标签:
Kmeans是最简单的聚类算法之一,但是运用十分广泛,最近看到别人找实习笔试时有考到Kmeans,故复习一下顺手整理成一篇笔记。Kmeans的目标是:把n 个样本点划分到k 个类簇中,使得每个点都属于离它最近的质心对应的类簇,以之作为聚类的标准。质心,是指一个类簇内部所有样本点的均值。
Step 1. 从数据集中随机选取K个点作为初始质心 将每个点指派到最近的质心,形成k个类簇 Step 2. repeat 重新计算各个类簇的质心(即类内部点的均值) 重新将每个点指派到最近的质心,形成k个类簇 until 质心不再波动
例如下图的样本集,我们目标是分成3个类簇,初始随机选择的3个质心比较集中,但是迭代4次之后,质心趋于稳定,并将样本集分为3部分。
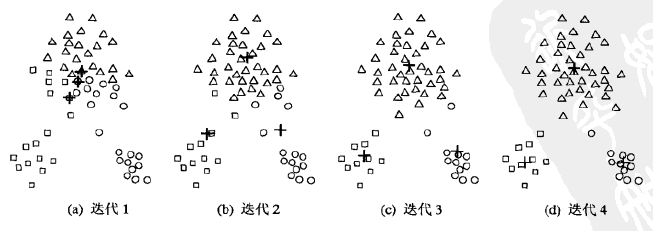
Kmeans算法,对于距离度量可以使用余弦相似度,也可以使用欧式距离或其它标准;质心,是指一个类簇内部所有样本点的均值;随机初始化的质心,当随机效果不理想时,Kmeans算法的迭代次数变多。Kmeans算法思想比较简单,但实用。
package kmeans;
public class Point {
public double[] x; // 特征维度
public int len_arr; // 特征维数
public boolean isSample = false; // True判断是数据集的点,False是第二次kmenas所计算得来的质心
public int id; // 质心分配的id=0
public String text; // 用于描述鸢尾花种类
public Point(double[] x, int len_arr, boolean isSample, int id) {
this.x = x;
this.len_arr = len_arr;
this.isSample = isSample;
this.id = id;
}
// 计算欧氏距离
public double Distance(Point other) {
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len_arr; i++) {
sum += Math.pow(x[i] - other.x[i], 2);
}
sum = Math.sqrt(sum);
return sum;
}
// 以下两个方法用于数据结构Set, 第一次kmeans生成k个随机点时用到
@Override
public boolean equals(Object other) {
if (other.getClass() != Point.class) {
return false;
}
return id == ((Point) other).id;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return id;
}
}
package kmeans;
import java.util.*;
public class Cluster {
public int id; // 簇id
public Point center; // 簇质心
public List<Point> members = new ArrayList<>(); // 簇中成员(数据集点)
public Cluster(int id, Point center) {
this.id = id;
this.center = center;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o.getClass() != Cluster.class) {
return false;
}
return id == ((Cluster) o).id;
}
}
package kmeans;
import java.util.*;
public class Kmeans {
public List<Point> samples; // 数据集点
public List<Cluster> clusters = new ArrayList<>(); // 存放聚类类簇结果
public int k; // 聚类个数
public int arr_len; // 数据集点特征维数
public int steps; // 最大迭代次数
public Kmeans(List<Point> samples, int k, int arr_len, int steps) {
this.samples = samples;
this.k = k;
this.arr_len = arr_len;
this.steps = steps;
}
public void run() {
FirstStep(); // 算法Step 1
double oldDist = Loss(); // 计算各个类簇内点到质心的距离和
double newDist = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < steps; i++) {
SecondStep(); // 算法Step 2
newDist = Loss();
if (oldDist - newDist < 0.01) { // 如果质心不再变化,则停止学习
break;
}
System.out.println("Step " + i + ":" + (oldDist - newDist));
oldDist = newDist;
}
// 打印结果
for (int i = 0; i < clusters.size(); i++) {
System.out.println("第" + i + "个簇:");
for (Point p : clusters.get(i).members) {
if (!p.isSample) {
continue;
}
System.out.print("(");
for (int xi = 0; xi < p.x.length; xi++) {
if (xi != 0) {
System.out.print(",");
}
System.out.print(p.x[xi]);
}
System.out.print(")");
System.out.println("\t" + p.text);
}
}
}
public void FirstStep() { // 算法Step 1
Set<Point> centers = new HashSet<>(); // 从样本数据集中随机选取k个不重复的质心
int id = 0; // 类簇id
while (centers.size() < k) {
Random r = new Random(); // 随机选取样本数据集的数据下标
int ti = r.nextInt(samples.size()) % samples.size();
if (centers.contains(samples.get(ti))) {
continue;
}
centers.add(samples.get(ti));
