标签:
一。概述
Android 中的异步消息处理主要分为四个部分组成,Message、Hndler、MessageQueue 和 Looper。其关系如下图所示:
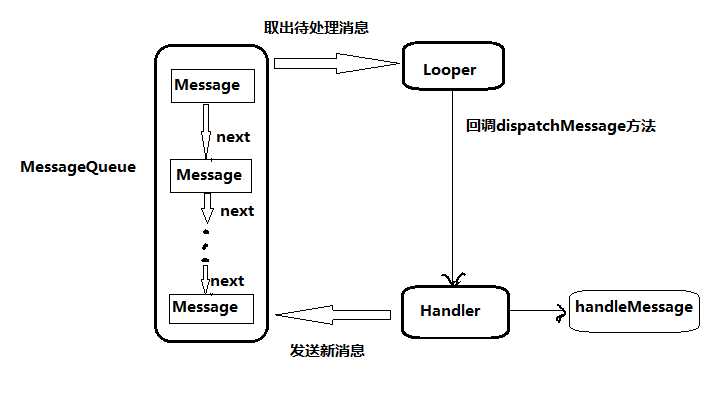
1. Message 是线程之间传递的消息,它可以在内部携带少量信息,用于在不同线程之间交换数据。
2. MessageQueue 是消息队列,它主要用于存放所有由 Handler 发送过来的消息,这部分消息会一直在消息队列中,等待被处理。每个线程中只会有一个 MessageQueue 对象。
3. Handler 是处理者,它主要用于发送和处理消息。 发送消息一般使用 handler 的 sendMessage()方法,处理消息会调用 handleMessage() 方法。
4. Looper 是每个线程中 MessageQueue 的管家, 调用 loop() 方法后,就会进入到一个无限循环当中,然后每当发现 MessageQueue 中存在一条消息,就会将其取出,并传递到 handleMessage
()方法当中。每个线程中也只会有一个Looper对象。
二。详细介绍
对于Looper主要是prepare()和loop()两个方法。
public static final void prepare() { if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) { throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread"); } sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(true)); }
sThreadLocal是一个ThreadLocal对象,可以在一个线程中存储变量。Looper 就是存储在sThreadLocal里面。这个方法被调用后,首先会判断当前线程里面有没有 Looper对象,如果没有就会创建一
个 Looper 对象,如果存在则会抛出异常。可见,prepare()方法,不能被调用两次。这就保证了一个线程只有一个Looper对象。
接下来我们看一下Looper的构造函数:
private Looper(boolean quitAllowed) { mQueue = new MessageQueue(quitAllowed); mRun = true; mThread = Thread.currentThread(); }
在 Looper 的构造函数中,创建了 MessageQueue 对象,这也保证了一个线程只有一个 MessageQueue 对象。
然后我们看看 loop() 方法:
public static void loop() { final Looper me = myLooper(); if (me == null) { throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn‘t called on this thread."); } final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue; // Make sure the identity of this thread is that of the local process, // and keep track of what that identity token actually is. Binder.clearCallingIdentity(); final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity(); for (;;) { Message msg = queue.next(); // might block if (msg == null) { // No message indicates that the message queue is quitting. return; } // This must be in a local variable, in case a UI event sets the logger Printer logging = me.mLogging; if (logging != null) { logging.println(">>>>> Dispatching to " + msg.target + " " + msg.callback + ": " + msg.what); } msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg); if (logging != null) { logging.println("<<<<< Finished to " + msg.target + " " + msg.callback); } // Make sure that during the course of dispatching the // identity of the thread wasn‘t corrupted. final long newIdent = Binder.clearCallingIdentity(); if (ident != newIdent) { Log.wtf(TAG, "Thread identity changed from 0x" + Long.toHexString(ident) + " to 0x" + Long.toHexString(newIdent) + " while dispatching to " + msg.target.getClass().getName() + " " + msg.callback + " what=" + msg.what); } msg.recycle(); } }
这个方法先调用 myLooper() 方法,得到 sThreadLocal 中保存的 Looper 对象,并得到 looper 对象对应的 MessageQueue 对象,然后就进入无限循环。
该循环主要包括:取出一条消息,如果没有消息则阻塞; 调用 msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);把消息交给msg的target的dispatchMessage方法去处理。
Looper主要作用:
1、 与当前线程绑定,保证一个线程只会有一个Looper实例,同时一个Looper实例也只有一个MessageQueue。
2、 loop()方法,不断从MessageQueue中去取消息,交给消息的target属性的dispatchMessage去处理。
在使用Handler之前,我们都是初始化一个实例,比如用于更新UI线程,我们会在声明的时候直接初始化,或者在onCreate中初始化Handler实例。
private Handler mHandler = new Handler() { public void handleMessage(android.os.Message msg) { switch (msg.what) { case value: break; default: break; } }; };
三。小结
1、首先Looper.prepare()在本线程中保存一个Looper实例,然后该实例中保存一个MessageQueue对象;因为Looper.prepare()在一个线程中只能调用一次,所以MessageQueue在一个线程中只会
存在一个。大家可能还会问,那么在Activity中,我们并没有显示的调用Looper.prepare()和Looper.loop()方法,为啥Handler可以成功创建呢,这是因为在Activity的启动代码中,已经在当前UI线程调用
了Looper.prepare()和Looper.loop()方法
2、Looper.loop()会让当前线程进入一个无限循环,不端从MessageQueue的实例中读取消息,然后回调msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg)方法。
3、Handler的构造方法,会首先得到当前线程中保存的Looper实例,并与Looper实例中的MessageQueue相关联。
4、Handler的sendMessage方法,会给msg的target赋值为handler自身,然后加入MessageQueue中。
5、在构造Handler实例时,我们会重写handleMessage方法,也就是msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg)最终调用的方法。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/kest/p/5078462.html