标签:
java中有好多集合:List,ArrayList,Vector,HashSetTreeSet,它们之间的区别,java集合的框架等等总是很模糊,称有时间总结下。
一、Collection接口和Iterator接口
1.Collection框架:
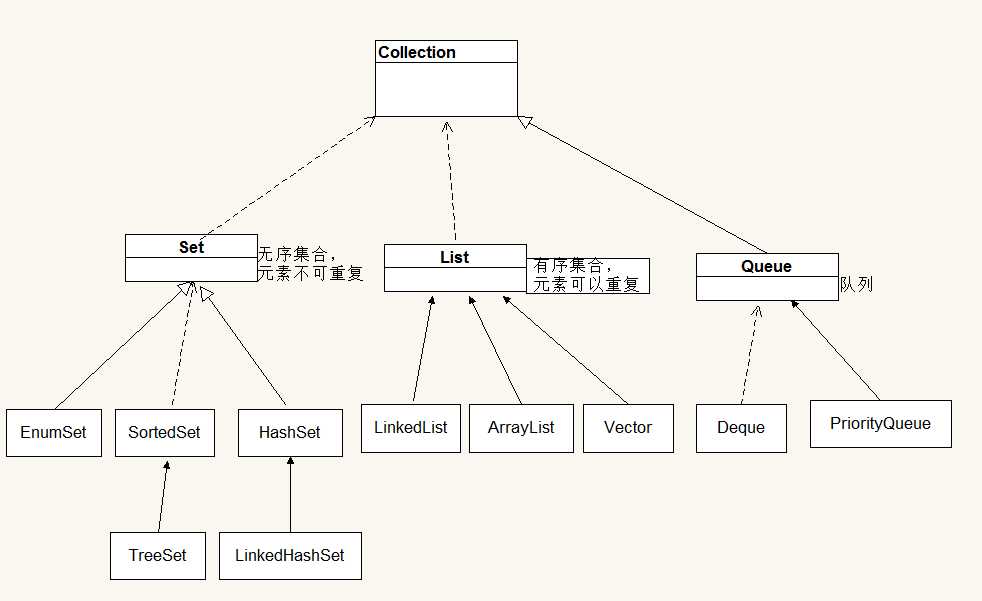
collection接口主要定义了一些操作集合元素的方法:
|
|
Ensures that this collection contains the specified element (optional operation).如果插入成功,返回true |
|
|
addAll Adds all of the elements in the specified collection to this collection (optional operation).改变返回true |
|
|
clear Removes all of the elements from this collection (optional operation). |
|
|
Returns true if this collection contains the specified element. |
|
|
containsAll Returns true if this collection contains all of the elements in the specified collection. |
|
|
Compares the specified object with this collection for equality. |
|
|
hashCode Returns the hash code value for this collection. |
。。。。。。具体可看文档
2.使用Iterator接口遍历几何元素
Iterrator接口隐藏了各种Collection实现类的细节,向应用程序提供了遍历Collection集合元素的统一编程接口。Iterator接口里定义了如下三个方法:
Boolean hashNext(): 如果被迭代的集合元素还没有被遍历,则返回true.
Object next(): 返回集合里的下一个元素。
Void remove(): 删除集合里上一次next方法返回的元素。
**当使用Iterator迭代访问Collection集合元素时,Collection集合里的元素不能被改变,只有通过Iterator的remove方法删除上一次next方法返回的集合元素才可以;否则将引发java.util.Concurrent ModificationException异常。
下面开始一个个类介绍
二、set集合
Set集合的方法与Collection基本上完全一样,它没有提供额外的方法。实际上Set就是Collection,只是行为略有不同(Set不允许包含重复元素)。
Set判断两个对象是否相同是根据equals方法。也就是说,只要两个对象用equals方法方法比较返回false,Set就会接受这两个对象。
1.HashSet是Set的典型实现,HashSet按Hash算法来存储集合中的元素,因此具有很好的存取和查找性能。
特点:不能保证元素的排列顺序;不是同步的,不是线程安全;集合值可以是null。
HashSet集合判断两个元素的相等的标准是两个对象通过equals方法比较相等,并且两个对象的hashCode()方法返回值也相等。
示例:
import java.util.*;
//类A的equals方法总是返回true,但没有重写其hashCode()方法
class A
{
public boolean equals(Object obj)
{
return true;
}
}
//类B的hashCode()方法总是返回1,但没有重写其equals()方法
class B
{
public int hashCode()
{
return 1;
}
}
//类C的hashCode()方法总是返回2,但没有重写其equals()方法
class C
{
public int hashCode()
{
return 2;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj)
{
return true;
}
}
public class TestHashSet
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
HashSet books = new HashSet();
//分别向books集合中添加2个A对象,2个B对象,2个C对象
books.add(new A());
books.add(new A());
books.add(new B());
books.add(new B());
books.add(new C());
books.add(new C());
System.out.println(books);
}
}
输出:[B@1, B@1, C@2, A@659e0bfd, A@2a139a55]
可以看出HashSet把A,B当成两个对象,C只有一个。
2.LinkedHashSet类
LinkedHashSet集合同样是根据元素的hashCode值来决定元素的存储位置,但是它同时使用链表维护元素的次序。这样使得元素看起 来像是以插入顺序保存的,也就是说,当遍历该集合时候,LinkedHashSet将会以元素的添加顺序访问集合的元素。
LinkedHashSet在迭代访问Set中的全部元素时,性能比HashSet好,但是插入时性能稍微逊色于HashSet。
import java.util.*;
public class TestLinkedHashSet
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedHashSet books = new LinkedHashSet();
books.add("第一个");
books.add("第二个");
//删除 Struts2权威指南
books.remove("第一个");
//重新添加 Struts2权威指南
books.add("第一个");
System.out.println(books);//[第二个, 第一个]
}
}
输出:[第二个, 第一个] 可以看到顺序是按插入顺序排列的。
3.TreeSet类
TreeSet是SortedSet接口的实现类,TreeSet可以确保集合元素处于排序状态。TreeSet支持两种排序方式,自然排序 和定制排序,其中自然排序为默认的排序方式。向TreeSet中加入的应该是同一个类的对象。
TreeSet判断两个对象不相等的方式是两个对象通过equals方法返回false,或者通过CompareTo方法比较没有返回0。向TreeSet中添加的应该是同一个类的对象,且最好是不可变对象。
1.自然排序
自然排序使用要排序元素的CompareTo(Object obj)方法来比较元素之间大小关系,然后将元素按照升序排列。