Cluster clu = new Cluster(id++, samples.get(ti));
clusters.add(clu);
}
Classify(); // 开始根据k个质心进行聚类
}
public void SecondStep() { // 算法Step 2
List<Cluster> newClusters = new ArrayList<>();
for (Cluster clu : clusters) {
double[] tx = new double[arr_len];
for (Point p : clu.members) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr_len; i++) {
tx[i] += p.x[i];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr_len; i++) {
tx[i] /= clu.members.size();
} // 重新在各个类簇内部计算新的质心
Point newCenter = new Point(tx, arr_len, false, 0);
Cluster newClu = new Cluster(clu.id, newCenter);
newClusters.add(newClu);
}
clusters.clear();
clusters = newClusters;
Classify(); // 根据新的质心重新聚类
}
public void Classify() { // 聚类步骤,将各个点分配到距离最近的质心所在的类簇
for (int i = 0; i < samples.size(); i++) {
double mindistance = Double.MAX_VALUE;
int clu_Id = -1;
for (Cluster clu : clusters) {
if (samples.get(i).Distance(clu.center) < mindistance) {
mindistance = samples.get(i).Distance(clu.center);
clu_Id = clu.id;
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < clusters.size(); j++) {
if (clusters.get(j).id == clu_Id) {
clusters.get(j).members.add(samples.get(i));
break;
}
}
}
}
public double Loss() { // 计算类簇内部各个点到质心的距离
double sum = 0;
for (Cluster clu : clusters) {
for (Point p : clu.members) {
sum += p.Distance(clu.center);
}
}
return sum;
}
}
package kmeans;
import java.util.*;
public class Keyven {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = input.nextInt();
int arr_len = input.nextInt();
List<Point> samples = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
double[] x = new double[arr_len];
for (int j = 0; j < arr_len; j++) {
x[j] = input.nextDouble();
}
String text = input.nextLine();
Point p = new Point(x, arr_len, true, i + 1);
p.text = text;
samples.add(p);
}
Kmeans km = new Kmeans(samples, 3, arr_len, 1000);
km.run();
input.close();
}
}
鸢尾花的数据集下载:http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/
(1)离群点的处理:离群点一般称为噪音,离群点有可能影响类簇的发现,导致实验效果不合理,因此在进行Kmeans之前发现并提出离群点是有必要的。
(2)初始质心的选取:初始质心的随机选取有可能出现过度集中的情况,导致迭代次数增多,这时可以使用Kmeans++来解决这个问题,Kmeans++算法步骤如下图:

也可以使用另外一种方法:随机地选择第一个点,或取所有点的质心作为第一个点。然后,对于每个后继初始质心,选择离已经选取过的初始质心最远的点。使用这种方法,确保了选择的初始质心不仅是随机的,而且是散开的。但是,这种方法可能选中离群点。此外,求离当前初始质心集最远的点开销也非常大。
(3)算法终止条件:一般是目标函数达到最优或者达到最大的迭代次数即可终止。对于不同的距离度量,目标函数往往不同。当采用欧式距离时,目标函数一般为最小化对象到其簇质心的距离的平方和,如下:
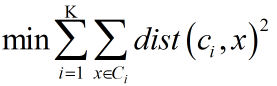
当采用余弦相似度时,目标函数一般为最大化对象到其簇质心的余弦相似度和,如下:
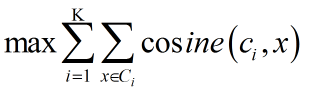
(4)K值得选取:Kmeans算法的聚类个数K 值是由用户设定的,因为一开始我们并不知道数据集的分布,Kmeans又不像EM算法那样自动学习聚类成K 个类簇。为解决这个问题,可以将Kmeans与层次聚类结合,首先采用层次聚类算法粗略决定聚类个数,并找到初始聚类,然后用Kmeans来优化聚类结果。
其它聚类算法:谱聚类、层次聚类,等。这里仅简单地介绍层次聚类。
层次聚类,是一种很直观的算法。顾名思义就是要一层一层地进行聚类,可以从下而上地把小的cluster合并聚集,也可以从上而下地将大的cluster进行分割,一般采用从下而上地聚类。
从下而上地合并cluster,就是每次找到距离最短的两个cluster,然后进行合并成一个大的cluster,直到全部合并为一个cluster。整个过程就是建立一个树结构,类似于下图。
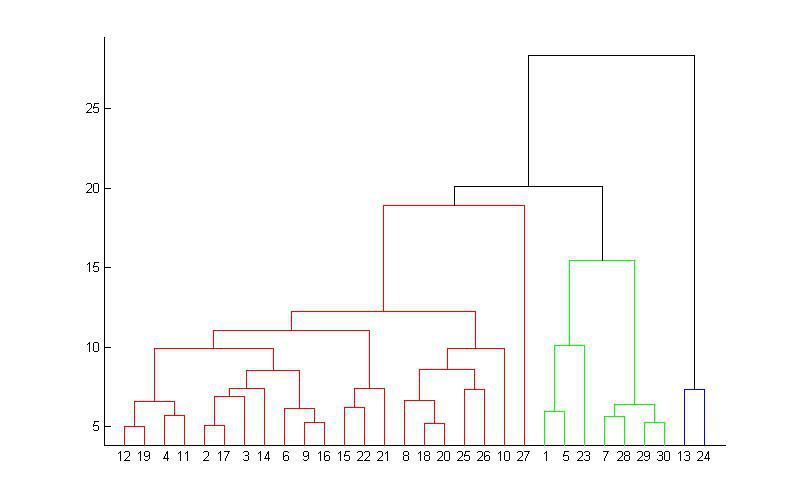
那么,如何判断两个cluster之间的距离呢?一开始每个数据点独自作为一个类,它们的距离就是这两个点之间的距离。而对于包含不止一个数据点的cluster,就可以选择多种方法了,最常用的就是average-linkage ,这种方法就是把两个集合中的点两两的距离全部放在一起求一个平均值。
只要得到了上面那样的聚类树,想要分多少个cluster都可以直接根据树结构来得到结果。
聚类(2)——层次聚类 Hierarchical Clustering
标签:
原文地址:http://my.oschina.net/keyven/blog/518670