标签:
SQLite是内置于Android的一款轻量级关系型数据库,她运算速度快,占用资源少,通常只需要几百K的内存就足够了,因而特别适合在移动设备上使用。
SQLite不仅支持标准的SQL语法,还遵循数据库的ACID事务,所以如果有其他数据库基础,会上手很快。与其他数据库不同的是,SQLite不用设置用户名和密码就可以使用。
和其他数据库不同的是,SQLite没有其他数据库那么多繁杂的数据类型,它的数据类型很简单:integer表示整型,real表示浮点型,text表示文本类型,blob表示二进制类型
SQLiteOpenHelper抽象类可以帮我们对数据库进行创建和升级。
继承SQLiteOpenHelper需要实现它的两个方法:onCreate()和onUpgrade(),然后在这两个方法中去实现创建、升级数据库的逻辑。
SQLiteOpenHelper中还有两个方法getReadableDatabase()和getWirtableDatabase(),这两个方法都可以创建或打开一个现有的数据库并返回一个可对数据库进行读写操作的对象。不同的是,当数据库不可写入的时候,getReadableDatabase()方法返回的对象将以只读的方式去打开数据库,而getWirtableDatabase()将抛出异常。
一个简单的例子:
MainActivity.java
package cn.lixyz.sqlitedemo; import android.app.Activity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.Menu; import android.view.MenuItem; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; public class MainActivity extends Activity { private Button bt_createDB; private MyDatabaseHelper myDatabaseHelper; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); bt_createDB = (Button) findViewById(R.id.bt_createDB); myDatabaseHelper = new MyDatabaseHelper(this,"BookStore.db",null,1); bt_createDB.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { myDatabaseHelper.getWritableDatabase(); } }); } @Override public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) { // Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present. getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.menu_main, menu); return true; } @Override public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) { // Handle action bar item clicks here. The action bar will // automatically handle clicks on the Home/Up button, so long // as you specify a parent activity in AndroidManifest.xml. int id = item.getItemId(); //noinspection SimplifiableIfStatement if (id == R.id.action_settings) { return true; } return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item); } }
MyDatabaseHelper.java
package cn.lixyz.sqlitedemo; import android.content.Context; import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase; import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper; import android.widget.Toast; /** * Created by LGB on 2015/10/16. */ public class MyDatabaseHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper { public static final String CREATE_BOOK = "create table book (id integer primary key autoincrement,author text ,price real,pages integer,name text)"; private Context mContext; public MyDatabaseHelper(Context context, String name, SQLiteDatabase.CursorFactory factory, int version) { super(context, name, factory, version); mContext = context; } @Override public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) { db.execSQL(CREATE_BOOK); Toast.makeText(mContext,"创建成功",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } @Override public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) { } }
activity_main.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <Button android:id="@+id/bt_createDB" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="创建数据库" /> </LinearLayout>
执行结果:
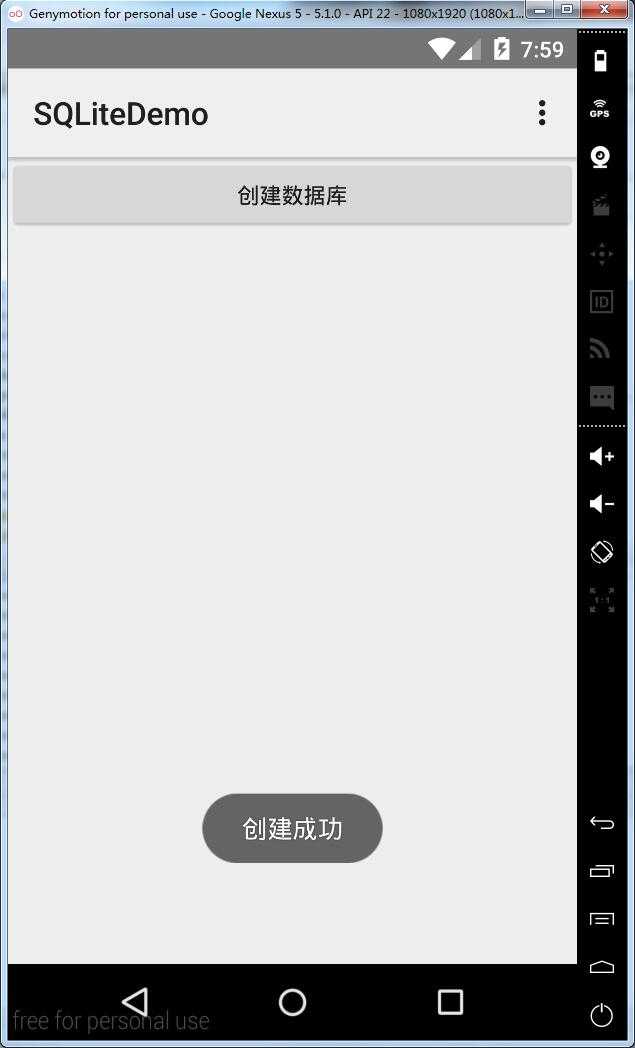
在DDMS中查看
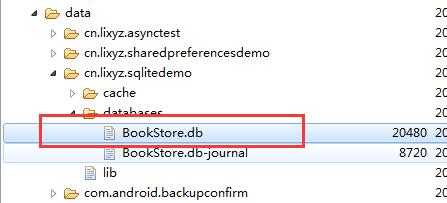
我们使用navicat打开这个db文件:
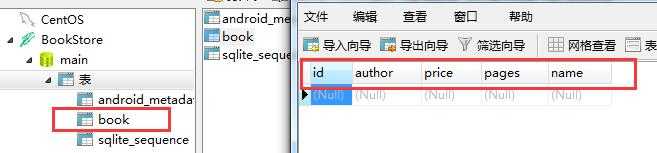
可见,数据库和表创建成功了。
Android笔记(三十九) Android中的数据存储——SQLite(一)
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/xs104/p/4886249.html