标签:
1.创建一个 CALayer 的子类
2.在. m 文件中覆盖 drawInContext:方法,在里面绘图
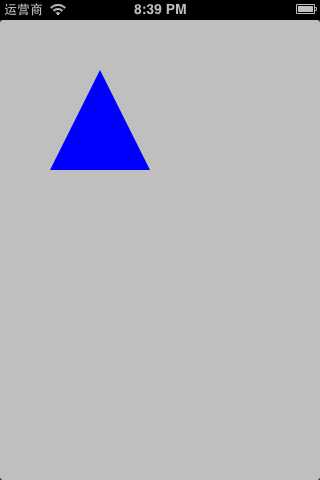
- (void)drawInContext:(CGContextRef)ctx { 5 // 设置为蓝色 6 CGContextSetRGBFillColor(ctx, 0, 0, 1, 1); 7 8 9 // 设置起点 10 CGContextMoveToPoint(ctx, 50, 0); 11 // 从(50, 0)连线到(0, 100) 12 CGContextAddLineToPoint(ctx, 0, 100); 13 // 从(0, 100)连线到(100, 100) 14 CGContextAddLineToPoint(ctx, 100, 100); 15 // 合并路径,连接起点和终点 16 CGContextClosePath(ctx); 17 18 // 绘制路径 19 CGContextFillPath(ctx); 20 }
3.在控制器中添加图层到屏幕上
2 // 设置层的宽高 3 layer.bounds = CGRectMake(0, 0, 100, 100); 4 // 设置层的位置 5 layer.position = CGPointMake(100, 100); 6 // 开始绘制图层 7 [layer setNeedsDisplay]; 注意 //使用此方法才会触发 drawInContext 方法 8 [self.view.layer addSublayer:layer];
方法描述:设置CALayer的delegate,然后让delegate实现drawLayer:inContext:方法,当CALayer需要绘图时,会调用delegate的drawLayer:inContext:方法进行绘图。
* 这里要注意的是:不能再将某个UIView设置为CALayer的delegate,因为UIView对象已经是它内部根层的delegate,再次设置为其他层的delegate就会出问题。UIView和它内部CALayer的默认关系图:

1 CALayer *layer = [CALayer layer]; 2 // 设置delegate 3 layer.delegate = self; 4 // 设置层的宽高 5 layer.bounds = CGRectMake(0, 0, 100, 100); 6 // 设置层的位置 7 layer.position = CGPointMake(100, 100); 8 // 开始绘制图层 9 [layer setNeedsDisplay]; 10 [self.view.layer addSublayer:layer];
* 在第3行设置了CALayer的delegate,这里的self是指控制器
* 注意第9行,需要调用setNeedsDisplay这个方法,才会通知delegate进行绘图
1 #pragma mark 画一个矩形框 2 - (void)drawLayer:(CALayer *)layer inContext:(CGContextRef)ctx { 3 // 设置蓝色 4 CGContextSetRGBStrokeColor(ctx, 0, 0, 1, 1); 5 // 设置边框宽度 6 CGContextSetLineWidth(ctx, 10); 7 8 // 添加一个跟层一样大的矩形到路径中 9 CGContextAddRect(ctx, layer.bounds); 10 11 // 绘制路径 12 CGContextStrokePath(ctx); 13 }
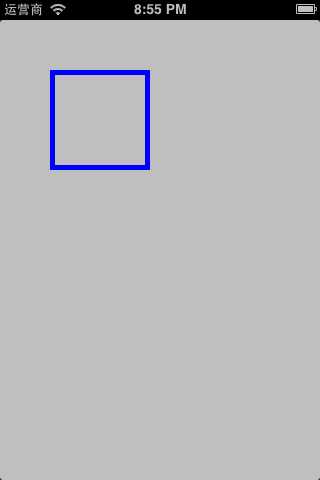
无论采取哪种方法来自定义层,都必须调用CALayer的setNeedsDisplay方法才能正常绘图。
* 当UIView需要显示时,它内部的层会准备好一个CGContextRef(图形上下文),然后调用delegate(这里就是UIView)的drawLayer:inContext:方法,并且传入已经准备好的CGContextRef对象。而UIView在drawLayer:inContext:方法中又会调用自己的drawRect:方法
* 平时在drawRect:中通过UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext()获取的就是由层传入的CGContextRef对象,在drawRect:中完成的所有绘图都会填入层的CGContextRef中,然后被拷贝至屏幕
CV模式代码----(感谢 http://www.cnblogs.com/mjios/archive/2013/04/14/3020975.html)
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/GLbog/p/4993448.html