标签:
优先队列可以说是堆的一个非常重要的应用,和堆对应,优先队列也分最小优先队列和最大优先队列。
优先队列是一种用来维护由一组元素构成的集合S的数据结构,其中每一个元素都有一个关键字(key),关键字赋予了一个元素的优先级,故名为优先队列。之所以用堆来实现优先队列,我想最大的原因是堆很容易对元素按关键字进行排序。
优先队列的应用:
最大优先队列:其中最为典型的就是“共享计算机系统的作业调度”,通过记录各个作业的优先级,来调度一个作业的执行、删除和插入等操作。
最小优先队列:可以被用于“基于事件驱动的模拟器”,队列中保存要模拟的事件,每个事件都有一个发生时间作为关键字。事件必须按发生的时间顺序进行模拟,因为某一事件的模拟结果可能会触发对其他事件的模拟。
优先队列的实现:
为了实现优先队列,需要实现这样的几个过程:
1)Insert(S, x):插入x到集合S中;
2)Maximum(S):返回S中具有最大关键字的元素;
3)Extract_Max(S):去掉并返回集合S中具有最大关键字的元素;
4)Increase_Key(S, x, key):将元素x的关键字增加到key。
我们暂且不用管这些奇怪的函数为什么要这么定义,因为这是前人的成功经验总结,肯定是在实际应用中这几个函数用得是最多的,总之,知道这样的四个函数就行了,等用到的时候就知道它们的好处了。
首先,基于堆,Maximum可以在O(1)的时间内完成,如:
1 int PriorityQueue::HeapMaximum() //return the maximum key from priority queue; 2 { 3 return GetQueueElement(0); //the first element is max; 4 }
其次,Extract_Max(S)和Maximum()的区别就在于,得到了之后还要删除,在不改变结构的情况下,最好的删除方法就是用最后一个元素来代替第一个元素,但是要注意,删除之后,有可能堆的性质就不能保证了,所以,这个时候调用Max_Heapify()调整一下。如下:
1 int PriorityQueue::HeapExtractMax() //delete and return the maximum key from queue; 2 { 3 if (IsEmptyHeap()) 4 throw "heap underflow"; 5 6 int heap_size = GetHeapSize(); 7 int maxNum = GetQueueElement(0); 8 SetQueueElement(0, GetQueueElement(heap_size-1)); //A[1] = A[heap_size] 9 SetHeapSizeMinus1(); 10 MaxHeapify(0); //Max_Heapify() 11 return maxNum; 12 }
对于Increase_Key(S, x, key),我们直接用Key替换X,但是替换之后堆的性质也可能改变了,可以知道的是,X后面的元素仍然满足堆的性质,因为Key>X,这时就之用维护X前面的元素,一层层往上调用Max_Heapify()即可,如:
1 void PriorityQueue::HeapIncreaseKey(int srcIndex, int dstKey) //increasing the srcKey to dstKey 2 { 3 if (dstKey < GetQueueElement(srcIndex)) 4 throw "new key is smaller than current key!"; 5 SetQueueElement(srcIndex, dstKey); //x = key 6 while(srcIndex > 0 && GetQueueElement(getParent(srcIndex)) < GetQueueElement(srcIndex)) { 7 Swap(srcIndex, getParent(srcIndex)); 8 srcIndex = getParent(srcIndex); //get parent 9 } 10 }
最后,Insert(S, x)操作,我们可以在最后增加一个-∞的元素,然后将其转换成将-∞增加到x,即转换成Increase_Key(S, -∞, x)。如:
1 void PriorityQueue::HeapInsert(int key) //insert key to the priority queue; 2 { 3 AddQueueElement(INT_MIN); //add the INT_MIN to the end of heapQueue; 4 int heap_size = GetHeapSize(); 5 HeapIncreaseKey(heap_size-1, key); 6 }
除此之外,习题6.5-8要求在O(lgn)的时间内实现一个Delete(S, i)操作。很容易想到相当于对A[i]为根的堆进行Extract_Max()操作。如:
1 Heap-Delete(A, i) 2 A[i] = A[A.heap-size] 3 A.heap-size = A.heap-size - 1 4 Heapify(A, i)
以上所有的操作,除了Maximum()之外,其余所有的函数的时间复杂度皆为O(lgn),所以,这也是为什么用堆来实现优先队列一个非常重要的原因。下面给出一个非常简单的优先队列的实现(元素的值就是Key)。

1 //PriorityQueue.h 2 3 4 #ifndef _PRIORITY_QUEUE_H_ 5 #define _PRIORITY_QUEUE_H_ 6 7 /************************************************************************/ 8 /* priority queue 9 /************************************************************************/ 10 class PriorityQueue { 11 public: 12 PriorityQueue() { m_heapSize = 0; m_length = 0; } 13 ~PriorityQueue() {} 14 15 //inline 16 int getParent(int index) { return (index-1)/2; } 17 int getLeft(int index) { return 2*index + 1; } 18 int getRight(int index) { return 2*index + 2; } 19 20 //heap operation 21 