标签:
---恢复内容开始---
搜索的过程总的来说就是将词典及倒排表信息从索引中读出来,根据用户的查询语句合并倒排表,得到结果文档集并对文档进行打分的过程。
如图:
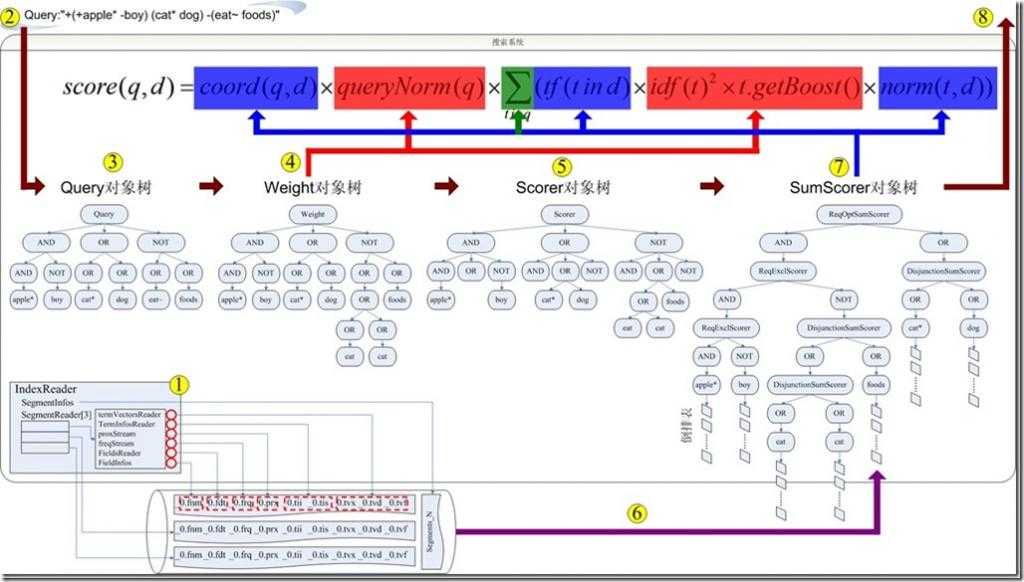
总共包含以下几个过程:
lucene搜索详细过程:
为了解析Lucene对索引文件搜索的过程,预先写入索引了如下几个文件:
file01.txt: apple apples cat dog
file02.txt: apple boy cat category
file03.txt: apply dog eat etc
file04.txt: apply cat foods
打开IndexReader指向索引文件夹
Indexreader reader = IndexReader.open(FSDirectory.open(indexDir));
其实调用的是DirectoryReader.open(Directory,IndexDeletionPolicy,IndexCommit,boolean,int),其主要的作用是生成一个SegmentInfo.FindSegmentsFIle对象;并用它来找到该索引文件中的所有段。
源码跟踪:
IndexReader reader = IndexReader.open(indexpath);
|__open方法
public static IndexReader open(final Directory directory) throws CorruptIndexException, IOException {
return open(directory, null, null, true, DEFAULT_TERMS_INDEX_DIVISOR);
}
|__进入return 的open(),对一些没有传进的参数设null值
private static IndexReader open(final Directory directory, final IndexDeletionPolicy deletionPolicy, final IndexCommit commit, final boolean readOnly, int termInfosIndexDivisor) throws CorruptIndexException, IOException {
return DirectoryReader.open(directory, deletionPolicy, commit, readOnly, termInfosIndexDivisor);
}
到了这里就执行到了DirectoryReader.open(directory, deletionPolicy, commit, readOnly, termInfosIndexDivisor);
所以,在调用indexReader.open(...)的最终执行到的是DirectoryReader.open(),其主要作用是生成一个SegmentInfos.FindSegmentsFile对象,并用它来找到此索引文件中所有的段,并打开这些段。
具体的源代码如下:从directoryReader.open()到segmentInfos.FindSegmentsFile,directoryReader.open()所调用的方法:
static IndexReader open(final Directory directory, final IndexDeletionPolicy deletionPolicy, final IndexCommit commit, final boolean readOnly,
final int termInfosIndexDivisor) throws CorruptIndexException, IOException {
return (IndexReader) new SegmentInfos.FindSegmentsFile(directory) {
@Override
protected Object doBody(String segmentFileName) throws CorruptIndexException, IOException {
SegmentInfos infos = new SegmentInfos();
infos.read(directory, segmentFileName);
if (readOnly)
return new ReadOnlyDirectoryReader(directory, infos, deletionPolicy, termInfosIndexDivisor);
else
return new DirectoryReader(directory, infos, deletionPolicy, false, termInfosIndexDivisor);
}
}.run(commit);
}
在segmentInfos.FindSegmentsFile(directory)中,调用了 public abstract static class FindSegmentsFile,它是segmentInfos类的内部抽象类。这是一个工具类,就是获取当前段的信息,这是在lock-less中是必要的。因为可能在你找到当前段文件的名称,打开它,读取内容,检查是否被修改过等期间,它可能已经被提交了删除的请求。(源码注释)
在抽象类中有个run方法:
public Object run(IndexCommit commit) throws CorruptIndexException, IOException {
if (commit != null) {
if (directory != commit.getDirectory())
throw new IOException("the specified commit does not match the specified Directory");
return doBody(commit.getSegmentsFileName());
}
String segmentFileName = null;
long lastGen = -1;
long gen = 0;
int genLookaheadCount = 0;
IOException exc = null;
boolean retry = false;
int method = 0;
// Loop until we succeed in calling doBody() without
// hitting an IOException. An IOException most likely
