标签:
利用了pyinotify库,我用的是这里的这个,https://github.com/seb-m/pyinotify
其实网上yum上也有pyinotify库可以安装。
写入数据库是pymysql这里做一下记录,
先务pyinotify实现一个tail -f 的功能:
#!/opt/python3/bin/python3
#
import pyinotify
import time
import os
import sys
class ProcessTransientFile(pyinotify.ProcessEvent):
def process_IN_MODIFY(self,event):
line = file.readline()
if line:
print(line, end=‘‘)
if __name__ == ‘__main__‘:
filename = sys.argv[1]
file = open(filename,‘r‘)
st_results = os.stat(filename)
st_size = st_results[6]
file.seek(st_size)
wm = pyinotify.WatchManager()
notifier = pyinotify.Notifier(wm)
wm.watch_transient_file(filename, pyinotify.IN_MODIFY, ProcessTransientFile)
notifier.loop()
然后通过pytaif /usr/local/nginx/logs/www.tbbpay.com.access.log就可以进行日志的实时查看。
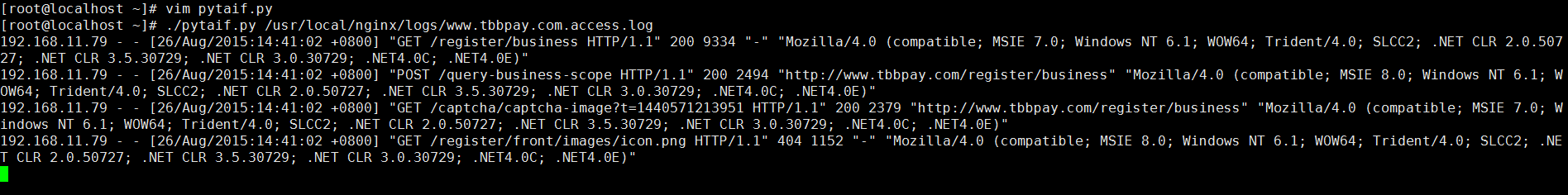
这个是实时查看,和tail -f 功能一样。只打印一行,
现在就是定义一个nginxloganalyzer函数进行日志分析,是默认的nginx日志,这个没有用正则,用了土办法查找特定字符。
def nginxLogAnalyzer(line):
#print(line)
g1 = line.find(‘[‘)
g2 = line.find(‘]‘)
h1 = line.find(‘"‘)
h2 = line.find(‘"‘, h1+1)
h3 = line.find(‘"‘, h2+1)
h4 = line.find(‘"‘, h3+1)
h5 = line.find(‘"‘, h4+1)
h6 = line.find(‘"‘, h5+1)
#print("g1:%d"%g1)
#print("g2:%d"%g2)
#print("h1:%d"%h1)
#print("h2:%d"%h2)
#print("h3:%d"%h3)
#print("h4:%d"%h4)
#print("h5:%d"%h5)
#print("h6:%d"%h6)
remote_addr = ""
remote_user = ""
time=""
time_local = ""
time_zone = ""
request = ""
status = ""
body_bytes_sent = ""
http_referer = ""
http_user_agent = ""
http_x_forwarded_for = ""
time = line[g1+1:g2]
time_local = time.split()[0]
time_zone = time.split()[1]
request = line[h1+1:h2]
http_referer = line[h3+1:h4]
http_user_agent = line[h5+1:h6]
remote_addr = line.split()[0]
remote_user = line.split()[1]
status = line.split()[8]
body_bytes_sent = line.split()[9]
request = urllib.parse.unquote(request)
print("time:%s"%(time) )
print("time_local:%s"%(time_local) )
print("time_zone:%s"%(time_zone) )
print("request:%s"%(request) )
print("http_referer:%s"%(http_referer) )
print("http_user_agent:%s"%(http_user_agent) )
print("status:%s"%(status) )
print("body_bytes_sent:%s"%(body_bytes_sent) )
print("request--------:%s"%(urllib.parse.unquote(request)) )
l = []
l.append(remote_addr)
l.append(remote_user)
l.append(time)
l.append(time_local)
