标签:
[1]定义:基本包装类型是特殊的引用类型。每当读取一个基本类型值的时候,后台就会创建一个对应的基本包装类型的对象,从而可能调用一些方法来操作这些数据。
e.g. var s1 = ‘some text‘;
var s2 = s1.substring(2);
//在上述过程中,实际上发生了三个步骤
var s1 = new String(‘some text‘); //(1)创建String类型的一个实例
var s2 = s1.substring(2); //(2)在实例上调用指定的方法
s1 = null; //(3)销毁这个实例
[注意]引用类型和基本包装类型的主要区别是对象的生存期。使用new操作符创建的引用类型的实例,在执行流离开当前作用域之前都一直保存在内存中。而自动创建的基本包装类型的对象,则只存在于一行代码的执行瞬间,然后立即被销毁。这意味着我们不能在运行时为基本类型值添加属性和方法。
var s1 = ‘some text‘; s1.color = ‘red‘; alert(s1.color);//undefined
[2]显式创建包装类型的两种方式:
[2.1]Object方式[不建议使用]
[2.1.1]var s = new Object(‘abc‘);
[2.1.2]var b = new Object(true);
[2.1.3]var n = new Object(123);
[2.2]构造函数方式[不建议使用]
[2.2.1]var s = new String(‘abc‘);
[2.2.2]var b = new Boolean(true);
[2.2.3]var n = new Number(123);
[注意]使用new调用基本包装类型的构造函数与直接调用同名的转型函数是不一样的
var value = ‘25‘; var number = Number(value); console.log(typeof number);//number var obj = new Number(value); console.log(typeof obj);//object
[3]Boolean类型是与布尔值对应的引用类型,在布尔表达式中使用Boolean对象容易造成误解[不建议使用]
[3.1]继承的方法
[3.1.1]valueOf():返回基本类型值true 或 false
[3.1.2]toString()和toLocaleString():返回字符串‘true‘ 或‘false‘
[4]Number类型是与数字值对应的引用类型,在使用typeof和instance操作符时容易产生误解[不建议使用]
[4.1]继承的方法
[4.1.1]valueOf():返回基本类型的数值
[4.1.2]toString()和toLocaleString():返回字符串形式的数值
[tips]可以为toString()方法传递一个表示基数的参数
var num = 10; console.log(num.toString());//‘10‘ console.log(num.toString(2));//‘1010‘ console.log(num.toString(8));//‘12‘ console.log(num.toString(10));//‘10‘ console.log(num.toString(16));//‘a‘
[4.2]数值格式化为字符串的方法
[4.2.1]toFixed():按照指定的小数位返回数值四舍五入后的字符串表示(常用于处理货币值)
[注意]toFixed()里的参数只接受0-20,若不传参则相当于参数是0
var num = 10.456; console.log(num.toFixed(2));//10.46 console.log(num.toFixed());//10
[4.2.2]toExponential():返回指数表示法(e表示法)的数值的字符串表示,参数表示转换后的小数位数
[注意]toExponential()里的参数只接受0-20,若不传参则相当于不针对小数进行四舍五入
var num = 10.456; console.log(num.toExponential(2));//1.05e+1 console.log(num.toExponential());//1.0456e+1
[4.2.3]toPrecision():接收一个参数,即表示数值的所有数字的位数(不包括指数部分),自动调用toFixed()或toExponential()
[注意]toFixed()里的参数只接受1-21,若不传参则不对原数字进行任何操作
var num = 10; console.log(num.toPrecision(3));//10.0 console.log(num.toPrecision(2));//10 console.log(num.toPrecision(1));//1e+1 console.log(num.toPrecision());//10
[5]String类型是与字符串对应的引用类型
[5.1]length属性:String类型的每个实例都有一个length属性,表示字符的个数。该属性只可读取,不可改变
[5.2]继承的方法:valueOf()、toString()和toLocaleString():返回字符串表示
[5.3]访问字符方法:接收一个基于0的字符位置的参数,并以单字符字符串的形式返回
[5.3.1]charAt():返回给定位置的字符
[注意]当参数为空时,默认参数为0;当参数超出范围时,则什么都不输出
[5.3.2]中括号加数字索引(ECMAScript5):返回给定位置的字符(IE7-不支持,输出undefined)
[注意]当参数为空或参数超出范围时,则输出undefined
[5.3.3]charCodeAt():返回给定位置的字符编码,字符编码为Number类型
[注意]当参数为空时,默认参数为0;当参数超出范围时,则输出NaN
[5.3.4]String.fromCharCode():把一个或多个编码值转成一个字符串
[注意]参数范围为ASCII表的范围
