标签:
ASP.NET MVC允许使用 Area(区域)来组织Web应用程序,每个Area代表应用程序的不同功能模块。这对于大的工程非常有用,Area 使每个功能模块都有各自的文件夹,文件夹中有自己的Controller、View和Model,但对于管理也增加了一定的难度。
创建Area
右键工程选择 添加->区域,弹出如下填写Area的对话框:
和创建一个空MVC工程结构类似,Admin Area 有自己的 Controllers、Models 和 Views 文件夹,不一样的地方就是多了一个 AdminAreaRegistration.cs 文件,这个文件中定义了一个叫 AdminAreaRegistration 的类,它的内容如下:
namespace MvcApplication1.Areas.Admin { public class AdminAreaRegistration : AreaRegistration { public override string AreaName { get { return "Admin"; } } public override void RegisterArea(AreaRegistrationContext context) { context.MapRoute( "Admin_default", "Admin/{controller}/{action}/{id}", new { action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional } ); } } }
系统自动生成的 AdminAreaRegistration 类继承至抽象类 AreaRegistration,并重写了 AreaName 属性和 RegisterArea 方法。在 RegisterArea 方法中它为我们定义了一个默认路由,我们也可在这个方法中定义专属于Admin Area的的其他路由。但有一点要注意,在这如果要给路由起名字,一定要确保它和整个应用程序不一样。
AreaRegistrationContext 类的 MapRoute 方法和 RouteCollection 类的 MapRoute 方法的使用是一样的,只是 AreaRegistrationContext 类限制了注册的路由只会去匹配当前 Area 的 controller,所以,如果你把在 Area 中添加的 controller 的默认命名空间改了,路由系统将找不到这个controller 。
RegisterArea 方法不需要我们手动去调用,在 Global.asax 中的 Application_Start 方法已经有下面这样一句代码为我们做好了这件事:
protected void Application_Start() { AreaRegistration.RegisterAllAreas(); WebApiConfig.Register(GlobalConfiguration.Configuration); FilterConfig.RegisterGlobalFilters(GlobalFilters.Filters); RouteConfig.RegisterRoutes(RouteTable.Routes); BundleConfig.RegisterBundles(BundleTable.Bundles); }
调用 AreaRegistration.RegisterAllAreas 方法让MVC应用程序在启动后会寻找所有继承自 AreaRegistration 的类,并为每个这样的类调用它们的 RegisterArea 方法。
注意:不要轻易改变 Application_Start 中注册方法的顺序,如果你把RouteConfig.RegisterRoutes方法放到AreaRegistration.RegisterAllAreas方法之前,Area 路由的注册将会在路由注册之后,路由系统是按顺序来匹配的,所以这样做会让请求 Area 的 Controller 匹配到错误的路由。
Area的运行
在Area中添加controller、view和model和一般的添加是一样的。在这,我们在Admin Area中添加一个名为 Home 的controller,代码如下:
public class HomeController : Controller {
public ActionResult Index() {
return View();
}
}
然后我们再为Index Acton添加一个View,代码如下:
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Index";
Layout = null;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" />
<title>Index</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<h2>Admin Area Index</h2>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Controller的歧义问题
试想一下,如果我们现在在根目录的 Controller 文件夹中也添加一个名为 Home 的 Controller,然后我们通过把URL定位到 /Home/Index,路由系统能匹配到根目录下的 Controller 吗?
在根目录的 Controllers 文件夹中添加好 HomeController 后,为Index添加View,内容随意:
...
<body>
<div>
<h2>Root Index</h2>
</div>
</body>
...
路由不改动,我们使用 RouteConfig.cs 文件中系统定义的默认路由:
public static void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes) {
routes.IgnoreRoute("{resource}.axd/{*pathInfo}");
routes.MapRoute(
name: "Default",
url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}",
defaults: new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }
);
}
运行程序,将URL定位到 /Home/Index。结果我们会看到如下错误信息:
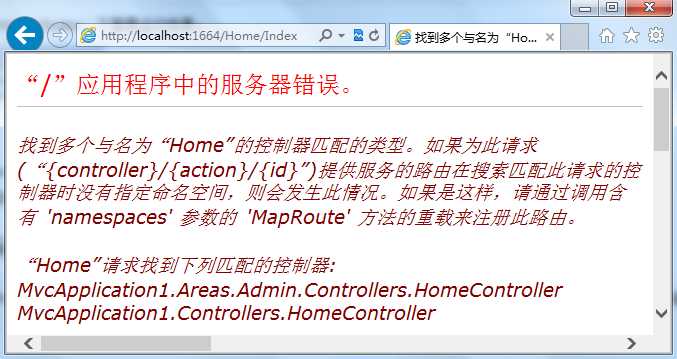
出现这个问题是因为路由系统进行匹配的时候出现了Controller同名的歧义。
当Area被注册的时候,Area中定义的路由被限制了只寻找 Area 中的Controller,所以我们请求 /Admin/Home/Index 时能正常得到 MvcApplication1.Areas.Admin.Controllers 命名空间的 HomeController。然而我们在RouteConfig.cs文件的RegisterRoutes方法中定义的路由并没有类似的限制。
为了解决这个问题,我们需要在RouteConfig.cs文件中定义的路由中加上对应的 namespaces 参数。RouteConfig.cs 中修改后的路由如下:
public static void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes) {
routes.IgnoreRoute("{resource}.axd/{*pathInfo}");
routes.MapRoute(
name: "Default",
url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}",
defaults: new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional },
namespaces: new[] { "MvcApplication1.Controllers" }
);
}
运行程序,如下结果说明解决了同名歧义问题:
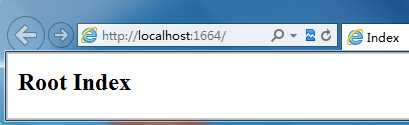
添加了namespaces 参数后,路由系统在对这个路由进行匹配时,优先匹配指定命名空间的controller,如果匹配到则即刻停止查找,如果在指定的命名空间下没有匹配到对应的controller,再按照一般的方式进行匹配。
参考文章:http://www.cnblogs.com/willick/p/3331519.html
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/cxeye/p/4976951.html