标签:
1、使用JavaApi文档中的Arrays类中的sort()进行快速排序
首先我们直接看代码如下:
1 package himi.text; 2 3 import java.util.Arrays; 4 5 public class TestDemo01 { 6 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 int[] array = {2,12,3,44,27}; 9 /** 10 * 利用使用JavaApi文档中的Arrays类中的sort()进行快速排序 11 */ 12 Arrays.sort(array);//调用Array的静态方法Sort进行排序,升序排列 13 for(int show:array) { 14 System.out.print(show+" ");//升序输出 15 } 16 System.out.println(); 17 System.out.println("---------------"); 18 19 for(int i=0; i<array.length-1; i++) 20 System.out.print(array[array.length-1-i]+" ");//降序输出 21 22 23 } 24 25 }
代码运行结果如下:

2.冒泡法排序:
冒泡法算法思路:如果有N个数,则要进行N-1次比较,在每一次比较中要进行N-1次两两比较。所谓的两两比较就是从头到尾将相邻两个数进行比较,并将其中较大的数放在前或者放在后(放在前就是降序,放在后就是升序)
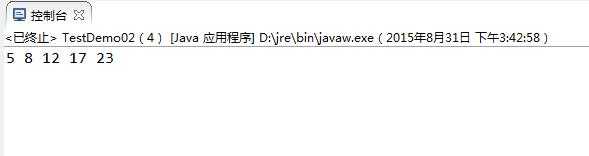
1 package himi.text; 2 3 public class TestDemo02 { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 int[] arrays = { 12, 23, 8, 17, 5 }; 7 bubbleSort(arrays); 8 for (int show : arrays) 9 System.out.print(show + " "); 10 } 11 12 public static void bubbleSort(int[] array) { 13 int temp; 14 for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) { 15 for (int j = 0; j < array.length - 1 - i; j++) { 16 if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) { 17 //方式1 18 // temp = array[j]; 19 // array[j]=array[j+1]; 20 // array[j+1]=temp; 21 22 //方式2 23 array[j] = array[j] ^ array[j + 1]; 24 array[j + 1] = array[j + 1] ^ array[j]; 25 array[j] = array[j] ^ array[j + 1]; 26 } 27 } 28 } 29 } 30 31 }
输出结果:
3.选择排序:
首先以一个元素为基准,从一个方向开始扫描,比如从左到右扫描,以A[0]为基准,接下来从A[0]….A[9]中找出最小的元素,将其与A[0]交换。然后将其基准位置右移一位,重复上面的动作,比如,以A[1]为基准,找出A[1]~A[9]中最小的,将其与A[1]交换。一直进行到将基准位置移到数组最后一个元素时排序结束。
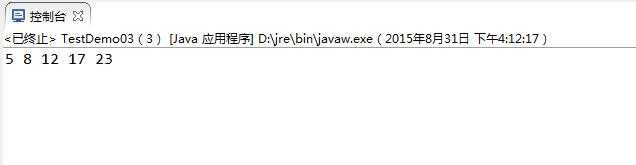
1 package himi.text; 2 3 public class TestDemo03 { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 int[] arrays = {12,23,8,17,5}; 7 int[] temp = selectSort(arrays); 8 for(int show:temp) 9 System.out.print(show+" "); 10 } 11 12 13 public static int[] selectSort(int[] args){//选择排序算法 14 for (int i=0;i<args.length-1 ;i++ ){ 15 int min=i; 16 for (int j=i+1;j<args.length ;j++ ){ 17 if (args[min]>args[j]){ 18 min=j; 19 } 20 } 21 if (min!=i){ 22 int temp=args[i]; 23 args[i]=args[min]; 24 args[min]=temp; 25 } 26 } 27 return args; 28 } 29 30 }
运行结果如下:
4.插入排序算法:
所谓插入排序法,就是检查第i个数字,如果在它的左边的数字比它大,进行交换,这个动作一直继续下去,直到这个数字的左边数字比它还要小,就可以停止了。插入排序法主要的回圈有两个变数:i和j,每一次执行这个回圈,就会将第i个数字放到左边恰当的位置去。
1 package himi.text; 2 3 public class TestDemo04 { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 int[] arrays = {12,23,8,17,5}; 7 int[] temp = insertSort(arrays); 8 for(int show:temp) 9 System.out.print(show+" "); 10 } 11 public static int[] insertSort(int[] args){//插入排序算法 12 for(int i=1;i<args.length;i++){ 13 for(int j=i;j>0;j--){ 14 if (args[j]<args[j-1]){ 15 int temp=args[j-1]; 16 args[j-1]=args[j]; 17 args[j]=temp; 18 }else break; 19 } 20 } 21 return args; 22 } 23 24 }
运行结果:

标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/hebao0514/p/4773333.html