标签:
JSON & XML解析
JSON(数据传输):
JSON具有对象(字典)和数组两种数据格式。字典用“{}”,数组用“[]”。其实也是key-value(字符串,数值,布尔类型,对象,空对象,数组)键值对。
JSON 可以与Object-C相互转换 ->则是JSON的解析过程(正向与逆向的解析-为了说明自己定义的正逆)->可用于数据的持久化,将JSON数据写入文件中保存(逆向);从文件中读出数据(正向)。
JSON ->Object-C(正向):jsondata->jsonarray/jsondictionary
Object-C -> JSON(逆向):jsonarray/jsondictionary ->jsonstring->jsondata
系统为JSON解析提供了NSJSONSerialization这个类,这个类里面提供了众多解析方法。
// 字典转换为JSON
NSDictionary *dic=@{
@"name":@"jessi",
@"age":@19,
@"married":@(true),
@"friend":@[@"pwy",@"wm",@"zjay"
],
};
//NSData的对象是二进制数据 把dictionary转化为二进制数据进行传输转化 又通过字符串转换为字符串
NSData *jsonData;
if ([NSJSONSerialization isValidJSONObject:dic])
{
jsonData=[NSJSONSerialization dataWithJSONObject:dic options:NSJSONWritingPrettyPrinted error:nil ];
}
NSString *str=[[NSString alloc]initWithData:jsonData encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
// 数组转换JSON
NSArray *array=@[@123,@"pwy",@"sting",@1];
NSData *data;
if ([NSJSONSerialization isValidJSONObject:array])
{
data=[NSJSONSerialization dataWithJSONObject:array options:NSJSONWritingPrettyPrinted error:nil];
}
NSString *str1=[[NSString alloc]initWithData:data encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
// JSON转字典和数组 可变性
// 正确的JSON字符串格式才能转成功
// NSJSONReadingMutableContainers 转为可变的字典和数组
// NSJSONReadingMutableLeaves /NSJSONReadingAllowFragments 转为不可变的字典和数组
str1=@"{\"name\":\"jessi\",\"age\":12,\"height\":165}";
NSLog(@"str1%@",str1);
data=[str1 dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
NSDictionary *dic1=[NSJSONSerialization JSONObjectWithData:data options:NSJSONReadingMutableContainers error:nil];
XML(数据传输):
XML 只有字典一种数据格式 ,是一种树型存储结构,必须有根节点,逐级嵌套(用树的思想来思考)。XML不像JSON一样是键值对存储数据,不过也稍微有那样的意思,XML是用标签和值来存储数据。XML数据写入(保存)文件可以数据的持久性,便于网络传输。
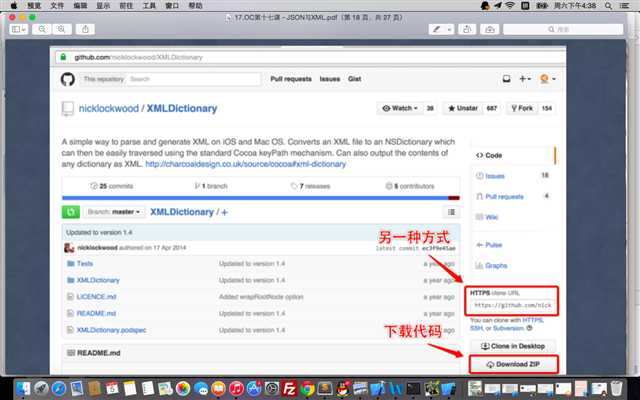
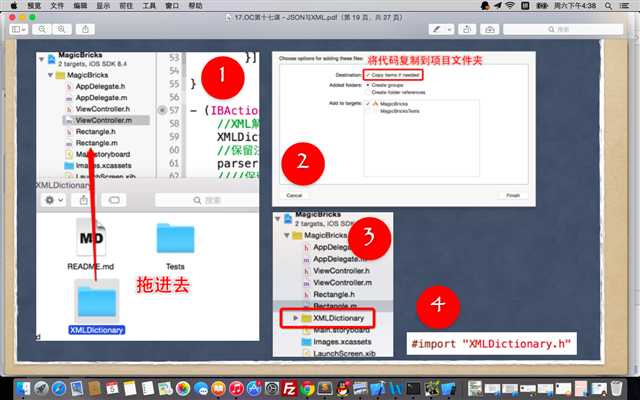
XML的解析工具有多种,包括:libxml2->hpple, GDataXML, KissXML, NSXMLParser-> XMLDictionary,目前我们经常使用的则是XMLDictionary,hpple。
Xml解析方法1:
SAX(simple API for xml)逐行解析,快捷消耗内存少,不需要在内存中构建文档树->NSXMLParser-> XMLDictionary
解析前准备:
// xml的解析器 (加载解析器之后 再解析XML文件的内容)判断完之后才开始做解析
// 单例模型
XMLDictionaryParser *parser=[XMLDictionaryParser sharedInstance];
// 保存节点名称,默认只保存根节点名称
parser.nodeNameMode=XMLDictionaryNodeNameModeAlways;
//保留注释
// parser.preserveComments=YES;
// 用字典保存属性值
parser.attributesMode=XMLDictionaryAttributesModeDictionary;
NSDictionary *xmDic=[NSDictionary dictionaryWithXMLFile: @"/Users/apple/Desktop/test1.xml"];
NSDictionary *dic=@{
@"__name":@"Student",
@"__attributes":@{@"id":@"abc",@"class":@"conquer"},
@"name":@"jessi",
@"age":@18,
@"gender":@"female",
@"friends":@{
@"friend":@[
@{@"__text":@"nobody",}
]
}
};
NSString *xmlstring=[dic XMLString];
[xmlstring writeToFile: @"/Users/apple/Desktop/test2.xml" atomically:YES encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding error:nil];
NSString *xmlFilePath;
xmlFilePath = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"test1" ofType:@"xml"];
NSLog(@"xmlfilepath->%@",xmlFilePath);
// xmlparse 解析xml文件
xmlDocPtr doc = xmlParseFile([xmlFilePath UTF8String]);
// xmlparse 解析xml文件 从内存里边读出来
NSString *xmlStr = [NSString stringWithContentsOfFile:xmlFilePath encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding error:nil];
// nssstring -> cstring
xmlDocPtr doc1 = xmlParseMemory([xmlStr UTF8String], (int)[xmlStr lengthOfBytesUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]);
// 获取根节点
xmlNodePtr root = xmlDocGetRootElement(doc);
if (xmlStrcmp(root->name, (const xmlChar *)"student") == 0)
{
NSLog(@"rootname is student");
// 获取子节点
root = root->xmlChildrenNode;//父节点指向子节点
// 子节点不为空则可以继续子节点的查找
while (root != NULL)
{
if (!xmlStrcmp(root->name, (const xmlChar *)"Books"))
{
// Books的子节点book
xmlNodePtr book = root->xmlChildrenNode;
while (book != NULL)
{
if (!xmlStrcmp(book->name, (const xmlChar *)"Book"))
{
NSLog(@"name:%s",book->name);
// 获取type的属性
NSLog(@"type:%s",xmlGetProp(book,(const xmlChar *)"type"));
xmlChar *content = xmlNodeListGetString(doc, book->children, 1);
NSLog(@"content:%@",[NSString stringWithCString:(const char *)content encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]);
