标签:
(1)相关概念
01 NSOperation是对GCD的包装
02 两个核心概念【队列+操作】(2)基本使用
01 NSOperation本身是抽象类,只能使用它的子类
02 三个子类分别是:NSBlockOperation、NSInvocationOperation以及自定义继承自NSOperation的类
03 NSOperation和NSOperationQueue结合使用实现多线程并发
04 NSOperation和NSOperationQueue实现多线程的具体步骤:
1.先将需要执行的操作封装到一个NSOperation对象中
2.然后将NSOperation对象添加到NSOperationQueue中
3.系统会自动将NSOperationQueu中的NSOperation取出来
4.将去除的NSOperation封装的操作放到一条线程(新线程,或者之前未被销毁的子线程)中执行
(3)相关代码
// 01 NSInvocationOperation(需要手动启动)
//1.封装操作
/*
第一个参数:目标对象
第二个参数:该操作要调用的方法,最多接受一个参数
第三个参数:调用方法传递的参数,如果方法不接受参数,那么该值传nil
*/
NSInvocationOperation *operation = [[NSInvocationOperation alloc]
initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(run) object:nil];
//2.启动操作
[operation start];
-------------------------------------------------
// 02 NSBlockOperation(需要手动启动)
//1.封装操作
/*
NSBlockOperation提供了一个类方法,在该类方法中封装操作
*/
NSBlockOperation *operation = [NSBlockOperation blockOperationWithBlock:^{
//在主线程中执行
NSLog(@"---download1--%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
}];
//2.追加操作,追加的操作在子线程中执行
[operation addExecutionBlock:^{
NSLog(@"---download2--%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
}];
[operation addExecutionBlock:^{
NSLog(@"---download3--%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
}];
//3.启动执行操作
[operation start];
----------------------------------------------
// 03 自定义NSOperation(需要手动启动)
//如何封装操作?
//自定义的NSOperation,通过重写内部的main方法实现封装操作
-(void)main
{
NSLog(@"--main--%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
}
//如何使用?
//1.实例化一个自定义操作对象
ZYQOperation *op = [[ZYQOperation alloc]init];
//2.执行操作
[op start];(1)NSOperation中的两种队列
01 主队列 通过mainQueue获得,凡是放到主队列中的任务都将在主线程执行
02 非主队列 直接alloc init出来的队列。非主队列同时具备了并发和串行的功能,通过设置最大并发数属性来控制任务是并发执行还是串行执行(2)相关代码
//自定义NSOperation
-(void)customOperation
{
//1.创建队列(非主队列)
NSOperationQueue *queue = [[NSOperationQueue alloc]init];
//2.封装操作
//好处:
//1.信息隐蔽
//2.代码复用
XMGOperation *op1 = [[XMGOperation alloc]init];
XMGOperation *op2 = [[XMGOperation alloc]init];
//3.添加操作到队列中
[queue addOperation:op1];
[queue addOperation:op2];
}
//NSBlockOperation
- (void)block
{
//1.创建队列
NSOperationQueue *queue = [[NSOperationQueue alloc]init];
//2.封装操作
NSBlockOperation *op1 = [NSBlockOperation blockOperationWithBlock:^{
NSLog(@"1----%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
}];
NSBlockOperation *op2 = [NSBlockOperation blockOperationWithBlock:^{
NSLog(@"2----%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
}];
// 添加操作
[op2 addExecutionBlock:^{
NSLog(@"3----%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
}];
[op2 addExecutionBlock:^{
NSLog(@"4----%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
}];
//3.添加操作到队列中
[queue addOperation:op1];
[queue addOperation:op2];
//补充:简便方法
[queue addOperationWithBlock:^{
NSLog(@"5----%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
}];
}
//NSInvocationOperation
- (void)invocation
{
/*
GCD中的队列:
串行队列:自己创建的,主队列
并发队列:自己创建的,全局并发队列
NSOperationQueue