l.append(time_zone)
l.append(request)
l.append(status)
l.append(body_bytes_sent)
l.append(http_referer)
l.append(http_user_agent)
l.append(http_x_forwarded_for)
print(l)
return l
CREATE DATABASE `nginxlog` CHARSET=utf8; use nginxlog; CREATE TABLE `nginxlog` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `remote_add` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL, `remote_user` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL, `time` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL, `time_local` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL, `time_zone` varchar(10) DEFAULT NULL, `request` varchar(1024) DEFAULT NULL, `status` varchar(10) DEFAULT NULL, `body_bytes_sent` varchar(10) DEFAULT NULL, `http_referer` varchar(1024) DEFAULT NULL, `http_user_agent` varchar(1024) DEFAULT NULL, `http_x_forwarded_for` varchar(1024) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`), ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1001 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON nginxlog.* TO ‘nginxlog‘@‘192.168.1.112‘ IDENTIFIED BY ‘nginxlog‘;
def intodb(line):
l = nginxLogAnalyzer(line)
s = "INSERT INTO `nginxlog`.`nginxlog` (`id` ,`remote_add` ,`remote_user` ,`time` ,`time_local` ,`time_zone` ,`request` ,`status` ,`body_bytes_sent` ,`http_referer` ,`http_user_agent` ,`http_x_forwarded_for` )VALUES (‘null‘, ‘%s‘, ‘%s‘, ‘%s‘, ‘%s‘, ‘%s‘, ‘%s‘, ‘%s‘, ‘%s‘, ‘%s‘, ‘%s‘, ‘%s‘);"%(l[0],l[1],l[2],l[3],l[4],l[5],l[6],l[7],l[8],l[9],l[10])
print(s)
cur.execute(s)
conn.commit()
[root@localhost ~]# cat nginxLogtoMysql.py
#!/opt/python3/bin/python3
#
import pyinotify
import time
import os
import sys
import urllib
import urllib3
import pymysql
class ProcessTransientFile(pyinotify.ProcessEvent):
def process_IN_MODIFY(self,event):
line = file.readline()
if line:
#nginxLogAnalyzer(line)
intodb(line)
def nginxLogAnalyzer(line):
print(line,end=‘‘)
g1 = line.find(‘[‘)
g2 = line.find(‘]‘)
h1 = line.find(‘"‘)
h2 = line.find(‘"‘, h1+1)
h3 = line.find(‘"‘, h2+1)
h4 = line.find(‘"‘, h3+1)
h5 = line.find(‘"‘, h4+1)
h6 = line.find(‘"‘, h5+1)
remote_addr = ""
remote_user = ""
time=""
time_local = ""
time_zone = ""
request = ""
status = ""
