标签:
1. TreeSet类概述:
• 能够对元素按照某种规则进行排序。
• 或者根据创建set时提供的Comparator进行排序
• 具体取决于使用的构造方法
2. 代码示例:
1 package cn.itcast_05; 2 3 import java.util.TreeSet; 4 5 /* 6 * TreeSet:能够对元素按照某种规则进行排序。 7 * 排序有两种方式 8 * A:自然排序 9 * B:比较器排序 10 * 11 * TreeSet集合的特点:排序和唯一 12 * 13 * 通过观察TreeSet的add()方法,我们知道最终要看TreeMap的put()方法。 14 */ 15 public class TreeSetDemo { 16 public static void main(String[] args) { 17 // 创建集合对象 18 // 自然顺序进行排序 19 TreeSet<Integer> ts = new TreeSet<Integer>(); 20 21 // 创建元素并添加 22 // 20,18,23,22,17,24,19,18,24 23 ts.add(20); 24 ts.add(18); 25 ts.add(23); 26 ts.add(22); 27 ts.add(17); 28 ts.add(24); 29 ts.add(19); 30 ts.add(18); 31 ts.add(24); 32 33 // 遍历 34 for (Integer i : ts) { 35 System.out.println(i); 36 } 37 } 38 }
运行效果,如下:
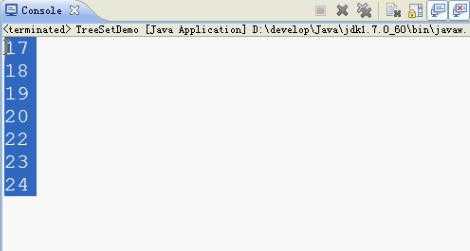
3. TreeSet 保证元素排序的源码解析:
通过观察TreeSet的add()方法,我们知道最终要看TreeMap的put()方法。
1 interface Collection {...} 2 3 interface Set extends Collection {...} 4 5 interface NavigableMap { 6 7 } 8 9 class TreeMap implements NavigableMap { 10 public V put(K key, V value) { 11 Entry<K,V> t = root; 12 if (t == null) { 13 compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check 14 15 root = new Entry<>(key, value, null); 16 size = 1; 17 modCount++; 18 return null; 19 } 20 int cmp; 21 Entry<K,V> parent; 22 // split comparator and comparable paths 23 Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator; 24 if (cpr != null) { 25 do { 26 parent = t; 27 cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key); 28 if (cmp < 0) 29 t = t.left; 30 else if (cmp > 0) 31 t = t.right; 32 else 33 return t.setValue(value); 34 } while (t != null); 35 } 36 else { 37 if (key == null) 38 throw new NullPointerException(); 39 Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key; 40 do { 41 parent = t; 42 cmp = k.compareTo(t.key); 43 if (cmp < 0) 44 t = t.left; 45 else if (cmp > 0) 46 t = t.right; 47 else 48 return t.setValue(value); 49 } while (t != null); 50 } 51 Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent); 52 if (cmp < 0) 53 parent.left = e; 54 else 55 parent.right = e; 56 fixAfterInsertion(e); 57 size++; 58 modCount++; 59 return null; 60 } 61 } 62 63 class TreeSet implements Set { 64 private transient NavigableMap<E,Object> m; 65 66 public TreeSet() { 67 this(new TreeMap<E,Object>()); 68 } 69 70 public boolean add(E e) { 71 return m.put(e, PRESENT)==null; 72 } 73 }
真正的比较是依赖于元素的compareTo()方法,而这个方法是定义在 Comparable里面的。所以,你要想重写该方法,就必须是先 Comparable接口。这个接口表示的就是自然排序。
Java基础知识强化之集合框架笔记43:Set集合之TreeSet存储Integer类型的元素并遍历
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/hebao0514/p/4857605.html