var stringValue = ‘hello world‘; console.log(stringValue.charAt(1));//‘e‘ console.log(stringValue.charCodeAt(1));//101 console.log(typeof stringValue.charCodeAt(1));//‘number‘ console.log(String.fromCharCode(104,101,108,108,111));//‘hello‘ console.log(String.fromCharCode(0x6211,0x662f,0x5c0f,0x706b,0x67f4));//‘我是小火柴‘ console.log(stringValue[1]);//‘e‘
[5.4]字符串拼接方法
[5.4.1]concat():可以接受任意多个参数,用于将一个或多个字符串拼接起来,返回拼接得到的新字符串
[5.4.2]+:加号操作符在多数情况下比concat()更简便
var stringValue = ‘hello ‘; console.log(stringValue.concat(‘world‘,‘!‘));//‘hello world!‘ console.log(stringValue + ‘world‘ + ‘!‘);//‘hello world!‘
[5.5]子字符串创建方法:返回被操作字符串的一个子字符串,若无参数则返回原字符串
[5.5.1]substr:接受两个参数:子字符串开始位置、子字符串长度(可选,默认到原字符串结束)
[a1]当第一个参数为正数且大于等于原字符串长度时,不输出
[a2]当第一个参数为负数且绝对值小于原字符串长时,相当于第一个参数+原字符串长度之后的值
[a3]当第一个参数为负数且绝对值大于等于原字符串长时,相当于第0个位置
[b1]当第二个参数为负数时,被置0
[b2]当第二个参数的值大于等于可以提供的字符个数时,以最大字符数输出
[注意]IE8-在处理第一个参数为负值时存在问题,输出原字符串
var stringValue = ‘hello world‘; console.log(stringValue.substr());//‘hello world‘ console.log(stringValue.substr(2));//‘llo world‘ console.log(stringValue.substr(20));//空 console.log(stringValue.substr(-2,2));//‘ld‘ console.log(stringValue.substr(-2,20));//‘ld‘ console.log(stringValue.substr(-20,2));//‘he‘ console.log(stringValue.substr(-20,-2));//空
[5.5.2]substring:接受两个参数:子字符串开始位置、子字符串结束后一位的位置(可选,默认为原字符串长度)
[a1]当有参数为负数时,被置0
[b1]若第二个参数小于第一个参数,则替换位置
[b2]若第二个参数大于第一个参数或者第二个参数不存在时,第一个参数大于原字符串长度时,无输出
[b3]若第二个参数大于等于字符串长度时,等于字符串长度
var stringValue = ‘hello world‘; console.log(stringValue.substring());//‘hello world‘ console.log(stringValue.substring(2));//‘llo world‘ console.log(stringValue.substring(20));//空 console.log(stringValue.substring(-2,2));//‘he‘ console.log(stringValue.substring(-2,20));//‘hello world‘ console.log(stringValue.substring(-20,2));//‘he‘ console.log(stringValue.substring(-20,-2));//空
[5.5.3]slice:接受两个参数:子字符串开始位置、子字符串结束后一位的位置(可选,默认为原字符串长度)
[a1]当参数为负数且绝对值小于原字符串长时,相当于参数+原字符串长度之后的值
[a2]当参数为负数且绝对值大于等于原字符串长时,相当于第0个位置
[b1]当第一个参数为正数且大于等于原字符串长度时,不输出
[b2]当第一个参数大于等于第二个参数不输出
[c1]若第二个参数大于等于字符串长度时,等于字符串长度
var stringValue = ‘hello world‘; console.log(stringValue.slice());//‘hello world‘ console.log(stringValue.slice(2));//‘llo world‘ console.log(stringValue.slice(20));//空 console.log(stringValue.slice(-2,2));//空 console.log(stringValue.slice(-2,-20));//空 console.log(stringValue.slice(-2,20));//‘ld‘ console.log(stringValue.slice(-20,2));//‘he‘ console.log(stringValue.slice(-20,-2));//‘hello wor‘
[总结]
[a]substr:子串长度为负则置0
[b]substring:参数为负则置0,大小要调换
[c]slice:不置0,不调换
[5.6]字符串位置方法:两个参数:要查找的子字符串、表示查找起点位置的索引(可选)。返回第一个满足条件的子字符串在字符串中的位置,如果没有找到则返回-1(位置方法不会影响原字符串)
[注意]返回值是Number类型
[5.6.1]indexOf:从左到右搜索
[5.6.2]lastIndexOf:从右到左搜索
var string = ‘hello world world‘; console.log(string.indexOf(‘ld‘,10));//15 console.log(string.lastIndexOf(‘ld‘,10));//9
[tips]查找出字符串所有符合条件的子字符串