// means a commit was in process and has finished, in
// the time it took us to load the now-old infos files
// (and segments files). It‘s also possible it‘s a
// true error (corrupt index). To distinguish these,
// on each retry we must see "forward progress" on
// which generation we are trying to load. If we
// don‘t, then the original error is real and we throw
// it.
// We have three methods for determining the current
// generation. We try the first two in parallel, and
// fall back to the third when necessary.
while(true) {
if (0 == method) {
// Method 1: list the directory and use the highest
// segments_N file. This method works well as long
// as there is no stale caching on the directory
// contents (NOTE: NFS clients often have such stale
// caching):
String[] files = null;
long genA = -1;
files = directory.listAll();
if (files != null)
genA = getCurrentSegmentGeneration(files);
message("directory listing genA=" + genA);
// Method 2: open segments.gen and read its
// contents. Then we take the larger of the two
// gen‘s. This way, if either approach is hitting
// a stale cache (NFS) we have a better chance of
// getting the right generation.
long genB = -1;
for(int i=0;i<defaultGenFileRetryCount;i++) {
IndexInput genInput = null;
try {
genInput = directory.openInput(IndexFileNames.SEGMENTS_GEN);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
message("segments.gen open: FileNotFoundException " + e);
break;
} catch (IOException e) {
message("segments.gen open: IOException " + e);
}
if (genInput != null) {
try {
int version = genInput.readInt();
if (version == FORMAT_LOCKLESS) {
long gen0 = genInput.readLong();
long gen1 = genInput.readLong();
message("fallback check: " + gen0 + "; " + gen1);
if (gen0 == gen1) {
// The file is consistent.
genB = gen0;
break;
}
}
} catch (IOException err2) {
// will retry
} finally {
genInput.close();
}
}
try {
Thread.sleep(defaultGenFileRetryPauseMsec);
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
throw new ThreadInterruptedException(ie);
}
}
message(IndexFileNames.SEGMENTS_GEN + " check: genB=" + genB);
// Pick the larger of the two gen‘s:
if (genA > genB)
gen = genA;
else
gen = genB;
if (gen == -1) {
// Neither approach found a generation
throw new FileNotFoundException("no segments* file found in " + directory + ": files: " + Arrays.toString(files));
}
}
// Third method (fallback if first & second methods
// are not reliable): since both directory cache and
// file contents cache seem to be stale, just
// advance the generation.
if (1 == method || (0 == method && lastGen == gen && retry)) {
method = 1;
if (genLookaheadCount < defaultGenLookaheadCount) {
gen++;
genLookaheadCount++;
message("look ahead increment gen to " + gen);
}
}
if (lastGen == gen) {
// This means we‘re about to try the same
// segments_N last tried. This is allowed,
// exactly once, because writer could have been in
// the process of writing segments_N last time.
