标签:
服务默默的在后台工作着,执行着不需要和用户交互的工作。
服务依赖于应用程序进程而存活
作为四大组件之一,服务具备共同的特点——需要在AndroidManifest中注册
需要注意的是——一定不要在子线程中进行UI操作,否则会阻塞主线程出现异常
1 /** 主要的逻辑是在这里完成,但是考虑到:服务默认是在主线程执行的,如果在这里进行比较费时的操作<br/> 2 * 就容易出现ANR(Application Not Responding).<br/> 3 * 所以标准的写法是在这里新建一个子线程执行逻辑处理<br/> 4 * 但是:这样做了之后,必须要使用stopService或stopSelf才能停得下来 5 */ 6 @Override 7 public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) { 8 Log.d("test", "service onStartCommand"); 9 new Thread(new Runnable() { 10 11 @Override 12 public void run() { 13 // 逻辑处理——不能进行UI更新 14 // ... 15 // 这里处理完之后调用停止服务 16 stopSelf(); 17 18 } 19 }).start(); 20 return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId); 21 }
通过异步消息处理机制进行UI操作
在主线程定义一个handler
public static final int SHOW_RESPONSE = 0; private Handler handler = new Handler() { @Override public void handleMessage(Message msg) { switch (msg.what) { case SHOW_RESPONSE: String response = (String) msg.obj; // 进行UI更新:根据子线程换回来的msg.obj的值和msg.what的值break; default: break; } } };
子线程通过handler发送数据
new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() {try { // 将获取到的数据交给Handler处理 Message msg = new Message(); msg.what = SHOW_RESPONSE; msg.obj = 对象; handler.sendMessage(msg); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { } } } }).start();
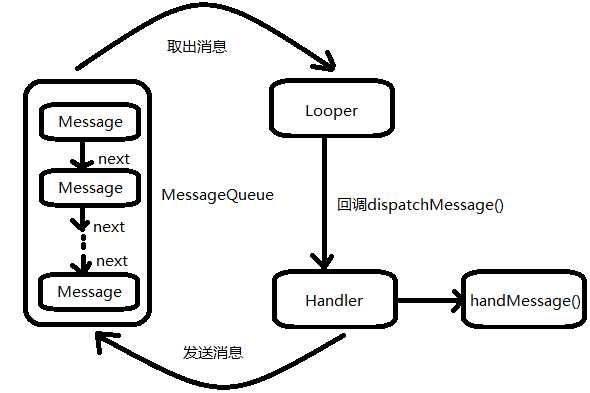
1.在主线程中创建Handler(处理者)对象,重写handMessage()方法,在该方法中进行UI操作
2.当子线程需要UI更新时,new一个Message(消息)对象,通过handler发送这个消息,包括.what,.obj等
3.消息会被发送到消息队列中,Looper(消息队列管家)会循环从队列中尝试取出消息,并转给handler
4.handler收到消息后,就会调用handMessage方法,进行UI更新操作
主要方法
1.onPreExecute(),在execute(Params... params)被调用后立即执行,一般用来在执行后台任务前对UI做一些标记。
2.doInBackground(Params... params),在onPreExecute()完成后立即执行,用于执行较为费时的操作,此方法将接收输入参数和返回计算结果。在执行过程中可以调用publishProgress(Progress... values)来更新进度信息。
3.onProgressUpdate(Progress... values),在调用publishProgress(Progress... values)时,此方法被执行,直接将进度信息更新到UI组件上。
4.onPostExecute(Result result),当后台操作结束时,此方法将会被调用,计算结果将做为参数传递到此方法中,直接将结果显示到UI组件上。
后续待看
:在doInBackground中进行耗时逻辑操作,在onProgressUpdate中进行UI操作
定义服务
public class MyService extends Service { @Override public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { // 当活动与服务绑定的时候,这个方法就会被执行 return null; } @Override public void onCreate() { // 主要初始化 super.onCreate(); Log.d("test", "service onCreate"); } /** 主要的逻辑是在这里完成,但是考虑到:服务默认是在主线程执行的,如果在这里进行比较费时的操作, * 就容易出现ANR(Application Not Responding).<br/> * 所以标准的写法是在这里新建一个子线程执行逻辑处理<br/> * 但是:这样做了之后,必须要使用stopService或stopSelf才能停得下来 */ @Override public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) { Log.d("test", "service onStartCommand"); new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { // 逻辑处理 // ... // 处理完之后调用停止服务 stopSelf(); } }).start(); return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId); } @Override public void onDestroy() { // 摧毁前调用 super.onDestroy(); Log.d("test", "service onDestroy"); } }
开启服务——和活动很相似!!
intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, MyService.class); // 启动服务 startService(intent);
停止服务
intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, MyService.class); // 暂停服务,也可用stopSelf() stopService(intent);
注册服务——在application中
<service android:name="com.example.servicetest.MyService"></service>
通常要做到:活动要让服务干活了,说一下立马行动;活动要知道服务的活干的怎么样了,服务要能立马汇报
1.在服务中定义一个Binder对象,该对象具有干活的方法
2.在onBind方法中,将改对象返回
3.在活动中也定义一个该Binder对象,用于接收onBind返回的对象
4.活动中定义一个ServiceConnection对象,重写onServiceConnected,onServiceDisconnected方法,并在onServiceConnected中为Binder对象赋值
5.调用bindService(intent, conn, BIND_AUTO_CREATE)绑定,绑定之后,就可以通过binder对象干活了

1 package com.example.servicetest; 2 3 import com.example.servicetest.MyService.DownloadBinder; 4 5 import android.app.Activity; 6 import android.content.ComponentName; 7 import android.content.Intent; 8 import android.content.ServiceConnection; 9 import android.os.Bundle; 10 import android.os.IBinder; 11 import android.util.Log; 12 import android.view.View; 13 import android.view.View.OnClickListener; 14 import android.widget.Button; 15 import android.widget.Toast; 16 17 18 public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener{ 19 20 private Button startButton; 21 private Button stoptButton; 22 private Button bindButton; 23 private Button unbindButton; 24 private Button workButton; 25 private Button progressButton; 26 private Button intentServiceButton; 27 private MyService.DownloadBinder downloadBinder = null; 28 private ServiceConnection conn = new ServiceConnection() { 29 30 @Override 31 public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) { 32 // 连接意外丢失时 33 34 } 35 36 @Override 37 public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) { 38 // 连接成功时 39 downloadBinder = (DownloadBinder) service; 40 41 } 42 }; 43 44 @Override 45 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 46 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 47 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); 48 49 startButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.start); 50 stoptButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.stop); 51 bindButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.bind); 52 unbindButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.unbind); 53 workButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.start_work); 54 progressButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.re_progress); 55 intentServiceButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.start_intent_service); 56 startButton.setOnClickListener(this); 57 stoptButton.setOnClickListener(this); 58 bindButton.setOnClickListener(this); 59 unbindButton.setOnClickListener(this); 60 workButton.setOnClickListener(this); 61 progressButton.setOnClickListener(this); 62 intentServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this); 63 64 } 65 66 @Override 67 public void onClick(View v) { 68 Intent intent; 69 switch (v.getId()) { 70 case R.id.start: 71 intent = new Intent(this, MyService.class); 72 // 启动服务 73 startService(intent); 74 break; 75 case R.id.stop: 76 intent = new Intent(this, MyService.class); 77 // 暂停服务 78 stopService(intent); 79 break; 80 case R.id.bind: 81 intent = new Intent(this, MyService.class); 82 // 绑定服务——BIND—_AUTO_CREATE标志位,表示活动与服务绑定后自动创建服务,调用服务的onCreate方法,但不调用onStartCommand 83 bindService(intent, conn, BIND_AUTO_CREATE); 84 break; 85 case R.id.unbind: 86 // 解除绑定服务 87 unbindService(conn); 88 break; 89 case R.id.start_work: 90 // 让服务开始干活——这里的判断条件还不明白 91 if(downloadBinder!=null){ 92 downloadBinder.startDownload(); 93 }else { 94 Toast.makeText(this, "ensure binded?", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); 95 } 96 break; 97 case R.id.re_progress: 98 // 让服务汇报进度 99 if(downloadBinder!=null){ 100 downloadBinder.getProgress(); 101 }else { 102 Toast.makeText(this, "ensure binded?", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); 103 } 104 break; 105 case R.id.start_intent_service: 106 // 让intentservice服务工作 107 Log.d("test", "MainActivity Thread name:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()); 108 Intent intent2 =new Intent(this, MyIntentService.class); 109 startService(intent2); 110 break; 111 112 default: 113 break; 114 } 115 116 } 117 118 }