function allIndexOf(str,value){ var result = []; var pos = str.indexOf(value); while(pos > -1){ result.push(pos); pos = str.indexOf(value,pos+value.length); } return result; } console.log(allIndexOf(‘helllhelllhelll‘,‘ll‘));//[2,7,12];
[5.7]trim()(ECMAScript5):返回删除前置及后缀空格的字符串副本
var string = ‘ hello world ‘; console.log(string.trim());//‘hello world‘;
[tips1]可以用trim()来判断输入的字符是否为空
if(usename.trim().length){ alert(‘correct‘); }else{ alert(‘error‘); }
[tips2]用正则模拟trim();
function fnTrim(str){ return str.replace(/^\s+|\s+$/,‘‘) } console.log(fnTrim(‘ hello world ‘));//‘hello world‘
[5.8]大小写转换方法
[5.8.1]toUpperCase():全部转换成大写
[5.8.2]toLowerCase():全部转换成小写
[5.8.3]toLocaleUpperCase():全部转换成大写(针对地区)
[5.8.4]toLocaleLowerCase():全部转换成小写(针对地区)
[注意]在不知道自己的代码将在哪个语言环境中运行的情况下,使用针对地区的方法更稳妥
var string = ‘Hello World‘; console.log(string.toLowerCase());//hello world console.log(string.toLocaleLowerCase());//hello world console.log(string.toUpperCase());//HELLO WORLD console.log(string.toLocaleUpperCase());//HELLO WORLD
[tips]大小写转换方法可以连续使用
e.g. console.log((string.toUpperCase()).toLowerCase());//hello world
[5.9]模式匹配方法
[5.9.1]match():只接受一个参数,正则或字符串,把匹配的内容保存到一个数组中返回
[注意]加上全局标记时,match()方法返回值中没有index和input属性
[a]不加/g
var string = ‘cat,bat,sat,fat‘; var pattern = /.at/; var matches = string.match(pattern); console.log(matches,matches.index,matches.input);//[‘cat‘] 0 ‘cat,bat,sat,fat‘
[b]加/g
var string = ‘cat,bat,sat,fat‘; var pattern = /.at/g; var matches = string.match(pattern); console.log(matches,matches.index,matches.input);//[‘cat‘,‘bat‘,‘sat‘,‘fat‘] undefined undefined
[c]字符串
var string = ‘cat,bat,sat,fat‘; var pattern = ‘at‘; var matches = string.match(pattern); console.log(matches,matches.index,matches.input);//[‘at‘] 1 ‘cat,bat,sat,fat‘
[5.9.2]search():只接受一个参数,正则或字符串,返回匹配的内容在字符串中首次出现的位置,类似于不能设置起始位置的indexOf,找不到返回-1
[a]正则(加/g和不加/g效果一样)
var string = ‘cat,bat,sat,fat‘; var pattern = /.at/; var pos = string.search(pattern); console.log(pos);//0
[b]字符串
var string = ‘cat,bat,sat,fat‘; var pattern = ‘at‘; var pos = string.search(pattern); console.log(pos);//1
[tips]找出匹配的所有位置
function fnAllSearch(str,pattern){ var pos = str.search(pattern); var length = str.match(pattern)[0].length; var index = pos+length; var result = []; var last = index; result.push(pos); while(true){ str = str.substr(index); pos = str.search(pattern); if(pos === -1){ break; } length = str.match(pattern)[0].length; index = pos+length; result.push(last+pos); last += index; } return result; } console.log(fnAllSearch(‘cat23fbat246565sa3dftf44at‘,/\d+/));//[3,9,17,22]
[5.9.3]replace():接收两个参数:第一个参数为正则表达式或字符串(待查找的内容)、第二个参数为字符串或函数(替换的内容)
[a]字符串替换
var string = ‘cat,bat,sat,fat‘; var result = string.replace(‘at‘,‘ond‘); console.log(result);//‘cond,bat,sat,fat‘
[b]正则无/g替换
var string = ‘cat,bat,sat,fat‘; var result = string.replace(/at/,‘ond‘); console.log(result);//‘cond,bat,sat,fat‘
