标签:
在TSQL中,有exists子句表示存在,表示匹配任意一行数据,但是,如何表示匹配全部的数据行。例如,表示一个学生选修了所有课程,这就是“匹配全部”语义的一个经典实例。
示例,获取“选修全部”课程的学生姓名
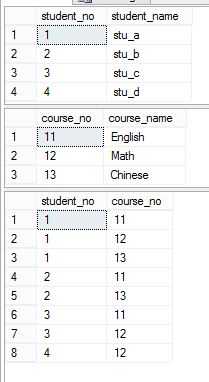
1,创建实例数据
--create table create table dbo.student ( student_no int, student_name varchar(10) ) create table dbo.course ( course_no int, course_name varchar(10) ) create table dbo.student_course ( student_no int, course_no int ) --insert data insert into dbo.student(student_no,student_name) values(1,‘stu_a‘),(2,‘stu_b‘),(3,‘stu_c‘),(4,‘stu_d‘) insert into dbo.course(course_no,course_name) values(11,‘English‘),(12,‘Math‘),(13,‘Chinese‘) insert into dbo.student_course(student_no,course_no) values(1,11),(1,12),(1,13),(2,11),(2,13),(3,11),(3,12),(4,12)
2,“双重否定”成肯定
exists表示匹配任意一个,使用两个 not exists 表示:不存在任何一个课程该学生没有选修
select s.student_name from dbo.student s where not exists ( select NULL from dbo.course c where not EXISTS ( select NULL from dbo.student_course sc where sc.student_no=s.student_no and sc.course_no=c.course_no ) )
3,使用group by 子句实现
根据学号对选课表进行分组
declare @CouseCount int select @CouseCount=count(0) from dbo.course ;with cte as ( select sc.student_no from dbo.student_course sc inner join dbo.course c on sc.course_no=c.course_no group by sc.student_no having count(0)=@CouseCount ) select s.student_name from dbo.student s inner join cte c on s.student_no=c.student_no
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/ljhdo/p/4929622.html