void BuildMaxHeap(); //build the max heap 22 void MaxHeapify(int index); //protect the max heap 23 void HeapSort(); //heap sort 24 25 //priority queue operation 26 void HeapInsert(int key); //insert key to the priority queue; 27 int HeapMaximum(); //return the maximum key from priority queue; 28 int HeapExtractMax(); //delete and return the maximum key from queue; 29 void HeapIncreaseKey(int srcIndex, int dstKey); //increasing the srcKey to dstKey 30 31 void HeapDelete(int key); //delete key 习题6.5-8 32 33 //other assist functions 34 void AddQueueElement(int key); 35 void DisplayQueue(); 36 void DisplayHeapQueue(); 37 38 public: 39 40 41 private: 42 int GetQueueElement(int index) { return m_vecQueue[index]; } 43 void SetQueueElement(int index, int key) { m_vecQueue[index] = key; } 44 void Swap(int i, int j) { 45 int temp = m_vecQueue[i]; 46 m_vecQueue[i] = m_vecQueue[j]; 47 m_vecQueue[j] = temp; 48 } 49 int GetHeapSize() { return m_heapSize; } 50 int GetArrayLength() { return m_length; } 51 void SetHeapSizeMinus1() { m_heapSize = m_heapSize - 1; } 52 void SetHeapSizePlus1() { m_heapSize = m_heapSize + 1; } 53 54 bool IsEmptyHeap() { return (m_heapSize > 1 ? false : true); } 55 56 private: 57 vector<int> m_vecQueue; 58 int m_heapSize; //堆元素个数 59 int m_length; //数组元素个数 60 61 }; 62 63 64 #endif//_PRIORITY_QUEUE_H_

1 //PriorityQueue.cpp 2 3 4 #include <iostream> 5 #include <vector> 6 using namespace std; 7 8 #include "PriorityQueue.h" 9 10 //heap operation 11 void PriorityQueue::BuildMaxHeap() //build the max heap 12 { 13 int heap_size = GetHeapSize(); 14 for (int i = (heap_size-1)/2; i >= 0; i --) 15 MaxHeapify(i); 16 } 17 18 void PriorityQueue::MaxHeapify(int index) //protect the max heap 19 { 20 if (index < 0 || index >= GetHeapSize()) 21 return; 22 23 int heap_size = GetHeapSize(); 24 bool isHeapify = true; 25 26 int largest = -1; 27 while (isHeapify && index < heap_size) { 28 int left = getLeft(index); 29 int right = getRight(index); 30 31 if (left < heap_size && GetQueueElement(left) > GetQueueElement(index) ) 32 largest = left; 33 else 34 largest = index; 35 if (right < heap_size && GetQueueElement(right) > GetQueueElement(largest) ) 36 largest = right; 37 38 if (largest != index) { 39 Swap(index, largest); 40 index = largest; 41 } 42 else 43 isHeapify = false; 44 } 45 46 } 47 48 void PriorityQueue::HeapSort() //heap sort 49 { 50 BuildMaxHeap(); 51 int heap_size = GetHeapSize(); 52 for (int i = heap_size-1; i >= 1; i --) { 53 Swap(0, i); 54 SetHeapSizeMinus1(); //heap_size--; 55 MaxHeapify(0); 56 } 57 } 58 59 //priority queue operation 60 void PriorityQueue::HeapInsert(int key) //insert key to the priority queue; 61 { 62 // SetHeapSizePlus1(); 63 // int heap_size = GetHeapSize(); 64 AddQueueElement(INT_MIN); //add the INT_MIN to the end of heapQueue; 65 int heap_size = GetHeapSize(); 66 HeapIncreaseKey(heap_size-1, key); 67 } 68 69 int PriorityQueue::HeapMaximum() //return the maximum key from priority