标签:
先给出一个结论:getMeasuredWidth()获取的是view原始的大小,也就是这个view在XML文件中配置或者是代码中设置的大小。getWidth()获取的是这个view最终显示的大小,这个大小有可能等于原始的大小也有可能不等于原始大小。
从源码上开始分析一下这两个方法的区别。首先来看一下getMeasuredWidth()这个方法。
1 public final int getMeasuredWidth() { 2 return mMeasuredWidth & MEASURED_SIZE_MASK; 3 } 4 5 protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { 6 setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec), 7 getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec)); 8 } 9 10 protected final void setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) { 11 boolean optical = isLayoutModeOptical(this); 12 if (optical != isLayoutModeOptical(mParent)) { 13 Insets insets = getOpticalInsets(); 14 int opticalWidth = insets.left + insets.right; 15 int opticalHeight = insets.top + insets.bottom; 16 17 measuredWidth += optical ? opticalWidth : -opticalWidth; 18 measuredHeight += optical ? opticalHeight : -opticalHeight; 19 } 20 setMeasuredDimensionRaw(measuredWidth, measuredHeight); 21 } 22 23 private void setMeasuredDimensionRaw(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) { 24 mMeasuredWidth = measuredWidth; 25 mMeasuredHeight = measuredHeight; 26 27 mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET; 28 }
从源码上来看,getMeasuredWidth()获取的是mMeasuredWidth的这个值。这个值是一个8位的十六进制的数字,高两位表示的是这个measure阶段的Mode的值,具体可以查看MeasureSpec的原理。这里mMeasuredWidth & MEASURED_SIZE_MASK表示的是测量阶段结束之后,view真实的值。而且这个值会在调用了setMeasuredDimensionRaw()函数之后会被设置。所以getMeasuredWidth()的值是measure阶段结束之后得到的view的原始的值。
再来看看getWidth()的源码:
1 public final int getWidth() { 2 return mRight - mLeft; 3 }
那么问题来了,mRight和mLeft是什么值,是在什么时候被设置的。我们再看layout阶段的源码:
1 public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) { 2 if ((mPrivateFlags3 & PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT) != 0) { 3 onMeasure(mOldWidthMeasureSpec, mOldHeightMeasureSpec); 4 mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT; 5 } 6 7 int oldL = mLeft; 8 int oldT = mTop; 9 int oldB = mBottom; 10 int oldR = mRight; 11 12 boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ? 13 setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b); 14 15 ... 16 }
在layout阶段会去调用setOpticalFrame()或者调用setFrame()方法,从源码中可知setOpticalFrame()方法,最终还是调用的setFrame()方法。