body_bytes_sent = ""
http_referer = ""
http_user_agent = ""
http_x_forwarded_for = ""
time = line[g1+1:g2]
time_local = time.split()[0]
time_zone = time.split()[1]
request = line[h1+1:h2]
http_referer = line[h3+1:h4]
http_user_agent = line[h5+1:h6]
remote_addr = line.split()[0]
remote_user = line.split()[1]
status = line.split()[8]
body_bytes_sent = line.split()[9]
request = urllib.parse.unquote(request)
#print("time:%s"%(time) )
#print("time_local:%s"%(time_local) )
#print("time_zone:%s"%(time_zone) )
#print("request:%s"%(request) )
#print("http_referer:%s"%(http_referer) )
#print("http_user_agent:%s"%(http_user_agent) )
#print("status:%s"%(status) )
#print("body_bytes_sent:%s"%(body_bytes_sent) )
#print("request--------:%s"%(urllib.parse.unquote(request)) )
l = []
l.append(remote_addr)
l.append(remote_user)
l.append(time)
l.append(time_local)
l.append(time_zone)
l.append(request)
l.append(status)
l.append(body_bytes_sent)
l.append(http_referer)
l.append(http_user_agent)
l.append(http_x_forwarded_for)
#print(l)
return l
def intodb(line):
l = nginxLogAnalyzer(line)
s = "INSERT INTO `nginxlog`.`nginxlog` (`id` ,`remote_add` ,`remote_user` ,`time` ,`time_local` ,`time_zone` ,`request` ,`status` ,`body_bytes_sent` ,`http_referer` ,`http_user_agent` ,`http_x_forwarded_for` )VALUES (‘null‘, ‘%s‘, ‘%s‘, ‘%s‘, ‘%s‘, ‘%s‘, ‘%s‘, ‘%s‘, ‘%s‘, ‘%s‘, ‘%s‘, ‘%s‘);"%(l[0],l[1],l[2],l[3],l[4],l[5],l[6],l[7],l[8],l[9],l[10])
#print(s)
cur.execute(s)
conn.commit()
if __name__ == ‘__main__‘:
conn = pymysql.connect(host=‘192.168.1.112‘, port=3306, user=‘nginxlog‘, passwd=‘nginxlog‘, db=‘nginxlog‘,charset="utf8")
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("SET NAMES utf8")
filename = sys.argv[1]
file = open(filename,‘r‘)
st_results = os.stat(filename)
st_size = st_results[6]
file.seek(st_size)
wm = pyinotify.WatchManager()
notifier = pyinotify.Notifier(wm)
wm.watch_transient_file(filename, pyinotify.IN_MODIFY, ProcessTransientFile)
notifier.loop()
[root@localhost ~]#
运行方式如下:
./nginxlogtomysql.py /usr/local/nginx/logs/www.tbbpay.com.access.log
效果如下

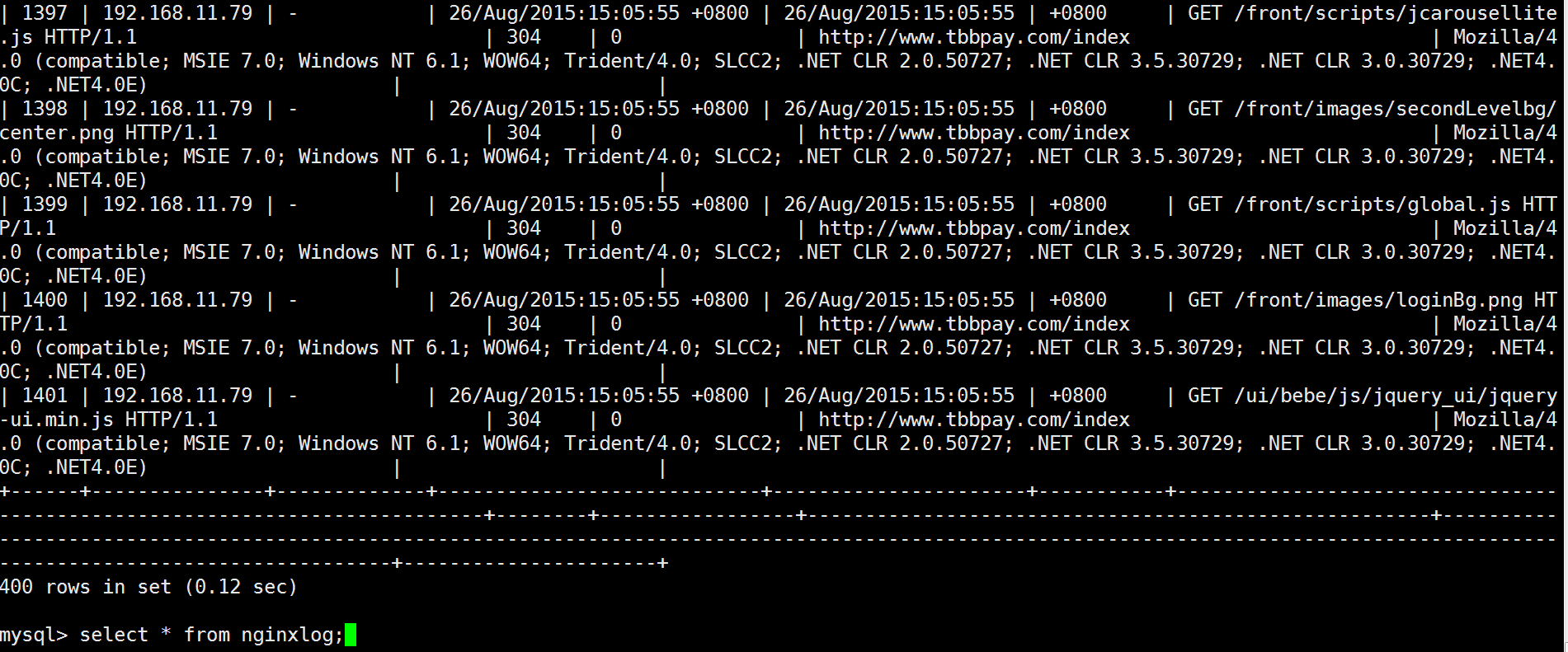
python利用inotify实现把nginx日志实时写入数据库
标签:
原文地址:http://my.oschina.net/lenglingx/blog/497321