标签:
1.1、简述
IO:input/output
IO流用来处理设备之间的数据传输
Java对数据的操作是通过流的方式
Java用于操作流的对象都在IO包中。
1.2、结构
字节流抽象类:
InputStream,OutputStream
字符流抽象类:
Reader、Writer。
ps:由这四4个派生出来子类名称都是以父类名作为子类名的后缀
如:InputStream的子类FileInputStream
如:Reader的子类FileReader;
1.3、分类
按操作数据方式为两种:字节流与字符流
按流向分:输入流,输出流
2.1、writer
写入字符流的抽象类。子类必须实现的方法仅有 write(char[], int, int)、flush() 和 close()。但是,多数子类将重写此处定义的一些方法,以提供更高的效率和/或其他功能。
| 字段摘要 | |
|---|---|
protected Object |
lock 用于同步针对此流的操作的对象。 |
| 构造方法摘要 | |
|---|---|
protected
|
Writer()
创建一个新的字符流 writer,其关键部分将同步 writer 自身。 |
protected
|
Writer(Object lock)
创建一个新的字符流 writer,其关键部分将同步给定的对象。 |
| 方法摘要 | |
|---|---|
Writer |
append(char c)
将指定字符添加到此 writer。 |
Writer |
append(CharSequence csq)
将指定字符序列添加到此 writer。 |
Writer |
append(CharSequence csq, int start,
int end) 将指定字符序列的子序列添加到此 writer.Appendable。 |
abstract
void |
close()
关闭此流,但要先刷新它。 |
abstract
void |
flush()
刷新该流的缓冲。 |
void |
write(char[] cbuf)
写入字符数组。 |
abstract
void |
write(char[] cbuf,
int off, int len) 写入字符数组的某一部分。 |
void |
write(int c)
写入单个字符。 |
void |
write(String str)
写入字符串。 |
void |
write(String str,
int off, int len) 写入字符串的某一部分。 |
3.1、FileWriter
| 构造方法摘要 | |
|---|---|
FileWriter(File file) 根据给定的 File 对象构造一个 FileWriter 对象。 |
|
FileWriter(File file,
boolean append) 根据给定的 File 对象构造一个 FileWriter 对象。 |
|
FileWriter(FileDescriptor fd)
构造与某个文件描述符相关联的 FileWriter 对象。 |
|
FileWriter(String fileName)
根据给定的文件名构造一个 FileWriter 对象。 |
|
FileWriter(String fileName,
boolean append) 根据给定的文件名以及指示是否附加写入数据的 boolean 值来构造 FileWriter 对象。 |
|
package com.pb.io.demo1; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Scanner; /* * close:关闭流,会将流关闭,不能再使用 * flush:flush刷新后,流可以继续使用, */ public class WriterDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); File file=null; //文件 FileWriter fw=null; //字符输出流 try { file=new File("d:/demo.txt"); // fw=new FileWriter(file);//如果有这个文件就会覆盖 //如果要追加到文件内容后面就使用true fw=new FileWriter(file,true); System.out.println("请输入内容,请输入 over后结束"); String str=null; //接收输入的内容 char [] buf=new char[1024];//定义缓冲区大小 do{ str=input.nextLine(); buf=str.toCharArray();//转换为字符数组 fw.write(buf); //将字符数组写入 fw.flush();//刷新流 }while(!str.equals("over")); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ //使用finally关闭流 try { if(fw!=null) fw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println("写入结束"); } }
3.2、FileReader
| 构造方法摘要 | |
|---|---|
FileReader(File file) 在给定从中读取数据的 File 的情况下创建一个新 FileReader。 |
|
FileReader(FileDescriptor fd)
在给定从中读取数据的 FileDescriptor 的情况下创建一个新 FileReader。 |
|
FileReader(String fileName)
在给定从中读取数据的文件名的情况下创建一个新 FileReader。 |
|
3.3示例 单个字符读取
package com.pb.io.demo1; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.IOException; /* * 单个字符读取 */ public class FileReaderDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { File file=null; //文件 FileReader fr=null; //字符输入流 try { file=new File("d:/demo.txt"); fr=new FileReader(file); int len=0;//接收读出内容 while((len=fr.read())!=-1){ System.out.println((char)len); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ try { //关闭流 if(fr!=null) fr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
3.4、示例 数组方式读取 建议使用
