标签:
1、SUN公司为了简化、统一对数据库的操作,定义了一套Java操作数据库的规范,称之为JDBC,JDBC(Java Data Base Connectivity,java数据库连接),由一些接口和类构成的API. J2SE的一部分,由java.sql,javax.sql包组成,开发还需要导入相应JDBC的数据库实现(即数据库驱动).
2、应用程序、JDBC API、数据库驱动级数据库之间的关系.
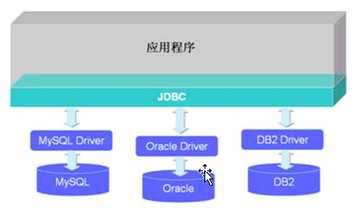
SUN公司定义标准也就是这些接口,数据库厂商实现这些接口,比如电脑显卡驱动是由显卡公司设计的驱动,实现了主板公司定义的标准,这样更换显卡时比较方便.
public class TestJDBC { public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException { //1、创建驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //2、建立连接 Connection conn= DriverManager.getConnection( "jdbc:mysql://223.202.100.234:3306/exagoods_product", "globebuy","lijiang"); //3、创建语句 Statement s = conn.createStatement(); //4、执行语句 ResultSet rs = s.executeQuery("select * from shop"); //5、处理结果 while(rs.next()){ System.out.println(rs.getObject(1)+"--"+rs.getObject(2)); } //6、释放资源 rs.close(); s.close(); conn.close(); //把socket关闭,不然数据库很快会挂掉 } }
观察上面代码发现和URL编程如出一辙,其实原理相同,都是基于网络的应用层编程,jdbc使用的是jdbc协议,URL编程使用的是http协议,Mysql服务器类比Tomcat服务器,底层都是socket编程.
1、注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //推荐这种方式,不会对具体的驱动类产生依赖.
DriverManager.registerDriver(com.mysql.jdbc.Driver); //并会对具体的驱动类产生依赖.
System.setProperty("jdbc.drivers", "driver1:driver2"); //注册不太方便,所以很少使用.
2、数据库URL
url格式: JDBC:子协议:子名称//主机名:端口/数据库名?属性名=属性值&… User,password可以用“属性名=属性值”方式告诉数据库; 其他参数如:useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8 注:localhost和默认端口可以省略,所以可能出现如下写法: jdbc:mysql:///exagoods_product
3、程序详解—Connection
createStatement():创建向数据库发送sql的statement对象. prepareStatement(sql) :创建向数据库发送预编译sql的PrepareSatement对象. prepareCall(sql):创建执行存储过程的callableStatement对象. setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit):设置事务是否自动提交. commit() :在链接上提交事务. rollback() :在此链接上回滚事务.
4、程序详解—Statement
executeQuery(String sql) :用于向数据发送查询语句.
executeUpdate(String sql):用于向数据库发送insert、update或delete语句
execute(String sql):用于向数据库发送任意sql语句
addBatch(String sql) :把多条sql语句放到一个批处理中.
executeBatch():向数据库发送一批sql语句执行.
statement存在sql注入攻击问题,例如登陆用户名采用‘or 1=1 or name=‘,对于防范 SQL 注入,可以采用PreparedStatement取代Statement.statement和PreparedStatement区别:
5、程序详解—ResultSet
1>Jdbc程序中的ResultSet用于代表Sql语句的执行结果.Resultset封装执行结果时,采用的类似于表格的方式.ResultSet 对象维护了一个指向表格数据行的游标,初始的时候,游标在第一行之前,调用ResultSet.next() 方法,可以使游标指向具体的数据行,进行调用方法获取该行的数据.
ResultSet既然用于封装执行结果的,所以该对象提供的都是用于获取数据的get方法:
获取任意类型的数据 getObject(int index) getObject(string columnName) 获取指定类型的数据,例如: getString(int index) getString(String columnName)
2>ResultSet还提供了对结果集进行滚动的方法:
next():移动到下一行 Previous():移动到前一行 absolute(int row):移动到指定行 beforeFirst():移动resultSet的最前面. afterLast() :移动到resultSet的最后面.