if (retry) {
// OK, we‘ve tried the same segments_N file
// twice in a row, so this must be a real
// error. We throw the original exception we
// got.
throw exc;
} else {
retry = true;
}
} else if (0 == method) {
// Segment file has advanced since our last loop, so
// reset retry:
retry = false;
}
lastGen = gen;
segmentFileName = IndexFileNames.fileNameFromGeneration(IndexFileNames.SEGMENTS,
"",
gen);
try {
Object v = doBody(segmentFileName);
if (exc != null) {
message("success on " + segmentFileName);
}
return v;
} catch (IOException err) {
// Save the original root cause:
if (exc == null) {
exc = err;
}
message("primary Exception on ‘" + segmentFileName + "‘: " + err + "‘; will retry: retry=" + retry + "; gen = " + gen);
if (!retry && gen > 1) {
// This is our first time trying this segments
// file (because retry is false), and, there is
// possibly a segments_(N-1) (because gen > 1).
// So, check if the segments_(N-1) exists and
// try it if so:
String prevSegmentFileName = IndexFileNames.fileNameFromGeneration(IndexFileNames.SEGMENTS,
"",
gen-1);
final boolean prevExists;
prevExists = directory.fileExists(prevSegmentFileName);
if (prevExists) {
message("fallback to prior segment file ‘" + prevSegmentFileName + "‘");
try {
Object v = doBody(prevSegmentFileName);
if (exc != null) {
message("success on fallback " + prevSegmentFileName);
}
return v;
} catch (IOException err2) {
message("secondary Exception on ‘" + prevSegmentFileName + "‘: " + err2 + "‘; will retry");
}
}
}
}
}
}
就是判断是否被提交了,判断的参数:commit,从中可以取到directory,得到当前段所在的位置,并判断是否被修改过,如果没有,就从commit中获取segmentFileName就执行doBody(segmentFileName)。
解释一下indexCommit:
public abstract class IndexCommit { public abstract String getSegmentsFileName(); public abstract Collection<String> getFileNames() throws IOException; public abstract Directory getDirectory(); public void delete() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException("This IndexCommit does not support this method."); } public boolean isDeleted() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException("This IndexCommit does not support this method."); } public boolean isOptimized() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException("This IndexCommit does not support this method."); } @Override public boolean equals(Object other) { if (other instanceof IndexCommit) { IndexCommit otherCommit = (IndexCommit) other; return otherCommit.getDirectory().equals(getDirectory()) && otherCommit.getVersion() == getVersion(); } else return false; } @Override public int hashCode() { return getDirectory().hashCode() + getSegmentsFileName().hashCode(); } public long getVersion() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException("This IndexCommit does not support this method."); } public long getGeneration() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException("This IndexCommit does not support this method."); } public long getTimestamp() throws IOException { return getDirectory().fileModified(getSegmentsFileName()); } public Map<String,String> getUserData() throws IOException { throw new UnsupportedOperationException("This IndexCommit does not support this method."); } }
indexcommit是getSegmentsFileName,getDirectory的vo,从中可以得到段名称和目录。
回到DirectoryReader.open()中,里面调用了segmentInfos.FindSegmentsFile(dir){doBody(){ }},实现了doBody方法,将段名称传给dobody(),然后run(commit).
上面找到段信息的主要执行流程:
找到最新的segment_N
|
String[] files = directory.listAll(); long genA = getCurrentSegmentGeneration(files); |
long getCurrentSegmentGeneration(String[] files) {
long max = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < files.length; i++) {
String file = files[i];
if (file.startsWith(IndexFileNames.SEGMENTS) //"segments_N"
&& !file.equals(IndexFileNames.SEGMENTS_GEN)) { //"segments.gen"
long gen = generationFromSegmentsFileName(file);
if (gen > max) {
max = gen;
}
}
}
return max;
}
另一方面,打开segment_gen,从中得到genB,在genA和genB中去较大者,为gen,并用此gen构造要打开的segments_N的文件名.
---恢复内容结束---
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/mggwct/p/4767177.html