1 protected boolean setFrame(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) { 2 boolean changed = false; 3 4 if (DBG) { 5 Log.d("View", this + " View.setFrame(" + left + "," + top + "," 6 + right + "," + bottom + ")"); 7 } 8 9 if (mLeft != left || mRight != right || mTop != top || mBottom != bottom) { 10 changed = true; 11 12 // Remember our drawn bit 13 int drawn = mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_DRAWN; 14 15 int oldWidth = mRight - mLeft; 16 int oldHeight = mBottom - mTop; 17 int newWidth = right - left; 18 int newHeight = bottom - top; 19 boolean sizeChanged = (newWidth != oldWidth) || (newHeight != oldHeight); 20 21 // Invalidate our old position 22 invalidate(sizeChanged); 23 24 mLeft = left; 25 mTop = top; 26 mRight = right; 27 mBottom = bottom; 28 mRenderNode.setLeftTopRightBottom(mLeft, mTop, mRight, mBottom); 29 30 mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS; 31 ... 32 }
所以最终的mLeft和mRight的值是在setFrame()方法中被设置的。而且这些mLeft,mRight代表了view最终显示在界面中的大小。
下面我们自定义一个简单的ViewGroup,在layout阶段改变left,right的值,观察getMeasuredWidth()和getWidth()方法之间的区别。
1 package com.gearmotion.app.customviewgroup; 2 3 import android.content.Context; 4 import android.util.AttributeSet; 5 import android.view.View; 6 import android.widget.RelativeLayout; 7 8 /** 9 * Created by Charles on 2015/11/21. 10 */ 11 public class CustomViewGroup extends RelativeLayout { 12 13 public CustomViewGroup(Context context) { 14 super(context); 15 } 16 17 public CustomViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { 18 super(context, attrs); 19 } 20 21 public CustomViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) { 22 super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr); 23 } 24 25 @Override 26 protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { 27 super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); 28 } 29 30 @Override 31 protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) { 32 super.onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b); 33 View child = this.getChildAt(1); //the textview 34 //add 100px for right 35 child.layout(child.getLeft(), child.getTop(),child.getRight() + 100,child.getBottom()); 36 37 38 } 39