1 package com.example.servicetest; 2 3 4 import android.app.Notification; 5 import android.app.PendingIntent; 6 import android.app.Service; 7 import android.content.Intent; 8 import android.os.Binder; 9 import android.os.IBinder; 10 import android.support.v4.app.NotificationCompat; 11 import android.support.v4.app.NotificationCompat.Builder; 12 import android.util.Log; 13 14 15 public class MyService extends Service { 16 private DownloadBinder mBinder = new DownloadBinder(); 17 class DownloadBinder extends Binder{ 18 public void startDownload(){ 19 Log.d("test", "startDownload is work by DownloadBinder"); 20 21 } 22 public int getProgress(){ 23 Log.d("test", "getProgress is work by DownloadBinder"); 24 return 0; 25 } 26 } 27 @Override 28 public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { 29 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 30 return mBinder; 31 } 32 33 @Override 34 public void onCreate() { 35 // 主要初始化 36 // 这里创建一个前台服务:后台服务可能会因系统内存不足而回收,如果希望一直运行,可以考虑前台服务,类似通知 37 super.onCreate(); 38 NotificationCompat.Builder mbuilder = new NotificationCompat.Builder(this); 39 mbuilder 40 .setTicker("this is ticker") 41 .setWhen(System.currentTimeMillis()) 42 .setContentTitle("this is title") 43 .setContentText("this is content") 44 .setSmallIcon(R.drawable.ic_launcher) 45 .setContentIntent(PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, new Intent(this, MainActivity.class), 0)); 46 47 Notification notification = mbuilder.build(); 48 startForeground(1, notification);// 将MyService变成一个前台服务!! 49 Log.d("test", "service onCreate"); 50 } 51 52 /** 主要的逻辑是在这里完成,但是考虑到:服务默认是在主线程执行的,如果在这里进行比较费时的操作, 53 * 就容易出现ANR(Application Not Responding).<br/> 54 * 所以标准的写法是在这里新建一个子线程执行逻辑处理<br/> 55 * 但是:这样做了之后,必须要使用stopService或stopSelf才能停得下来 56 */ 57 @Override 58 public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) { 59 Log.d("test", "service onStartCommand"); 60 new Thread(new Runnable() { 61 62 @Override 63 public void run() { 64 // 逻辑处理 65 // ... 66 // 处理完之后调用停止服务 67 stopSelf(); 68 // 但是如果再这里调用了停止服务的话,新的服务请求将得不到执行,因为服务将会停止 69 70 } 71 }).start(); 72 return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId); 73 } 74 75 @Override 76 public void onDestroy() { 77 // 摧毁前调用 78 super.onDestroy(); 79 Log.d("test", "service onDestroy"); 80 81 } 82 83 84 }

1 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 2 android:layout_width="match_parent" 3 android:layout_height="match_parent" 4 android:orientation="vertical" > 5 6 <Button 7 android:id="@+id/start" 8 android:layout_width="match_parent" 9 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 10 android:text="start service" /> 11 12 <Button 13 android:id="@+id/stop" 14 android:layout_width="match_parent" 15 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 16 android:text="stop service" /> 17 18 <Button 19 android:id="@+id/bind" 20 android:layout_width="match_parent" 21 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 22 android:text="Bind service" /> 23 24 <Button 25 android:id="@+id/unbind" 26 android:layout_width="match_parent" 27 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 28 android:text="Unbind service" /> 29 30 <Button 31 android:id="@+id/start_work" 32 android:layout_width="match_parent" 33 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 34 android:text="let service do work!" /> 35 36 <Button 37 android:id="@+id/re_progress" 38 android:layout_width="match_parent" 39 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 40 android:text="See the progress of service" /> 41 42 <Button 43 android:id="@+id/start_intent_service" 44 android:layout_width="match_parent" 45 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 46 android:text="let IntentService go work" /> 47 48 </LinearLayout>
注意:
MyService可以和应用程序内的任何活动进行绑定
当startService(...)时
onCreate()——只会执行一次,服务若已创建,则不再执行
onStartCommand()——startService一次就执行一次
当stopService()或stopSelf()时
onDestroy()会被执行
当binService()时
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/erhai/p/4942229.html