queue; 70 { 71 return GetQueueElement(0); //the first element is max; 72 } 73 74 int PriorityQueue::HeapExtractMax() //delete and return the maximum key from queue; 75 { 76 if (IsEmptyHeap()) 77 throw "heap underflow"; 78 79 int heap_size = GetHeapSize(); 80 int maxNum = GetQueueElement(0); 81 SetQueueElement(0, GetQueueElement(heap_size-1)); //A[1] = A[heap_size] 82 SetHeapSizeMinus1(); 83 MaxHeapify(0); //Max_Heapify() 84 return maxNum; 85 } 86 87 void PriorityQueue::HeapIncreaseKey(int srcIndex, int dstKey) //increasing the srcKey to dstKey 88 { 89 if (dstKey < GetQueueElement(srcIndex)) 90 throw "new key is smaller than current key!"; 91 SetQueueElement(srcIndex, dstKey); //x = key 92 while(srcIndex > 0 && GetQueueElement(getParent(srcIndex)) < GetQueueElement(srcIndex)) { 93 Swap(srcIndex, getParent(srcIndex)); 94 srcIndex = getParent(srcIndex); //get parent 95 } 96 } 97 98 void PriorityQueue::HeapDelete(int key) //delete key 习题6.5-8 99 { 100 int heap_size = GetHeapSize(); 101 int index = 0; 102 for (;index < heap_size; index ++) { 103 if (GetQueueElement(index) == key) 104 break; 105 } 106 SetQueueElement(index, GetQueueElement(heap_size-1)); 107 SetHeapSizeMinus1(); 108 MaxHeapify(index); 109 } 110 111 //other assist functions 112 void PriorityQueue::DisplayQueue() 113 { 114 int nLen = GetArrayLength(); 115 cout << "------------------------" << endl; 116 for (int i = 0; i < nLen; i ++) 117 cout << GetQueueElement(i) << " "; 118 cout << endl; 119 } 120 121 void PriorityQueue::DisplayHeapQueue() 122 { 123 int heap_size = GetHeapSize(); 124 cout << "------------------------" << endl; 125 for (int i = 0; i < heap_size; i ++) 126 cout << GetQueueElement(i) << " "; 127 cout << endl; 128 } 129 130 void PriorityQueue::AddQueueElement(int key) 131 { 132 m_vecQueue.push_back(key); 133 m_heapSize ++; 134 m_length ++; 135 } 136 137 138 // int main() 139 // { 140 // //int key, num; 141 // PriorityQueue PQ; 142 // 143 // // cout << "the number:" << endl; 144 // // cin >> num; 145 // int arr[] = {10,8,7,16,14,9,3,2,4,1}; 146 // cout << "the key:" << endl; 147 // for (int i = 0; i < 10; i ++) { 148 // PQ.AddQueueElement(arr[i]); 149 // } 150 // 151 // PQ.BuildMaxHeap(); 152 // PQ.DisplayQueue(); 153 // 154 // //Max 155 // cout << "Max:" << PQ.HeapMaximum() << endl; 156 // 157 // //IncreaseKey 158 // cout << "IncreaseKey:" << endl; 159 // PQ.HeapIncreaseKey(0, 18); 160 // PQ.DisplayHeapQueue(); 161 // 162 // //InsertKey 163 // cout << "InsertKey:" << endl; 164 // PQ.HeapInsert(20); 165 // PQ.DisplayHeapQueue(); 166 // 167 // //Extract_Max 168 // cout << "Extract_Max:" << PQ.HeapExtractMax() << endl; 169 // PQ.DisplayHeapQueue(); 170 // 171 // //Extract_Max 172 // cout << "Extract_Max:" << PQ.HeapExtractMax() << endl; 173 // PQ.DisplayHeapQueue(); 174 // 175 // return 0; 176 // }
习题精讲:
优先队列的讲述,基本就是这样,其实主要的设计思想还是堆。下面看两道有意思的习题:
1)习题6.5-6:在Heap_Increase_Key的第5行操作中,一般需要通过三次赋值来完成。想一想如何利用Insertion_Sort内循环部分的思想,只用一次赋值就完成这一交换操作?