主队列:[NSOperationQueue mainqueue];凡事放在主队列中的操作都在主线程中执行
非主队列:[[NSOperationQueue alloc]init],并发和串行,默认是并发执行的
*/
//1.创建队列
NSOperationQueue *queue = [[NSOperationQueue alloc]init];
//2.封装操作
NSInvocationOperation *op1 = [[NSInvocationOperation alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(download1) object:nil];
NSInvocationOperation *op2 = [[NSInvocationOperation alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(download2) object:nil];
NSInvocationOperation *op3 = [[NSInvocationOperation alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(download3) object:nil];
//3.把封装好的操作添加到队列中
[queue addOperation:op1];//[op1 start](自动调用start方法,start内部调用main方法);
[queue addOperation:op2];
[queue addOperation:op3];
}(1)设置最大并发数【控制任务并发和串行】
//1.创建队列
NSOperationQueue *queue = [[NSOperationQueue alloc]init];
//2.设置最大并发数
//注意点:该属性需要在任务添加到队列中之前进行设置
//该属性控制队列是串行执行还是并发执行
//如果最大并发数等于1,那么该队列是串行的,如果大于1那么是并行的
//系统的最大并发数有个默认的值,为-1,如果该属性设置为0,那么不会执行任何任务
queue.maxConcurrentOperationCount = 2;(2)暂停和恢复以及取消
//设置暂停和恢复
//suspended设置为YES表示暂停,suspended设置为NO表示恢复
//暂停表示不继续执行队列中的下一个任务,暂停操作是可以恢复的
if (self.queue.isSuspended) {
self.queue.suspended = NO;
}else
{
self.queue.suspended = YES;
}
//取消队列里面的所有操作
//取消之后,当前正在执行的操作的下一个操作将不再执行,而且永远都不在执行,就像后面的所有任务都从队列里面移除了一样
//取消操作是不可以恢复的
[self.queue cancelAllOperations];
---------自定义NSOperation取消操作--------------------------
-(void)main
{
//耗时操作1
for (int i = 0; i<1000; i++) {
NSLog(@"任务1-%d--%@",i,[NSThread currentThread]);
}
NSLog(@"+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++");
//苹果官方建议,每当执行完一次耗时操作之后,就查看一下当前队列是否为取消状态,如果是,那么就直接退出
//好处是可以提高程序的性能
if (self.isCancelled) {
return;
}
//耗时操作2
for (int i = 0; i<1000; i++) {
NSLog(@"任务1-%d--%@",i,[NSThread currentThread]);
}
NSLog(@"+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++");
}(1)开子线程下载图片
//1.创建队列
NSOperationQueue *queue = [[NSOperationQueue alloc]init];
//2.使用简便方法封装操作并添加到队列中
[queue addOperationWithBlock:^{
//3.在该block中下载图片
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://news.51sheyuan.com/uploads/allimg/111001/133442IB-2.jpg"];
NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfURL:url];
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageWithData:data];
NSLog(@"下载图片操作--%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
//4.回到主线程刷新UI
[[NSOperationQueue mainQueue] addOperationWithBlock:^{
self.imageView.image = image;
NSLog(@"刷新UI操作---%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
}];
}];
(2)下载多张图片合成综合案例(设置操作依赖)
//02 综合案例
- (void)download2
{
NSLog(@"----");
//1.创建队列
NSOperationQueue *queue = [[NSOperationQueue alloc]init];
//2.封装操作下载图片1
NSBlockOperation *op1 = [NSBlockOperation blockOperationWithBlock:^{
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://h.hiphotos.baidu.com/zhidao/pic/item/6a63f6246b600c3320b14bb3184c510fd8f9a185.jpg"];
NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfURL:url];
//拿到图片数据
self.image1 = [UIImage imageWithData:data];
}];
//3.封装操作下载图片2
