标签:
先看简单示例:点击按钮,2s之后,TextView改变内容。

package cn.lixyz.handlertest; import android.app.Activity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.os.Handler; import android.os.Message; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; import android.widget.TextView; /** * 实现点击按钮,开始播放幻灯片,每张幻灯片间隔2s。 */ public class MainActivity extends Activity { private TextView textView; private Button button; private Handler handler; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); textView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView); button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button); handler = new MyHandler(); button.setOnClickListener(new MyOnClickListener()); } class MyOnClickListener implements View.OnClickListener { @Override public void onClick(View v) { Thread t = new MyThread(); t.start(); } } class MyThread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { super.run(); try { Thread.sleep(2 * 1000); Message message = handler.obtainMessage(); message.obj = "更改后的内容"; handler.sendMessage(message); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } class MyHandler extends Handler { @Override public void handleMessage(Message msg) { super.handleMessage(msg); String str = (String) msg.obj; textView.setText(str); } } }

<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="center" android:padding="30dp" android:text="原来的内容" android:textSize="30dp" /> <Button android:id="@+id/button" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="center" android:layout_marginTop="30dp" android:text="BUTTON" /> </LinearLayout>
运行结果:


解释一下上面的代码:
1. 在onCreate中创建自定义的Handler对象
2. 设置按钮的点击监听事件,点击按钮之后,会启动一个线程
3. 线程启动之后,会先休眠2s,然后Handler对象会获取一个Message,设置Message的obj属性为“更改后的内容”,然后将Message发送出去
4. 在我们自定义的Handler类中,实现了handleMessage方法,在这个方法中,我们接收到message,然后将message中的obj取出,更新TextView。
再一个例子:

package cn.lixyz.handlertest; import android.app.Activity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.os.Handler; import android.os.Message; import android.util.Log; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; import android.widget.EditText; import android.widget.TextView; /** * 实现点击按钮,开始播放幻灯片,每张幻灯片间隔2s。 */ public class MainActivity extends Activity { private EditText editText; private Button button; private Handler handler; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); editText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText); button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button); handler = new MyHandler(); button.setOnClickListener(new MyOnClickListener()); } class MyOnClickListener implements View.OnClickListener { @Override public void onClick(View v) { Thread t = new MyThread(); t.start(); } } class MyThread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { super.run(); try { Thread.sleep(2 * 1000); String str = editText.getText().toString(); Message message = handler.obtainMessage(); message.obj = str; handler.sendMessage(message); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } class MyHandler extends Handler { @Override public void handleMessage(Message msg) { super.handleMessage(msg); String str = (String) msg.obj; Log.d("TTTT", "接收到的消息是" + str); } } }

<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <EditText android:id="@+id/editText" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="center" android:hint="输入要传送的内容" android:padding="30dp" /> <Button android:id="@+id/button" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="center" android:layout_marginTop="30dp" android:text="BUTTON" /> </LinearLayout>
运行结果:
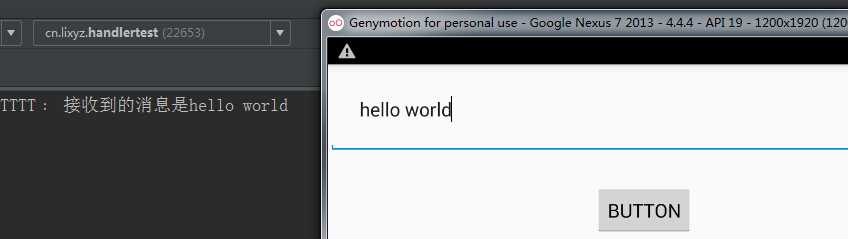
再稍微处理一下上面的代码,我们看一下他们的线程名:

package cn.lixyz.handlertest; import android.app.Activity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.os.Handler; import android.os.Message; import android.util.Log; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; import android.widget.EditText; import android.widget.TextView; /** * 实现点击按钮,开始播放幻灯片,每张幻灯片间隔2s。 */ public class MainActivity extends Activity { private TextView textView; private Button button; private Handler handler; private EditText editText; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); textView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView); button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button); editText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText); handler = new MyHandler(); button.setOnClickListener(new MyOnClickListener()); } class MyOnClickListener implements View.OnClickListener { @Override public void onClick(View v) { Thread t = new MyThread(); t.start(); } } class MyThread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { super.run(); try { Thread.sleep(2 * 1000); String str = "****" + editText.getText().toString() + "****"; Message message = handler.obtainMessage(); message.obj = str; handler.sendMessage(message); Log.d("TTTT", "这里是发送消息的线程,发送的内容是:" + str + " 线程名是:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } class MyHandler extends Handler { @Override public void handleMessage(Message msg) { super.handleMessage(msg); String str = (String) msg.obj; textView.setText(str); Log.d("TTTT", "这里是更改UI的线程,接收到的内容是:" + str + " 线程名是:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } } }

<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="center" android:padding="30dp" android:text="原来的内容" android:textSize="30dp" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/editText" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="输入要改变的文字" /> <Button android:id="@+id/button" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="center" android:layout_marginTop="30dp" android:text="Send" /> </LinearLayout>
运行结果:
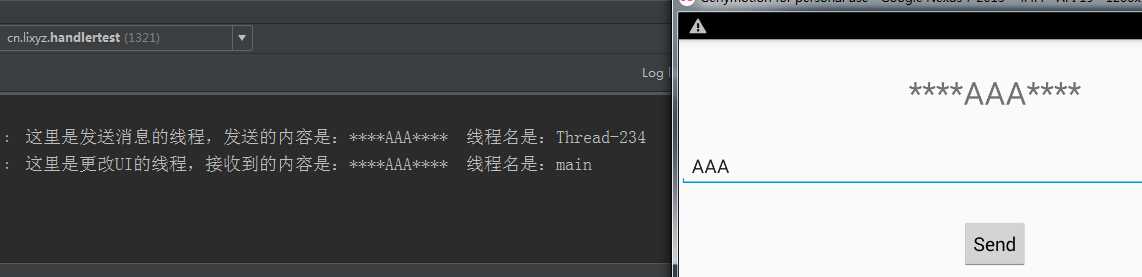
从运行结果我们可以看到,发送消息的线程是一个WorkerThread,更新UI的线程是一个MainThread,这样就解决了主线程和子线程之间的通信问题,我们可以在子线程中将数据处理完成之后回传给UI线程,让UI线程去更新UI组件。
Android笔记(三十一) Android中的异步更新(三) Handler (二)
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/xs104/p/4815073.html