标签:
Saturday, January 25, 2014
Eclipse MAT: Understand Incoming and Outgoing References
In [1], we have shown how to use OQL to query String instances starting with a specified substring (i.e., our objects of interest) from a heap dump.[7,8] To determine who is creating these objects, or find out what the purpose of some structures are, an object‘s incoming and outgoing references become handy.
In this article, we will examine the following topics:
- What are incoming references or outgoing references of an object?
Then look at two topics related to incoming references: - Path To GC Roots
- Immediate Dominators
Outgoing References
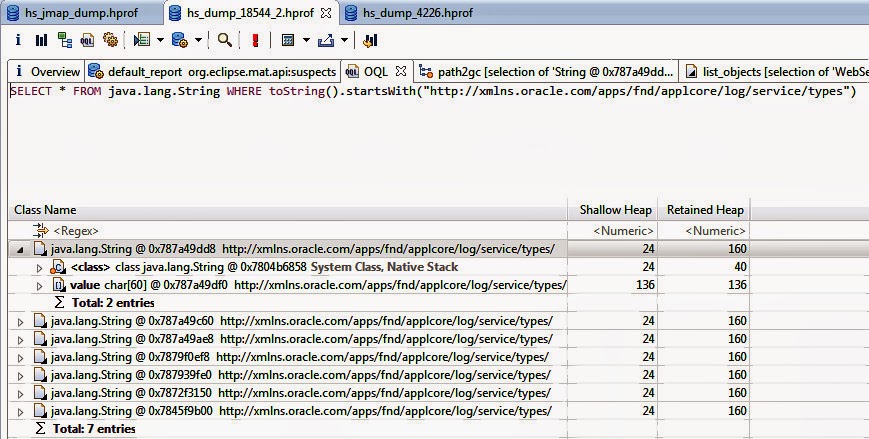
Using the following OQL statement, we have identified total 7 entries (see Figure above) as our objects of interest: SELECT * FROM java.lang.String WHERE toString().startsWith("http://xmlns.oracle.com/apps/fnd/applcore/log/service/types")
After expanding the first entry, it shows two outgoing references: - a reference to the Class instance for the String object
- a reference to an array of char values
Outgoing References show the actual contents of the instances, helping to find out their purpose. In our String instance, it holds two references. The memory overhead of this String instance is shown in two values: [3] - Shallow Heap
- Retained Heap
These sizes of String instances depends on the internal implementation of the JVM. Read [2,4] for more details.
Incoming References
To get incoming references of the first entry, choose List Objects with Incoming References from the context menu. 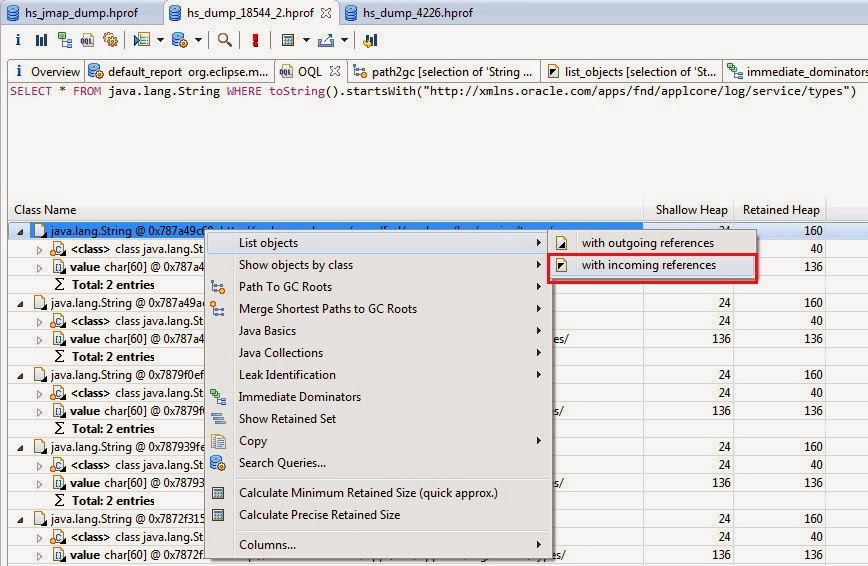
Now a tree structure is displayed, showing all instances with all incoming references (note the different icon highlighted in red). These references have kept the object alive and prevented it from being garbage collected.

Immediate Dominators
Similarly, from the context menu, you can display immediate dominators of the first entry (see Figure below). An Object X is said to dominate an Object Y if every path from the GC Root to Y must pass through X. So, immediate dominators is a very effective way to find out who is keeping a set of objects alive. For example, the immediate dominators of our first entry (note that we have used "java.*|com\.sun\..*" as our filter) is: - oracle.j2ee.ws.server.deployment.WebServiceEndpoint

Path To GC Roots
From context menu, you can also show "Path to GC Roots" of the first entry (see Figure below). Path to GC Roots shows the path to GC roots which should be found for a given object. As you can expect, its immediate dominators must also be on this path. Note that, when you display Path to GC Roots, you can specify which fields of certain classes to be ignored when finding paths. For example, we have specified that paths through Weak or Soft Reference referents to be excluded. 
Live Data Set
Now we know - oracle.j2ee.ws.server.deployment.WebServiceEndpoint
is keeping our String instance alive. Instead of viewing Path to GC Roots, it is easier to see it the other way around. So, we have chosen to display the outgoing references of WebServiceEndpoint instance (see Figure below). As you can see, our String instance is displayed as the leaf node of the tree structure. 
References
- Eclipse MAT: Querying Heap Objects Using OQL (Xml and More)
- Java memory usage of simple data structure
- Shallow vs. Retained Heap
- Create and Understand Java Heapdumps (Act 4)
- Diagnosing Java.lang.OutOfMemoryError (Xml and More)
- I Bet You Have a Memory Leak in Your Application by Nikita Salnikov-Tarnovski
- Classloader leak is the most common leak in web applications
- How to analyze heap dumps
- Leak can be induced
- Per call (or a class of objects)
- Per object
- Diagnosing Heap Stress in HotSpot (Xml and More)
Posted by XML and More at 10:45 AM
Eclipse MAT: Understand Incoming and Outgoing References
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/javafan/p/4896938.html