Java提供了一个Comparable接口,该接口里定义了一个compareTo(Object obj)方法,该方法返回一个整数值,实现了该接口的对象就可以比较大小。
obj1.compareTo(obj2)方法如果返回0,则说明被比较的两个对象相等,如果返回一个正数,则表明obj1大于obj2,如果是 负数,则表明obj1小于obj2。
如果我们将两个对象的equals方法总是返回true,则这两个对象的compareTo方法返回应该返回0
import java.util.*;
class R implements Comparable
{
int count;
public R(int count)
{
this.count = count;
}
public String toString()
{
return "R(count属性:" + count + ")";
}
public boolean equals(Object obj)
{
if (obj instanceof R)
{
R r = (R)obj;
if (r.count == this.count)
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public int compareTo(Object obj)
{
R r = (R)obj;
if (this.count > r.count)
{
return 1;
}
else if (this.count == r.count)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
return -1;
}
}
}
public class TestTreeSet2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
TreeSet ts = new TreeSet();
ts.add(new R(5));
ts.add(new R(-3));
ts.add(new R(9));
ts.add(new R(-2));
//打印TreeSet集合,集合元素是有序排列的
System.out.println(ts);
//取出第一个元素
R first = (R)ts.first();
//为第一个元素的count属性赋值
first.count = 20;
//取出最后一个元素
R last = (R)ts.last();
//为最后一个元素的count属性赋值,与倒数第二个元素count属性相同
last.count = -2;
//再次输出count将看到TreeSet里的元素处于无序状态,且有重复元素
System.out.println(ts);
//删除属性被改变的元素,删除失败
ts.remove(new R(-2));
System.out.println(ts);
//删除属性没有改变的元素,删除成功
ts.remove(new R(5));
ts.remove(new R(20));
System.out.println(ts);
}
}
输出结果:
/*
---------- java运行 ----------
[R(count属性:-3), R(count属性:-2), R(count属性:5), R(count属性:9)]
[R(count属性:20), R(count属性:-2), R(count属性:5), R(count属性:-2)] //这里改变之后并没有重新排序,所以TreeSet中最好放不可改变的对象。
[R(count属性:20), R(count属性:-2), R(count属性:5), R(count属性:-2)] //删除-2失败,因为属性被改变
[R(count属性:20), R(count属性:-2), R(count属性:-2)] //没有改变的5可以删除
输出完成 (耗时 0 秒) - 正常终止*/
2.定制排序
自然排序是根据集合元素的大小,以升序排列,如果要定制排序,应该使用Comparator接口,实现 int compare(T o1,T o2)方法,该方法用于比较o1和o2的大小:如果该方法返回正整数,则表示o1大于o2;如果方法返回0,则表示o1等于o2,如果该方法返回负整数,则表示o1小于o2。
如果需要定制排序,则需要在创建TreeSet集合时提供一个Comparator对象与该TreeSet集合关联,由Comparator对象负责几何元素的排序逻辑:
import java.util.*;
class M
{
int age;
public M(int age)
{
this.age = age;
}
public String toString(){
return "M age:"+age;
}
}
public class TestTreeSet3
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
TreeSet ts = new TreeSet(new Comparator()
{
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2)
{
/*int age1 = o1 instanceof M ? ((M)o1).age :((N)o1).age;
int age2 = o1 instanceof M ? ((M)o2).age :((N)o2).age;
return age1 - age2;*/
M m1 = (M)o1;
M m2 = (M)o2;
if (m1.age > m2.age)
{
return -1;
}
else if (m1.age == m2.age)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
return 1;
}
}
});
ts.add(new M(5));
ts.add(new M(-3));
ts.add(new M(9));
System.out.println(ts);//[M age:9, M age:5, M age:-3]
}
}
输出结果·(降序):[M age:9, M age:5, M age:-3]
4.各Set实现类比较:
HashSet和TreeSet是set的两个典型实现,HashSet的性能比TreeSet好(特别是最常用的添加,查询元素等操作).只有当需要一个保持排序的Set时,才应该使用TreeSet,否则使用HashSet
LinkedHashSet:对于普通的插入删除操作,比HashSet慢,遍历会更快。
另外:Set的三个实现类HashSet,TreeSet和EnemSet都是线程不安全的,如果有多个线程访问一个Set集合,则必须手动保持同步:
可用Collections的工具类:例如:
SortedSet s = Collections.synchronizedSortedSet(new TreeSet(…));
Set集合终于总结完啦。。
这篇已经够长啦,List集合在下一篇。。。
转发请注明:http://www.cnblogs.com/jycboy/p/set.html
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/jycboy/p/set.html