}
// 获取同级的下一个节点兄弟节点
book = book->next;
}
}
root = root->next;
}
xmlFree(doc);
}
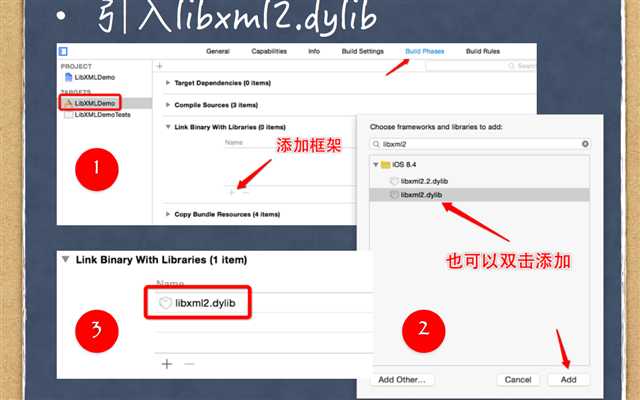
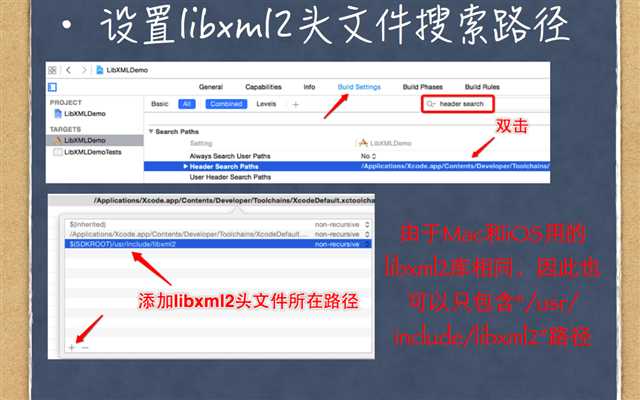
Xml解析方法2:
DOM(Document Object Model文档对象模型),解析时将整个文档读入内存当中,利用c库的libxml.dylib实现了解析,可以对文档进行修改和编辑->libxml2->hpple(常用于解析网络数据)
解析前准备:
解析糗事百科为例子:
NSData *dataout = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:@"/Users/apple/Desktop/qiubai1.html" ];
TFHpple *doc = [[TFHpple alloc] initWithHTMLData:dataout encoding:@"utf-8"];
// 取出一页的20个故事
NSArray *result = [doc searchWithXPathQuery:@"//div[@class = ‘article block untagged mb15‘]"];
for (TFHppleElement *elem in result)
{
// 爬出头像
NSArray *headimg = [elem searchWithXPathQuery:@"//div[@class = ‘author‘]/a/img"];
TFHppleElement *headerimg = [headimg firstObject];
NSString *headStr = [headerimg attributes][@"src"];
NSLog(@"headerStr->%@",headStr);
// 爬出用户名
TFHppleElement *nickname = [[elem searchWithXPathQuery:@"//div[@class = ‘author‘]/a"] firstObject];
NSString *nicknameStr1 = [nickname content];
// 去空白-此法无用
// NSString *nicknameStr2 = [nicknameStr1 stringByTrimmingCharactersInSet:[NSCharacterSet whitespaceCharacterSet]];
// 字符串分割 \n\n nickname \n
NSArray *nick = [nicknameStr1 componentsSeparatedByString:@"\n"];
NSString *nicknameStr = nick[2];
NSLog(@"nickname->%@",nicknameStr);
TFHppleElement *story = [[elem searchWithXPathQuery:@"//div[@class = ‘content‘]"] firstObject] ;
NSString *storycontent = [story content];
NSLog(@"storycontent->%@",storycontent);
TFHppleElement *fun = [[elem searchWithXPathQuery:@"//div[@class = ‘stats‘]/span"] firstObject];
NSString *funny = [fun content];
NSLog(@"funny->%@",funny);
TFHppleElement *conmment = [[elem searchWithXPathQuery:@"//div[@class = ‘stats‘]/span/a"] firstObject];
NSString *conmments1 = [conmment content];
NSArray *con = [ conmments1 componentsSeparatedByString:@"\n"];
NSString *conmments = con[1];
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/shareconquer/p/4783710.html