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <com.gearmotion.app.customviewgroup.CustomViewGroup xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context="com.gearmotion.app.customviewgroup.MainActivity"> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal"> <Button android:id="@+id/left" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:gravity="center" android:text="width" /> <Button android:id="@+id/right" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:gravity="center" android:text="measuredWidth" /> </LinearLayout> <TextView android:id="@+id/textview" android:layout_width="100px" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerInParent="true" android:background="#8EE5EE" android:gravity="center" android:text="textview" /> </com.gearmotion.app.customviewgroup.CustomViewGroup>
package com.gearmotion.app.customviewgroup; import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; import android.widget.TextView; import android.widget.Toast; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener { TextView mTextView; Button mLeftBtn; Button mRightBtn; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); mTextView = (TextView) this.findViewById(R.id.textview); mLeftBtn = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.left); mRightBtn = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.right); mLeftBtn.setOnClickListener(this); mRightBtn.setOnClickListener(this); } @Override public void onClick(View v) { int id = v.getId(); switch (id) { case R.id.left: //width Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "width:" + mTextView.getWidth(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); break; case R.id.right: //measuredWidth Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"measuredWidth:"+mTextView.getMeasuredWidth(),Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); break; } } }
在这个demo中,我们给textview设置宽度为100px,但是在layout阶段给它加大到200,最终结果是:点击width按钮,显示为200,点解measuredWidth按钮显示为100.
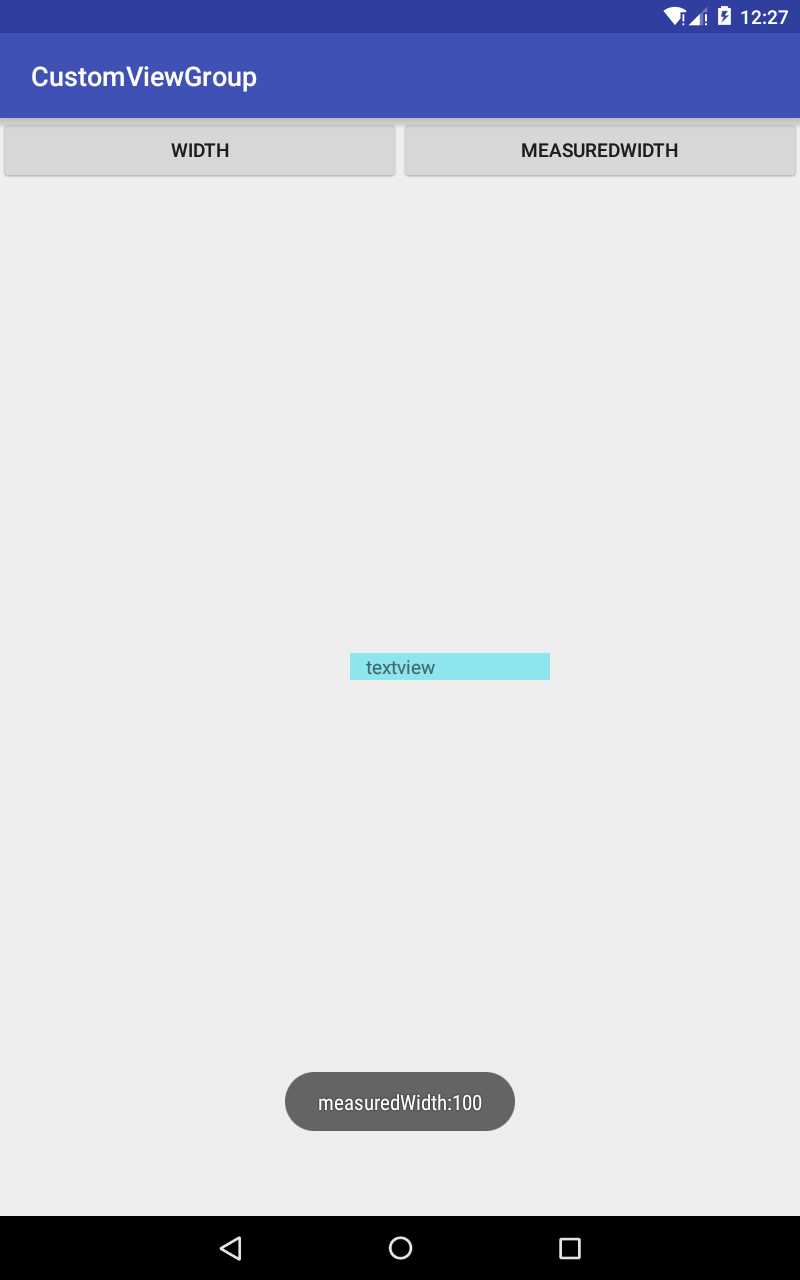
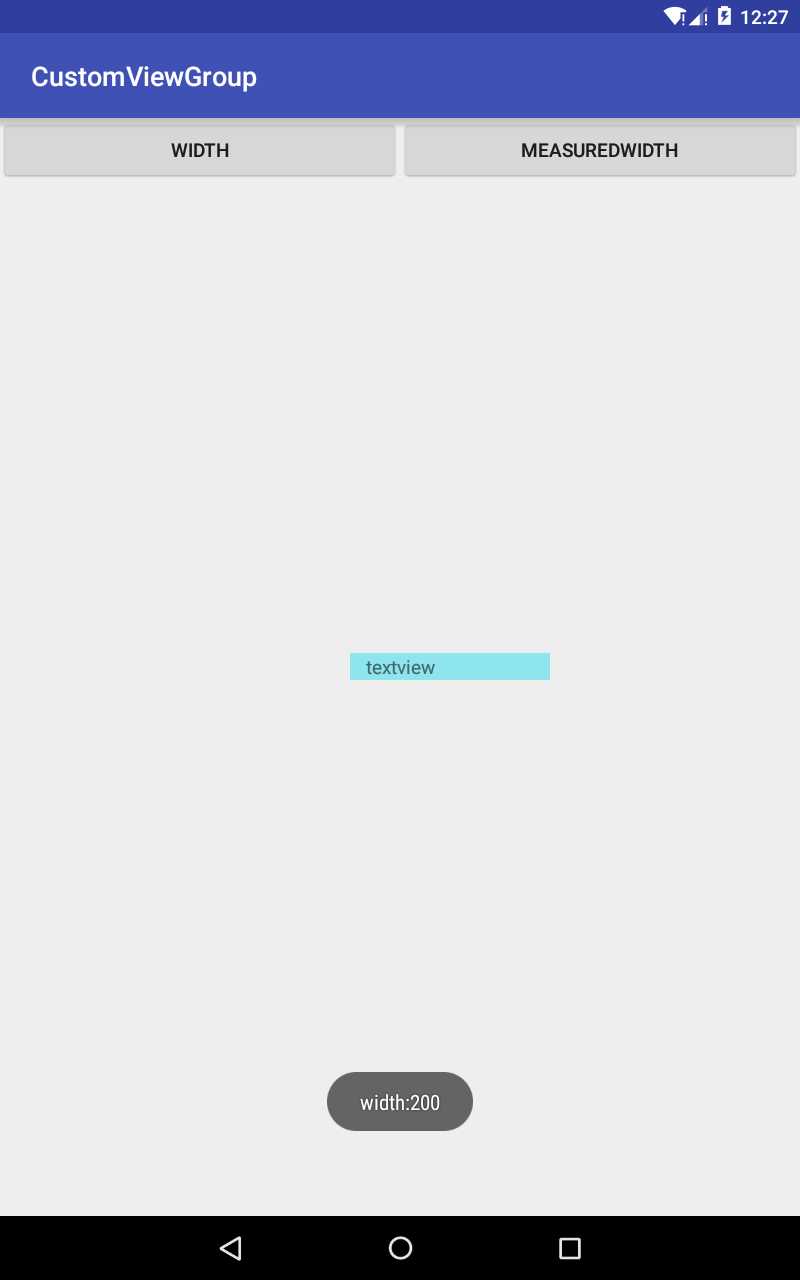
android中getWidth()和getMeasuredWidth()之间的区别
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/summerpxy/p/4983600.html