标签:
static void Main(string[] args) { byte[] a = new byte[]{0,0,0,0}; byte[] b = new byte[] {1,2,3,4}; IntPtr pt = Marshal.AllocHGlobal(a.Length); //从source数组的startIndex下标开始复制length个对象到ptr; Marshal.Copy(b,0,pt+0,b.Length); //从ptr复制length个对象到目标数组的,从目标数组的startIndex开始写入。 Marshal.Copy((pt+1),a,1,2); unsafe { byte* pb = (byte*) pt; for (int i = 0; i < a.Length; i++) { Console.WriteLine("/b:"+(*pb++) + "/a:" + a[i]); } } //释放非托管内存; Marshal.FreeHGlobal(pt); byte[] arBt = new byte[]{200,0,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,11,12,13,14,0x0f,199}; IntPtr ptr = Marshal.AllocHGlobal(arBt.Length); //写入数据; Marshal.Copy(arBt, 0, ptr, arBt.Length); short[] arSt = new short[arBt.Length / sizeof(short)]; int[] arInt = new int[arBt.Length / sizeof(int)]; //复制为short数据; Marshal.Copy(ptr, arSt, 0, arSt.Length); //调整数据 此时arSt不变 下面的arInt改变; Marshal.WriteByte(ptr, 1, 9); Marshal.WriteByte(ptr, 10, (byte)(Marshal.ReadByte(ptr,10)*9)); //复制为int数据; Marshal.Copy(ptr, arInt, 0, arInt.Length); for (int i = 0; i < arBt.Length; i++) { Console.Write(arBt[i] + "-"); } Console.WriteLine(); for (int i = 0; i < arBt.Length; i++) { Console.Write(Marshal.ReadByte(ptr,i) + "-"); } Console.WriteLine(); unsafe { //获取指定数组中指定索引处的元素的地址 short* ps = (short*)Marshal.UnsafeAddrOfPinnedArrayElement(arSt, 0); byte[] tmp0 = BitConverter.GetBytes(*ps); Console.WriteLine(*ps+ "/" + (ushort)*ps+ ",byte>>>&0=" + tmp0[0] + ",&1=" + tmp0[1]); //获取指定数组中指定索引处的元素的地址 int* pi = (int*)Marshal.UnsafeAddrOfPinnedArrayElement(arInt, 0); byte[] tmp1 = BitConverter.GetBytes(*pi); Console.WriteLine(*pi + "/" + (uint)*pi + ",byte>>>&0=" + tmp1[0] + ",&1=" + tmp1[1] +",&2="+ tmp1[2] + ",&3=" + tmp1[3]); Console.WriteLine("-----short 2 byte-----"); for (int i = 0; i < arSt.Length; i++) { byte[] tmp = BitConverter.GetBytes(arSt[i]); Console.WriteLine(arSt[i] + "/" + (ushort)arSt[i] + ",byte>>>&0=" + tmp[0] + ",&1=" + tmp[1]); } Console.WriteLine("-----int 2 byte-----"); for (int i = 0; i < arInt.Length; i++) { byte[] tmp = BitConverter.GetBytes(arInt[i]); Console.WriteLine(arInt[i] + "/" + (uint)arInt[i] + ",byte>>>&0=" + tmp[0] + ",&1=" + tmp[1] + ",&2=" + tmp[2] + ",&3=" + tmp[3]); } } Marshal.FreeHGlobal(ptr); unsafe { Test tt = new Test(); tt.t1 = 100; tt.t2 = true; tt.t3 = 6666; tt.t4 = 666666; tt.t6 = false; string s = "ABCD大师0X00"; char[] chs = s.ToCharArray(); char* block = stackalloc char[100]; fixed (char* cpt = chs) { for (int i = 0; i < chs.Length; i++) { tt.t5[i] = *(cpt + i); block[i] = *(cpt + i); } Console.WriteLine(new string(tt.t5)); } } }
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential, Pack = 4)] public unsafe struct Test { public byte t1; public bool t2; public ushort t3; public int t4; //固定大小的缓冲区 public fixed char t5[100]; public bool t6; }
//----------------------------------
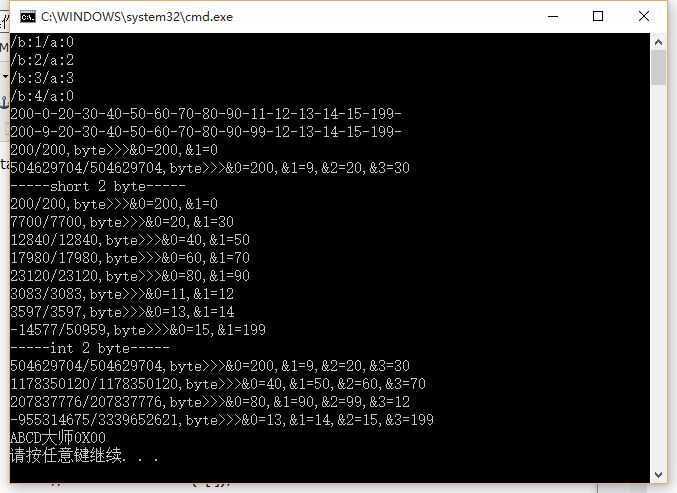
通过上面的例子,我们可以看出,使用C#指针操作内存,非常方便。使用Marshal我们可以获得非托管内存的指针IntPtr。该指针我们可以强制转换为
sbyte、byte、short、ushort、int、uint、long、ulong、char、float、double、decimal 或 bool的类型指针。之后我们可以Copy,Read ,Write等操作内存。
同C++一样我们获得的指针可以通过指针运算符 *,->,&,++,--进行指定内存的数据和位移操作。也可以通过Marshal,将我们的byte类型数据进行类型转换操作。
Marshal类提供的转换函数功能之强大。
可参阅https://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/system.runtime.interopservices.marshal_methods%28v=vs.80%29.aspx;
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/2Yous/p/4897812.html