分析:这是一种非常好的出题思路,能够打开我们的思维,让人有一种眼前一亮的感觉。我们可以先向下移动小于他的祖先,直到没有小于他的祖先后放在空出的位置上。如:
1 Heap-Increase-Key(A, i, key) 2 if A[i] < key 3 error "new key is smaller than original" 4 while i > 1 and A[Parent(i)] < key 5 A[i] = A[Parent(i)] 6 i = Parent(i) 7 A[i] = key
2)习题6.5-9:请设计一个能够在O(nlgk)的算法,它能够将k个有序链表合并成一个有序链表,这里n是所有输入链表包含的总的元素个数。(提示:使用最小堆来完成k路归并)。
这个题首先想到2路归并排序,但此处是k路,乍一看没什么思路,看了提示后,仍然没有什么头绪,看了网友Anker的思路后,发现可以这样来做(太水了):创建一个大小为k的数组,将k个链表中的第一个元素依次存放到数组中,然后将数组调整为最小堆,这样保证数组的第一个元素是最小的,假设为min,将min从最小堆取出并存放到最终结果的链表中,此时将min所在链表的下一个元素到插入的最小堆中,继续上面的操作,直到堆中没有元素为止。举个例子如下图所示(只给出不部分操作):
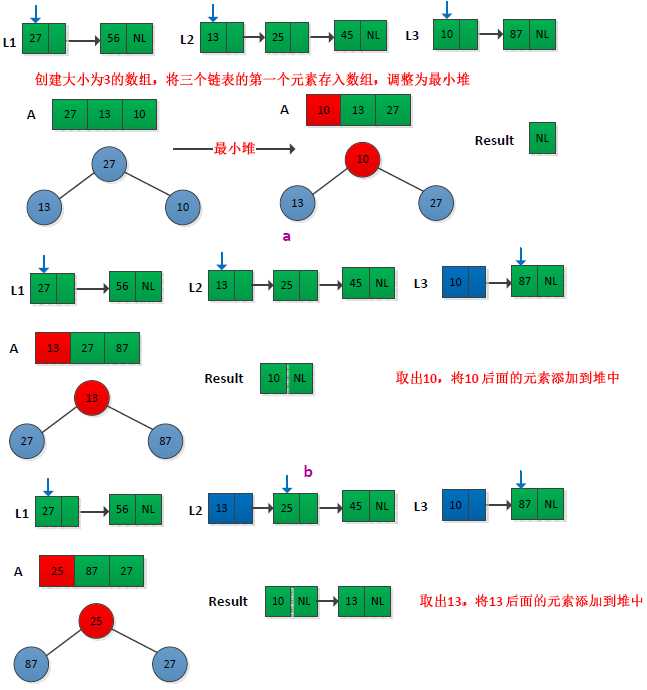
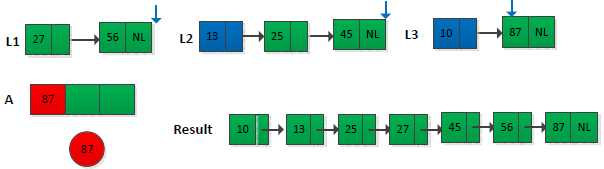
我们采用C++语言,借助STL实现此过程,链表采用vector,最小堆中存放的是vector的迭代器,表示vector中元素的位置。完整程序如下:

1 //MinHeap_KMerge.cpp 2 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <vector> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 #include "MinHeap.h" 9 10 //merge the k list to a heap; 11 template<class T> 12 MinHeap<T>::MinHeap(size_t kSize) 13 { 14 if (!m_minHeap) 15 delete []m_minHeap; 16 m_minHeap = new T[kSize+1]; 17 m_heapSize = 0; 18 } 19 20 //adjust the min heap; 21 template<class T> 22 void MinHeap<T>::MinHeapify(size_t index) 23 { 24 //assert 25 size_t heap_size = GetHeapSize(); 26 27 while (true) { 28 size_t left = LEFT(index); 29 size_t right = RIGHT(index); 30 31 size_t smallest; 32 if (left < heap_size && HeapCompare(left, index)) 33 smallest = left; 34 else smallest = index; 35 if (right < heap_size && HeapCompare(right, smallest)) 36 smallest = right; 37 38 if (smallest != index) { 39 Swap(index, smallest); 40 index = smallest; 41 } 42 else break; 43 } 44 } 45 46 //insert element 47 template<class T> 48 void MinHeap<T>::HeapInsert(const T &element) 49 { 50 m_minHeap[m_heapSize] = element; 51 m_heapSize += 1; 52 53 size_t index = m_heapSize-1; 54 55 while (index > 0 && HeapCompare(index, PARENT(index))) { 56 Swap(index, PARENT(index)); 57 index = PARENT(index); 58 } 59 } 60 61 //return and delete the min element 62 template<class T> 63 T MinHeap<T>::HeapExtractMin() 64 { 65 if (IsEmptyHeap()) 