6、程序详解—释放资源
7、基本的CRUD(创建、读取、更新、删除)
//模板代码
Connection conn = null; Statement st=null; ResultSet rs = null; try { //获得Connection //创建Statement //处理查询结果ResultSet } finally { //释放资源ResultSet, Statement,Connection }
ps:注意返回值的使用:
int num = st.executeUpdate(sql); if(num>0){ System.out.println("插入成功!!!"); }
//导包时注意不要导具体驱动的包 import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.Statement; import java.util.Properties; public class JdbcUtils { private static Properties config = new Properties(); static { try { config.load(JdbcUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream( "db.properties")); Class.forName(config.getProperty("driver")); } catch (Exception e) { throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(e); } } public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { return DriverManager.getConnection(config.getProperty("url"), config.getProperty("username"), config.getProperty("password")); } public static void release(Connection conn, Statement st, ResultSet rs) { if (rs != null) { try { rs.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } rs = null; } if (st != null) { try { st.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } st = null; } if (conn != null) { try { conn.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
//db.properties driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/day14 username=root password=root
//可以任意切换数据库而无需修改代码 #driver=oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver #url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl #username=system #password=itcast
//基本CRUDTest public class CRUDTest { @Test public void insert() throws SQLException{ Connection conn = null; Statement st = null; ResultSet rs = null; try{ conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); //oracle st = conn.createStatement(); String sql = "insert into users(id,name,password) values(4,‘eee‘,‘123‘)"; int num = st.executeUpdate(sql); if(num>0){ System.out.println("插入成功!!!"); } }finally{ JdbcUtils.release(conn, st, rs); } } @Test public void update() throws SQLException{ Connection conn = null; Statement st = null; ResultSet rs = null; try{ conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); st = conn.createStatement(); String sql = "update users set name=‘fff‘ where id=‘4‘"; int num = st.executeUpdate(sql); if(num>0){ System.out.println("更新成功!!"); } }finally{ JdbcUtils.release(conn, st, rs); } } @Test public void delete() throws SQLException{ Connection conn = null; Statement st = null; ResultSet rs = null; try{ conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); st = conn.createStatement(); String sql = "delete from users where id=4"; int num = st.executeUpdate(sql); if(num>0){ System.out.println("删除成功!!"); } }finally{ JdbcUtils.release(conn, st, rs); } } public void find() throws SQLException{ Connection conn = null; Statement st = null; ResultSet rs = null; try{ conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); st = conn.createStatement(); String sql = "select id,name,password,email,birthday from users where id=1"; rs = st.executeQuery(sql); User user = null; if(rs.next()){ user = new User(); user.setId(rs.getInt("id")); user.setName(rs.getString("name")); user.setPassword(rs.getString("password")); user.setEmail(rs.getString("email")); user.setBirthday(rs.getDate("birthday")); } System.out.println(user); }finally{ JdbcUtils.release(conn, st, rs); } } @Test public void getAll() throws SQLException{ Connection conn = null; Statement st = null; ResultSet rs = null; try{ conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); st = conn.createStatement(); String sql = "select id,name,password,email,birthday from users"; rs = st.executeQuery(sql); List list = new ArrayList(); while(rs.next()){ User user = new User(); user.setId(rs.getInt("id")); user.setName(rs.getString("name")); user.setPassword(rs.getString("password")); user.setEmail(rs.getString("email")); user.setBirthday(rs.getDate("birthday")); list.add(user); } }finally{ JdbcUtils.release(conn, st, rs); } } }
ps: 涉及知识web包结构、异常处理问题、JdbcUtils(结合配置文件简化代码)、DaoFactory(实现接口和实现分离,解耦合)、单例模式和工厂模式,代码见文件.
1、分页结构图,对象的封装思想,QueryInfo封装请求信息、QueryResurt封装dao层的查询信息、PageBean封装页面的数据.
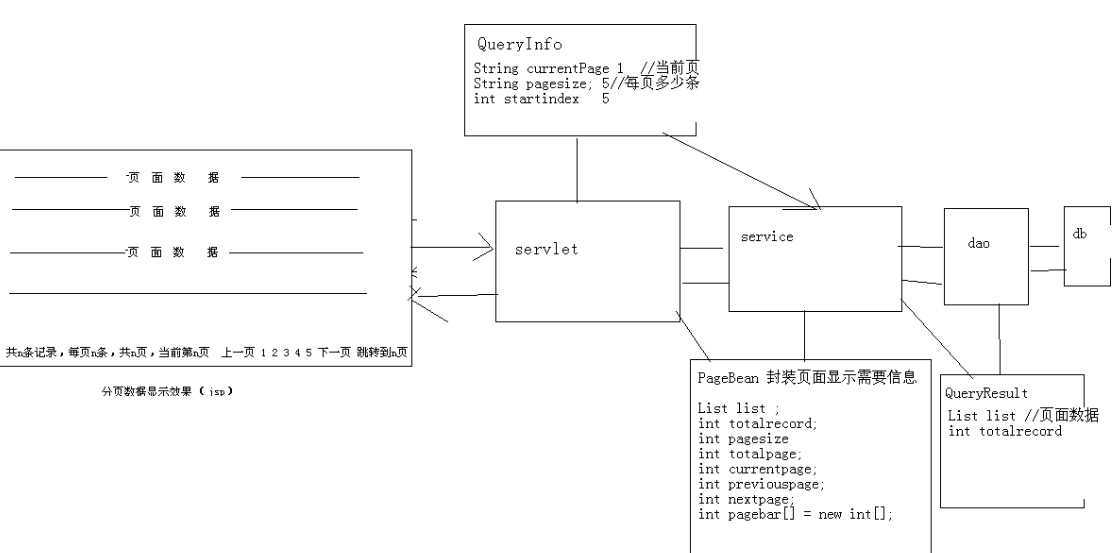
ps:参考day15_customer项目,代码经典见文件.