package com.pb.io.demo1; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Arrays; /* * 通过字符数组 读取 */ public class FileReaderDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { File file=null; //文件 FileReader fr=null; //字符输入流 try { file=new File("d:/demo.txt"); fr=new FileReader(file); //接收读出内容数组 char [] buf=new char [1024]; //一般为1024的整数倍 int len=0; while((len=fr.read(buf))!=-1){ //读取内容到字符数组 System.out.println(new String(buf,0,len));//读有多少,就输出多少 } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ try { //关闭流 if(fr!=null) fr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
4.1、字符输入流和字符输入流
package com.pb.io.demo1; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Scanner; public class FileWriterAndFileReader { public static void main(String[] args) { File file = new File("d:\\demo.txt"); Output(file); input(file); } // 写入文件 private static void Output(File file) { FileWriter fw = null; Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); try { fw = new FileWriter(file, true); // 声明变量来接收用户输入 System.out.println("请输入要写入的内容:输入over结束"); String str = null; // 声明缓冲区 char[] buf = new char[1024]; do { str = input.nextLine(); // 接收用户输入 buf = str.toCharArray(); // 转换为数组 fw.write(buf, 0, buf.length);// 写入 } while (!(str.equals("over"))); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (fw != null) { try { fw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } // 读写文件 private static void input(File file) { FileReader fr = null; try { fr = new FileReader(file); // 定义字符数组 char[] buf = new char[1024];// 缓冲区大小 int len = 0;// 长度读取的字符个数 while ((len = fr.read(buf)) != -1) { System.out.println(new String(buf, 0, len)); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (fr != null) { try { fr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
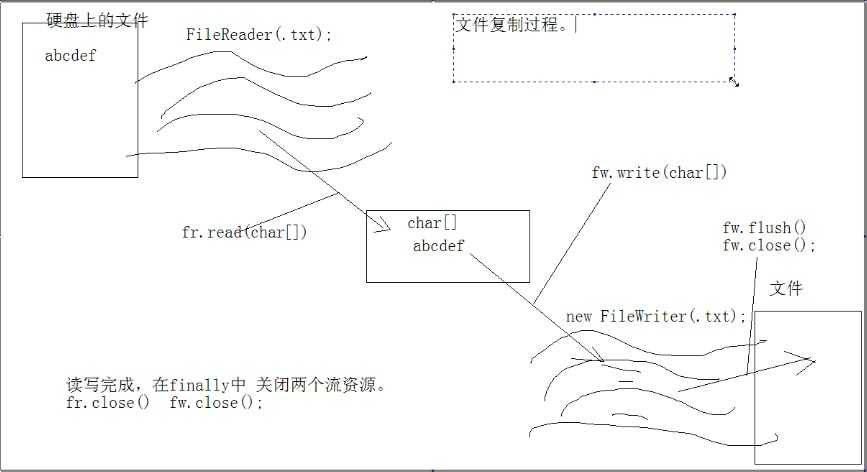
4.2、复制文件
package com.pb.io.demo1; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; /** * 复制的原理 将一个文件存储到另一个文件中 边读边写 先读再写 * */ public class CopyFileDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { File soure = new File("d:\\demo.txt"); File objFile = new File("e:\\q.txt"); copy1(soure, objFile); copy2(soure, objFile); } /* * 读一个复制一个 */ public static void copy1(File soure, File objFile) { FileReader fr = null; FileWriter fw = null; try { // 声明读,写流对象 fr = new FileReader(soure); fw = new FileWriter(objFile,true); int ch = 0; int count=0; // 开始读 while ((ch = fr.read()) != -1) { count++; System.out.println("正在读取"+count+"行"); fw.write(ch); fw.write("\r\n"); //换行 System.out.println("正在写入"+count+"行"); } System.out.println("读写完成"); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if (fw != null) fw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { if (fr != null) fr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } /* * 数组方式读取复制 */ public static void copy2(File soure, File objFile) { FileReader fr = null; FileWriter fw = null; try { // 声明读,写流对象 fr = new FileReader(soure); fw = new FileWriter(objFile,true); int ch = 0; int count=0; char [] buf=new char[1024]; // 开始读 while ((ch = fr.read(buf)) != -1) { count++; System.out.println("正在读取"+count+"行"); fw.write(buf,0,ch); fw.write("\r\n"); //换行 System.out.println("正在写入"+count+"行"); } System.out.println("读写完成"); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if (fw != null) fw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { if (fr != null) fr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
JAVA基础学习day19--IO流一、FileWrite与FileReader
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/liunanjava/p/4842612.html