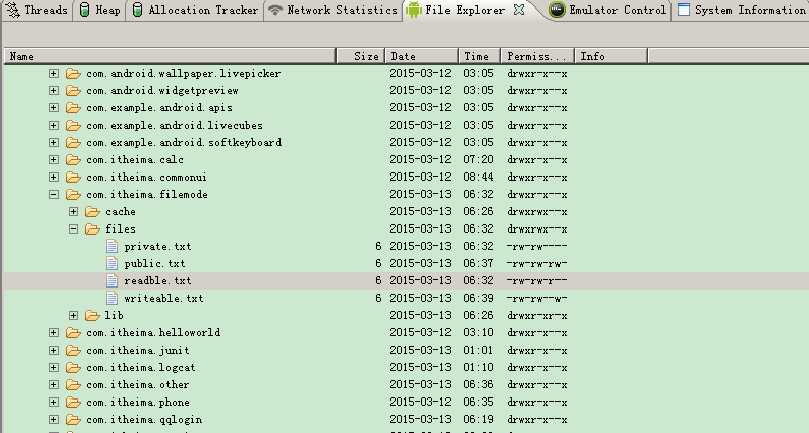
我们分别点击界面上不同的RadioButton,生成不同文件如下图:
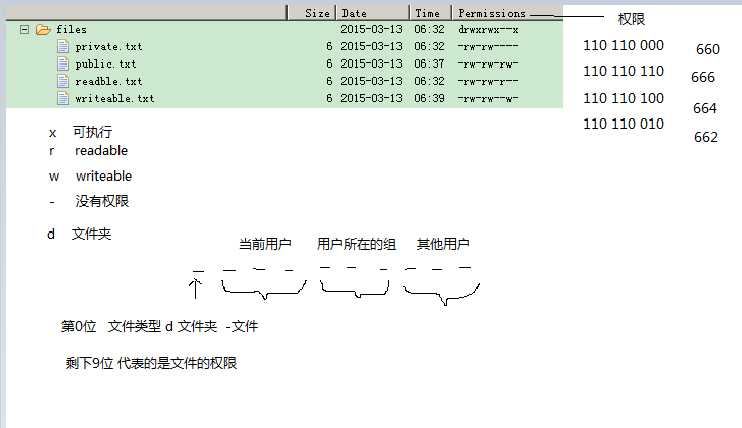
2.小结:android下文件访问的权限:
* 默认情况下所有的文件创建出来都是私有的。只有自己的应用程序可以访问里面的数据,别的应用程序是不可以访问数据的。
* 特殊情况利用api可以修改文件的权限。
openFileOutput("文件名","文件的访问模式"); 私有 只读 只写 可读可写
* 底层是通过Linux操作系统的文件模式来实现的。
Context.MODE_PRIVATE:为默认操作模式,代表该文件是私有数据,只能被应用本身访问,在该模式下,写入的内容会覆盖原文件的内容,如果想把新写入的内容追加到原文件中。可以使用Context.MODE_APPEND
Context.MODE_APPEND:模式会检查文件是否存在,存在就往文件追加内容,否则就创建新文件。
Context.MODE_WORLD_READABLE和Context.MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE用来控制其他应用是否有权限读写该文件。
MODE_WORLD_READABLE:表示当前文件可以被其他应用读取;
MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE:表示当前文件可以被其他应用写入。
Android(java)学习笔记184:生成4种模式的文件
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/hebao0514/p/4746202.html