标签:
有两个排序的数组a和b,内存在a的末尾有足够多的剩余空间容纳b
实现一个函数将b中所有的数字插入到a,最终结果是有序的
由于a、b两个数组已经排序,并且题目提示在a数组的末尾有足够多空间容纳b数组,因此我们将b数组赋值给a数组时,可以考虑从两个数组的末尾元素开始比较,每次比较a数组和b数组的最后一个元素,将较大的那个元素作为新的a数组的最后一个元素,这样时间复杂度为O(n),而空间复杂度为O(1)
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
//显示数组
void DisplayArray( char *arrayName, int *a, int len )
{
if ( a== NULL || len <= 0)
{
cout<<"数组 "<<arrayName<<" 为空"<<endl;
return;
}
cout<<"Element in array : "<<arrayName<<endl;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
/*合并两个数组
a:第一个数组,b:第二个数组
totalalen, a数组中的总长度, alen:a数组实际长度,blen:b数组长度
*/
void MergeArray(int *a, int *b, int totalalen, int alen, int blen )
{
//参数检查
if ( a== NULL || b== NULL )
{
cout<<"输入数组为空,请检查"<<endl;
return;
}
if ( alen <= 0 || blen <= 0 || totalalen < alen+blen)
{
cout<<"输入数组长度错误,请检查"<<endl;
return;
}
int newidx = alen + blen - 1;//合并后数组的索引
int aidx = alen -1;//a数组的索引
int bidx = blen -1;//b数组的索引
while (aidx >= 0 && bidx >= 0)
{
if (a[aidx] > b[bidx] )
a[newidx--] = a[aidx--];
else
a[newidx--] = b[bidx--];
}
while ( bidx >= 0)
{
a[newidx--] = b[bidx--];
}
}
各个测试用例调用该测试代码段
//测试代码
void Test(char *testName, int *arra1, int *arra2, int len, int len1, int len2 )
{
if (testName == NULL )
{
return;
}
cout<<testName<<" begins."<<endl;
cout<<"Befor merge"<<endl;
DisplayArray("A",arra1, len1);
DisplayArray("B", arra2, len2);
MergeArray(arra1, arra2, len, len1, len2);
cout<<"After merge"<<endl;
if ( len1 > 0)
{
DisplayArray("A", arra1, len1+len2);
}
else
cout<<"A 为空"<<endl;
}
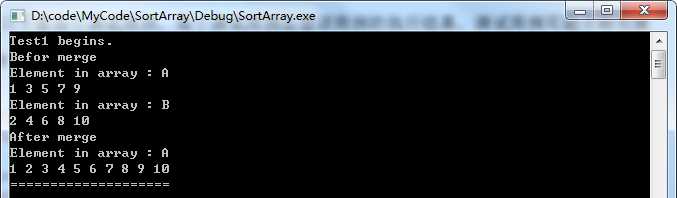
测试用例1
//测试用例1,a、b数组一样长
void Test1()
{
int a[10] = {1,3,5,7,9};
int b[] = {2,4,6,8,10};
Test("Test1", a, b, 10, 5, 5);
}
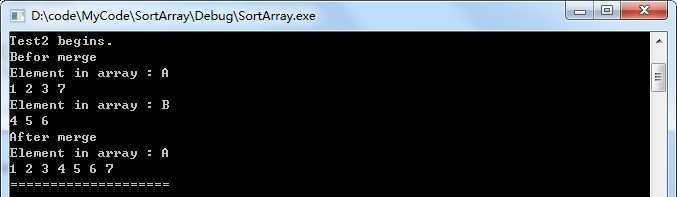
测试用例2
//测试用例2,a数组比b数组长
void Test2()
{
int a[20]={1,2,3,7};
int b[]={4,5,6};
Test("Test2", a, b, 20, 4, 3);
}
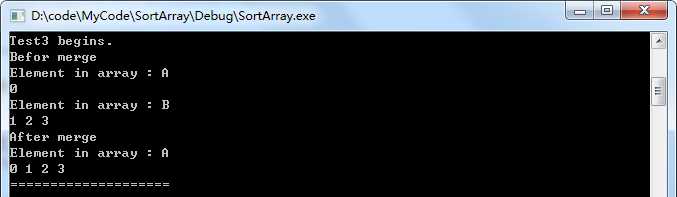
测试用例3
//测试用例3,a数组比b数组短
void Test3()
{
int a[20]={0};
int b[]={1,2,3};
Test("Test3", a, b, 20, 1, 3);
}
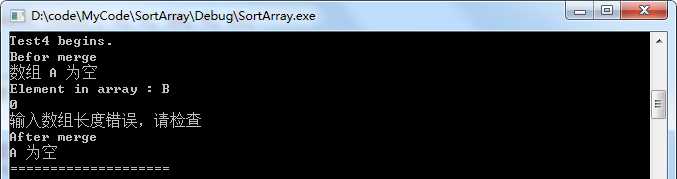
测试用例4
//测试用例4,a数组为空
void Test4()
{
int a[20];
int b[]={0};
Test("Test4", a, b, 20, 0, 1);
}
测试用例5
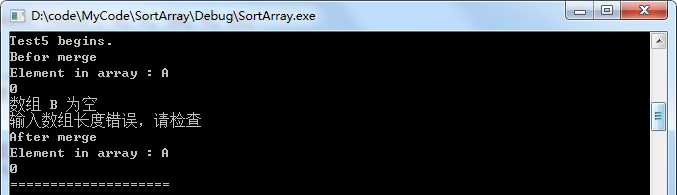
//测试用例5,b数组为空
void Test5()
{
int a[20]={0};
int b[3];
Test("Test5", a, b, 20, 1, 0);
}
测试用例6
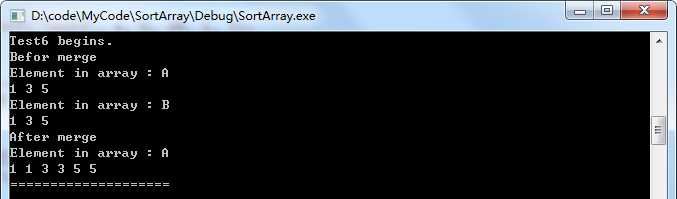
//测试用例6,a、b数组相同
void Test6()
{
int a[20]={1,3,5};
int b[3] = {1,3,5};
Test("Test6", a, b, 20, 3, 3);
}
int main()
{
Test1();
cout<<"===================="<<endl<<endl;
Test2();
cout<<"===================="<<endl<<endl;
Test3();
cout<<"===================="<<endl<<endl;
Test4();
cout<<"===================="<<endl<<endl;
Test5();
cout<<"===================="<<endl<<endl;
Test6();
cout<<"===================="<<endl<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/scut-linmaojiang/p/4779204.html