/**读写大文本 create table testclob ( id varchar(40) primary key, resume text ); */ public class Demo1 { @Test public void insert() throws SQLException, FileNotFoundException{ Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement st = null; ResultSet rs = null; try{ conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); String sql = "insert into testclob(id,resume) values(?,?)"; st = conn.prepareStatement(sql); st.setString(1, "1"); File file = new File("src/1.txt"); FileReader reader = new FileReader(file); st.setCharacterStream(2, reader, (int) file.length()); int num = st.executeUpdate(); if(num>0){ System.out.println("插入成功!!"); } }finally{ JdbcUtils.release(conn, st, rs); } } @Test public void read() throws SQLException, IOException{ Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement st = null; ResultSet rs = null; try{ conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); String sql = "select id,resume from testclob where id=‘1‘"; st = conn.prepareStatement(sql); rs = st.executeQuery(); if(rs.next()){ //String resume = rs.getString("resume"); Reader reader = rs.getCharacterStream("resume"); FileWriter writer = new FileWriter("c:\\1.txt"); try { int len = 0; char buffer[] = new char[1024]; while ((len = reader.read(buffer)) > 0) { writer.write(buffer, 0, len); } } finally { if (reader != null) { reader.close(); } writer.close(); } } }finally{ JdbcUtils.release(conn, st, rs); } } }
/* create table testblob ( id varchar(40) primary key, image blob ); */ public class Demo2 { @Test public void insert() throws SQLException, FileNotFoundException{ Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement st = null; ResultSet rs = null; try{ conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); String sql = "insert into testblob(id,image) values(?,?)"; st = conn.prepareStatement(sql); st.setString(1, "1"); File file = new File("src/1.jpg"); FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(file); st.setBinaryStream(2, in, (int) file.length()); st.executeUpdate(); }finally{ JdbcUtils.release(conn, st, rs); } } @Test public void read() throws SQLException, IOException{ Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement st = null; ResultSet rs = null; try{ conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); String sql = "select id,image from testblob where id=‘1‘"; rs = conn.prepareStatement(sql).executeQuery(); if(rs.next()){ InputStream in = rs.getBinaryStream("image"); OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("c:\\1.jpg");; try { int len = 0; byte buffer[] = new byte[1024]; while ((len = in.read(buffer)) > 0) { out.write(buffer, 0, len); } } finally { if (in != null) in.close(); if (out != null) out.close(); } } }finally{ JdbcUtils.release(conn, st, rs); } } }
1、采用Statement.addBatch(sql)方式实现批处理:
•优点:可以向数据库发送多条不同的sql语句.
•缺点:SQL语句没有预编译.当向数据库发送多条相同语句,但仅参数不同的SQL语句时,需重复写上很多条SQL语句.
2、采用PreparedStatement.addBatch()实现批处理:(使用多)
•优点:发送的是预编译后的SQL语句,执行效率高.
•缺点:只能应用在SQL语句相同,但参数不同的批处理中.因此此种形式的批处理经常用于在同一个表中批量插入数据,或批量更新表的数据.
/* create table testbatch ( id varchar(40) primary key, name varchar(40) ); */ public class Demo3 { //实现批处理第一种方式 @Test public void test1() throws SQLException{ Connection conn = null; Statement st = null; ResultSet rs = null; try{ conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); String sql1 = "insert into testbatch(id,name) values(‘1‘,‘aaa‘)"; String sql2 = "update testbatch set name=‘bbb‘ where id=‘1‘"; st = conn.createStatement(); st.addBatch(sql1); st.addBatch(sql2); st.executeBatch(); st.clearBatch(); }finally{ JdbcUtils.release(conn, st, rs); } } //实现批处理的第二种方式 @Test public void test2() throws SQLException{ Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement st = null; ResultSet rs = null; try{ conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); String sql = "insert into testbatch(id,name) values(?,?)"; //作批量插入 批量更新 st = conn.prepareStatement(sql); for(int i=1;i<=10000006;i++){ st.setString(1, i+""); st.setString(2, "aa" + i); st.addBatch(); if(i%1000==0){ st.executeBatch(); st.clearBatch(); } } st.executeBatch(); }finally{ JdbcUtils.release(conn, st, rs); } } }
/** create table test ( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(40) ); */ public class Demo4 { public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException { Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement st = null; ResultSet rs = null; try{ conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); String sql = "insert into test(name) values(‘aaa‘)"; st = conn.prepareStatement(sql,Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS); st.executeUpdate(); rs = st.getGeneratedKeys(); if(rs.next()){ System.out.println(rs.getInt(1)); } }finally{ JdbcUtils.release(conn, st, rs); } } }
// 调用存储过程 public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException { Connection conn = null; CallableStatement st = null; ResultSet rs = null; try{ conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); st = conn.prepareCall("{call demoSp(?,?)}"); st.setString(1, "aaaaa"); st.registerOutParameter(2, Types.VARCHAR); st.execute(); System.out.println(st.getString(2)); }finally{ JdbcUtils.release(conn, st, rs); } }
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/wangweiNB/p/5062731.html