66 throw "Heap is Empty!"; 67 T minElement = HeapMin(); 68 69 int heap_size = GetHeapSize(); 70 m_minHeap[0] = m_minHeap[heap_size-1]; 71 m_heapSize -= 1; 72 MinHeapify(0); 73 return minElement; 74 } 75 76 //return min element; 77 template<class T> 78 T MinHeap<T>::HeapMin() const 79 { 80 return m_minHeap[0]; 81 } 82 83 int main() 84 { 85 const size_t k = 3; 86 vector<int> vecList[k]; 87 vector<int>::iterator iterList[k]; 88 vector<int> vecSort; 89 vector<int>::iterator iterS; 90 91 vector<int>::iterator it; 92 93 MinHeap<vector<int>::iterator> minHeap(k); 94 //first list 95 vecList[0].push_back(12); 96 vecList[0].push_back(24); 97 vecList[0].push_back(52); 98 cout << "first list:" << endl; 99 for ( it = vecList[0].begin();it != vecList[0].end(); ++it) 100 cout << *it << "->"; 101 cout << "NULL" << endl; 102 103 vecList[1].push_back(9); 104 vecList[1].push_back(32); 105 106 cout << "second list:" << endl; 107 for ( it = vecList[1].begin();it != vecList[1].end(); ++it) 108 cout << *it << "->"; 109 cout << "NULL" << endl; 110 111 vecList[2].push_back(34); 112 vecList[2].push_back(42); 113 vecList[2].push_back(78); 114 cout << "third list:" << endl; 115 for ( it = vecList[2].begin();it != vecList[2].end(); ++it) 116 cout << *it << "->"; 117 cout << "NULL" << endl; 118 119 iterList[0] = vecList[0].begin(); 120 iterList[1] = vecList[1].begin(); 121 iterList[2] = vecList[2].begin(); 122 123 124 minHeap.HeapInsert(iterList[0]); 125 minHeap.HeapInsert(iterList[1]); 126 minHeap.HeapInsert(iterList[2]); 127 128 while(minHeap.GetHeapSize()) { 129 it = minHeap.HeapExtractMin(); 130 vecSort.push_back(*it); 131 ++it; 132 if (it != vecList[0].end() && it != vecList[1].end() && it != vecList[2].end()) { //!!!!Expression vector iterators incompatible 133 minHeap.HeapInsert(it); 134 } 135 } 136 137 cout << "merge:" << endl; 138 for (iterS = vecSort.begin(); iterS != vecSort.end(); ++ iterS) 139 cout << *iterS << "->"; 140 cout << "NULL" << endl; 141 142 return 0; 143 }
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/bakari/p/4823753.html