NSBlockOperation *op2 = [NSBlockOperation blockOperationWithBlock:^{
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://pic.58pic.com/58pic/13/87/82/27Q58PICYje_1024.jpg"];
NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfURL:url];
//拿到图片数据
self.image2 = [UIImage imageWithData:data];
}];
//4.合成图片
NSBlockOperation *combine = [NSBlockOperation blockOperationWithBlock:^{
//4.1 开启图形上下文
UIGraphicsBeginImageContext(CGSizeMake(200, 200));
//4.2 画image1
[self.image1 drawInRect:CGRectMake(0, 0, 200, 100)];
//4.3 画image2
[self.image2 drawInRect:CGRectMake(0, 100, 200, 100)];
//4.4 根据图形上下文拿到图片数据
UIImage *image = UIGraphicsGetImageFromCurrentImageContext();
// NSLog(@"%@",image);
//4.5 关闭图形上下文
UIGraphicsEndImageContext();
//7.回到主线程刷新UI
[[NSOperationQueue mainQueue]addOperationWithBlock:^{
self.imageView.image = image;
NSLog(@"刷新UI---%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
}];
}];
//5.设置操作依赖(必须在操作添加到队列之前进行设置)
[combine addDependency:op1];
[combine addDependency:op2];
//6.添加操作到队列中执行
[queue addOperation:op1];
[queue addOperation:op2];
[queue addOperation:combine];
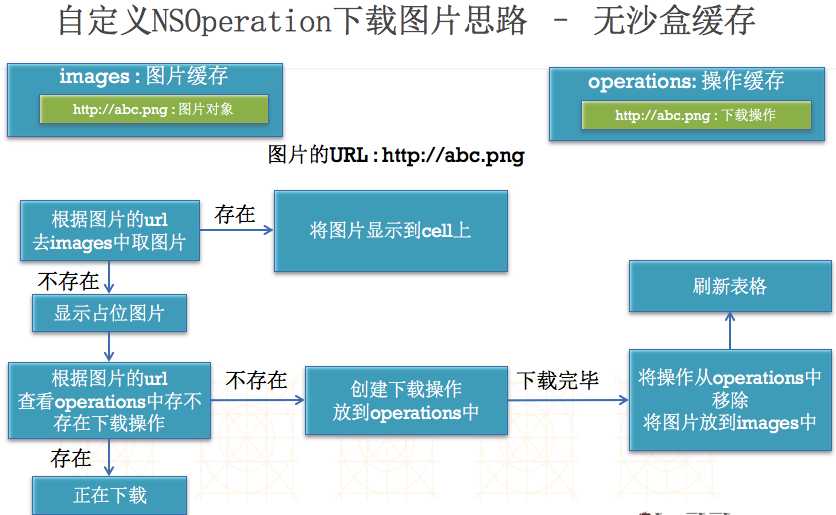
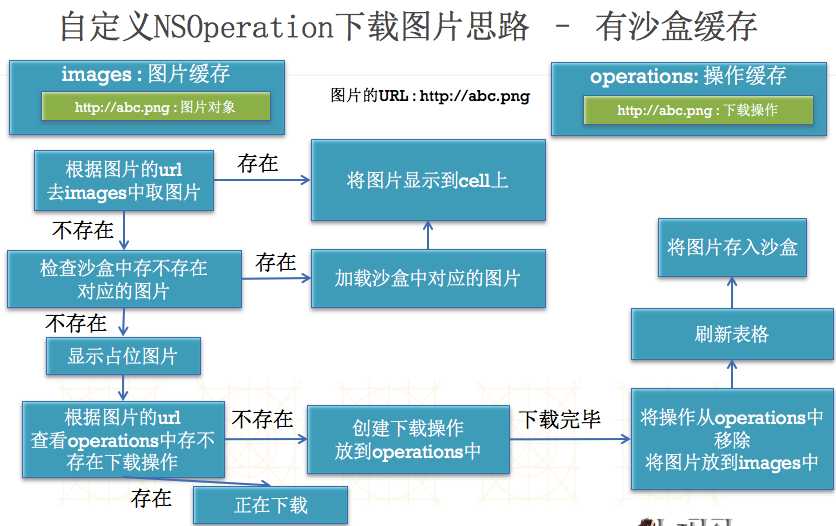
}(1)涉及知识点
01 字典转模型
02 存储数据到沙盒,从沙盒中加载数据
03 占位图片的设置(cell的刷新问题)
04 如何进行内存缓存(使用NSDictionary)
05 在程序开发过程中的一些容错处理
06 如何刷新tableView的指定行(解决数据错乱问题)
07 NSOperation以及线程间通信相关知识
实现原理:
(1)SDWebImage基本使用
01 设置imageView的图片
[cell.imageView sd_setImageWithURL:[NSURL URLWithString:app.icon] placeholderImage:[UIImage imageNamed:@"placehoder"]];
02 设置图片并计算下载进度
//下载并设置图片
/*
第一个参数:要下载图片的url地址
第二个参数:设置该imageView的占位图片
第三个参数:传一个枚举值,告诉程序你下载图片的策略是什么
第一个block块:获取当前图片数据的下载进度
receivedSize:已经下载完成的数据大小
expectedSize:该文件的数据总大小
第二个block块:当图片下载完成之后执行该block中的代码
image:下载得到的图片数据
error:下载出现的错误信息
SDImageCacheType:图片的缓存策略(不缓存,内存缓存,沙盒缓存)
imageURL:下载的图片的url地址
*/
[cell.imageView sd_setImageWithURL:[NSURL URLWithString:app.icon] placeholderImage:[UIImage imageNamed:@"placehoder"] options:SDWebImageRetryFailed progress:^(NSInteger receivedSize, NSInteger expectedSize) {
//计算当前图片的下载进度
NSLog(@"%.2f",1.0 *receivedSize / expectedSize);
} completed:^(UIImage *image, NSError *error, SDImageCacheType cacheType, NSURL *imageURL) {
}];
03 系统级内存警告如何处理
//取消当前正在进行的所有下载操作
[[SDWebImageManager sharedManager] cancelAll];
//清除缓存数据(面试)
//cleanDisk:删除过期的文件数据,计算当前未过期的已经下载的文件数据的大小,如果发现该数据大小大于我们设置的
最大缓存数据大小,那么程序内部会按照按文件数据缓存的时间从远到近删除,直到小于最大缓存数据为止。
//clearMemory:直接删除文件,重新创建新的文件夹
//[[SDWebImageManager sharedManager].imageCache cleanDisk];
[[SDWebImageManager sharedManager].imageCache clearMemory];
04 SDWebImage默认的缓存时间是1周
05 如何播放gif图片
/*
5-1 把用户传入的gif图片->NSData
5-2 根据该Data创建一个图片数据源(NSData->CFImageSourceRef)
5-3 计算该数据源中一共有多少帧,把每一帧数据取出来放到图片数组中
5-4 根据得到的数组+计算的动画时间->可动画的image
[UIImage animatedImageWithImages:images duration:duration];
*/
06 如何判断当前图片类型
+ (NSString *)sd_contentTypeForImageData:(NSData *)data;
(2)SDWebImage内部结构

标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhoudaquan/p/5080762.html