[c]正则有/g替换
var string = ‘cat,bat,sat,fat‘; var result = string.replace(/at/g,‘ond‘); console.log(result);//‘cond,bond,sond,fond‘
[d]函数替换:在只有一个匹配项(即与模式匹配的字符串的情况下,会向这个函数传递3个参数:模式的匹配项、模式匹配项在字符串中的位置、原始字符串。在正则表达式定义了多个捕获组的情况下,传递给函数的参数依次是模式的匹配项、第一个捕获组的匹配项、第二个捕获组的匹配项……第N个捕获组的匹配项,但最后两个参数仍然分别是模式的匹配项在字符串中的位置和原始字符串,这个函数返回一个字符串。
function htmlEscape(text){ return text.replace(/[<>"&]/g,function(match,pos,originalText){ switch(match){ case ‘<‘: return ‘<‘; case ‘>‘: return ‘>‘; case ‘&‘: return ‘&‘; case ‘\"‘: return ‘"‘; } }); } console.log(htmlEscape(‘<p class=\"greeting\">Hello world!</p>‘)); //<p class=" greeting">Hello world!</p> console.log(htmlEscape(‘<p class="greeting">Hello world!</p>‘)); //同上
[tips]关于$符号的用法
//$$ $ //$& 匹配整个模式的子字符串(与RegExp.lastMatch的值相同) //$` 匹配子字符串之前的子字符串(与RegExp.leftContext的值相同) //$‘ 匹配子字符串之后的子字符串(与RegExp.rightContext的值相同) //$n 匹配第n个捕获组的子字符串,其中n等于0-9。$1表示匹配第一个捕获组的子字符串(从第1个算起) //$nn 匹配第nn个捕获组的子字符串,其中nn等于01-99
console.log(‘cat,bat,sat,fat‘.replace(/(.a)(t)/g,‘$0‘))//$0,$0,$0,$0 console.log(‘cat,bat,sat,fat‘.replace(/(.a)(t)/g,‘$1‘))//ca,ba,sa,fa console.log(‘cat,bat,sat,fat‘.replace(/(.a)(t)/g,‘$2‘))//t,t,t,t console.log(‘cat,bat,sat,fat‘.replace(/(.a)(t)/g,‘$3‘))//$3,$3,$3,$3 console.log(‘cat,bat,sat,fat‘.replace(/(.a)(t)/g,‘$$‘))//$,$,$,$ console.log(‘cat,bat,sat,fat‘.replace(/(.a)(t)/g,‘$&‘))//cat,bat,sat,fat console.log(‘cat,bat,sat,fat‘.replace(/(.a)(t)/g,‘$`‘))//,cat,,cat,bat,,cat,bat,sat, console.log(‘cat,bat,sat,fat‘.replace(/(.a)(t)/g,"$‘"))//,bat,sat,fat,,sat,fat,,fat,
[5.9.4]split():基于指定的分隔符将一个字符串分割成多个字符串,并将结果放在一个数组中,分隔符可以是字符串,也可以是一个RegExp,该方法可以接受第二个参数(可选)用于指定数组的大小
[注意1]如果第二个参数为0-array.length范围内的值时,按照指定参数输出。其他情况将所有结果都输出。
[注意2]IE8-对split()中正则表达式,会忽略捕获组
[tips]如果是split(‘‘),则原来的数组会一个字符字符分割后传出来
var colorText = ‘red,blue,green,yellow‘; console.log(colorText.split(‘,‘));//["red", "blue", "green", "yellow"] console.log(colorText.split(‘,‘,2));//["red", "blue"] console.log(colorText.split(/\,/));//["red", "blue", "green", "yellow"] console.log(colorText.split(/e/));//["r", "d,blu", ",gr", "", "n,y", "llow"] console.log(colorText.split(/[^\,]+/));//将除去逗号以外的字符串变为分隔符["", ",", ",", ",", ""],IE8及以前会识别为[",",",",","]
[5.10]字符串比较方法localeCompare():用于比较两个字符串,如果字符串在字母表中排在字符串参数之前,则返回一个负数(大多数情况下为-1);如果字符串等于字符串参数,则返回0;如果字符串在字母表中排在字符串参数之后,则返回一个正数(大多数情况下为1)
[注意]在ASCII表中,大写字母排在小写字母前面
var stringValue = ‘yellow‘; console.log(stringValue.localeCompare(‘brick‘));//1 ‘y‘> ‘b‘ console.log(stringValue.localeCompare(‘yellow‘));//0 ‘yellow‘ == ‘yellow‘ console.log(stringValue.localeCompare(‘zoo‘));//-1 ‘yellow‘ < ‘zoo‘
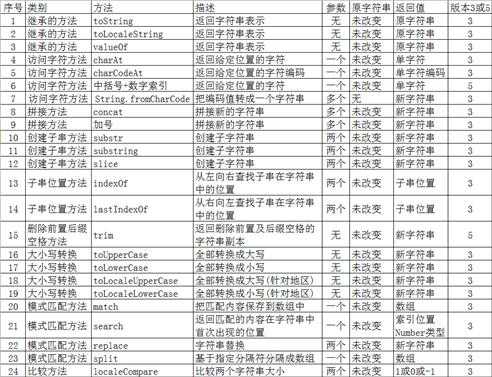
[字符串的24种方法概述]
Javascript引用类型之包装类型(Boolean、Number、String)
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaohuochai/p/4765283.html