标签:
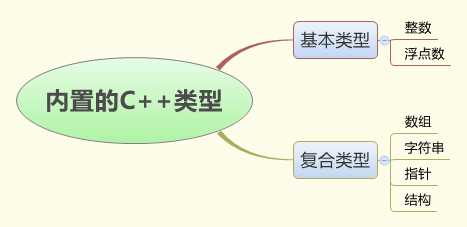
变量的作用
命名规则
1 int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) 2 { 3 using namespace std; 4 cout << sizeof(short) << endl; 5 cout << sizeof(int) << endl; 6 cout << sizeof(long) << endl; 7 cout << sizeof(long long) << endl; 8 return 0; 9 }
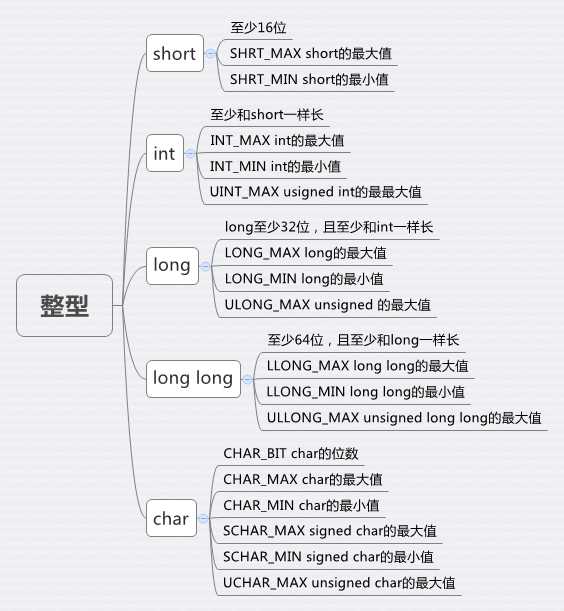
整型字面量
分为十进制、八进制、十六进制等等表示方法仅仅是为了表达上的方便,他们都是以二进制的形式被存储。
下面是cout输出各种进制的方式,
1 int waist = 42; 2 cout << waist << endl; 3 cout << hex;//十六进制输出 4 cout << waist << endl; 5 cout << oct;//8进制输出 6 cout << waist << endl; 7 cout << dec;//十进制输出 8 cout << waist << endl;
创建常量通用格式如下:
const type name=value;在声明中就必须对const进行初始化。
const对比#define的优点:
浮点数分为3种类型:float、double和long double。这些类型是按他们可以表示的有效数位和允许的指数最小范围来描述的。如:2.5, 3.32e+022,1.23f这些都是浮点数。
浮点数相对于整数的优缺点:
C++允许将一种类型的变量的值赋给另一种类型的变量。这种转换一般会造成数据精度的丢失。
1 int num1 = 5; 2 float num2 = num1;
这种转换方式要求比较严格,列表初始化不允许缩窄,如不允许将浮点数转换为整型
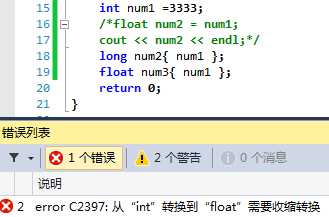
都和第一种转换方式差不多
通用格式如下:
C的方式:(typename)value
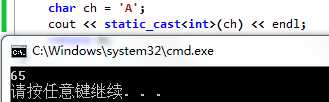
C++的方式:typename(value) static_cast<typename>(value)
1 char ch = ‘A‘; 2 cout << static_cast<int>(ch) << endl;
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/liunlls/p/type.html