标签:
归并排序:
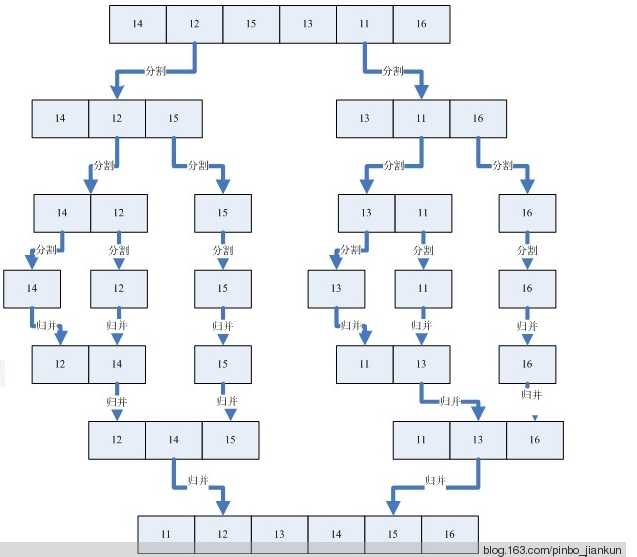
归并(Merge)排序法是将两个(或两个以上)有序表合并成一个新的有序表,即把待排序序列分为若干个子序列,每个子序列是有序的。然后再把有序子序列合并为整体有序序列。该算法是采用分治法(Divide and Conquer)的一个非常典型的应用。
//排序
int[] arr = new int[10] { 5, 34, 61, 72, 93, 45, 66, 82, 90 ,0};
Sort(arr);
/// <summary> /// 归并排序之归:归并排序入口 /// </summary> /// <param name="data">无序数组</param> /// <returns>有序数组</returns> public static int[] Sort(int[] data) { //若data为null,或只剩下1 or 0个元素,返回,不排序 if (null == data || data.Length <= 1) { return data; } //取数组中间下标 int middle = data.Length >> 1; //初始化临时数组let,right,并定义result作为最终有序数组,若数组元素奇数个,将把多余的那元素空间预留在right临时数组 int[] left = new int[middle]; int[] right = new int[data.Length - middle]; int[] result = new int[data.Length]; for (int i = 0; i < data.Length; i++) { if (i < middle) { left[i] = data[i]; } else { right[i - middle] = data[i]; //此处i-middle,让我省掉定义一个j,性能有所提高 } } left = Sort(left);//递归左数组 right = Sort(right);//递归右数组 result = Merge(left, right);//开始排序 return result; }
//合并两个有序表
int[] a = new int[5] { 18, 45, 66, 82, 90 };
int[] b = new int[5] { 5, 34, 61, 72, 93 };
Merage(a, b);
//遍历两个有序数组,依次取出较小的值存入结果数组,同时被取值的数组下标加1,直至数组遍历完成。 //1、比较a[0]与b[0],取较小的那个存入结果数组result[0],此处b[0]较小,取b[0],b下标加1 //2、然后比较a[0]与b[1],取较小的那个存入结果数组result[0],此处a[0]较小,取a[0],a下标加1 //3、然后比较a[1]与b[1],取较小的那个存入结果数组result[0],此处b[1]较小,取a[1],b下标加1 //4、依次遍历,直至a、b数组遍历结束 /// <summary> /// 归并排序之并:排序在这一步 /// </summary> /// <param name="a">左数组</param> /// <param name="b">右数组</param> /// <returns>合并左右数组排序后返回</returns> private static int[] Merge(int[] a, int[] b) { //定义结果数组,用来存储最终结果 int[] result = new int[a.Length + b.Length]; int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0; while (i < a.Length && j < b.Length) { if (a[i] < b[j])//左数组中元素小于右数组中元素 { result[k++] = a[i++];//将小的那个放到结果数组 } else//左数组中元素大于右数组中元素 { result[k++] = b[j++];//将小的那个放到结果数组 } } while (i < a.Length)//这里其实是还有左元素,但没有右元素 { result[k++] = a[i++]; } while (j < b.Length)//有右元素,无左元素 { result[k++] = b[j++]; } return result;//返回结果数组 }
转自:
http://blog.163.com/pinbo_jiankun/blog/static/133546488201391831822169/
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaochun126/p/5084526.html