标签:
目标读者:理解HTTP协议,对称和非对称加密,想要了解HTTPS协议的工作原理
读完本文,你能明白
HTTPS,也称作HTTP over TLS。TLS的前身是SSL,TLS 1.0通常被标示为SSL 3.1,TLS 1.1为SSL 3.2,TLS 1.2为SSL 3.3。本文着重描述TLS协议的1.2版本
下图描述了在TCP/IP协议栈中TLS(各子协议)和HTTP的关系
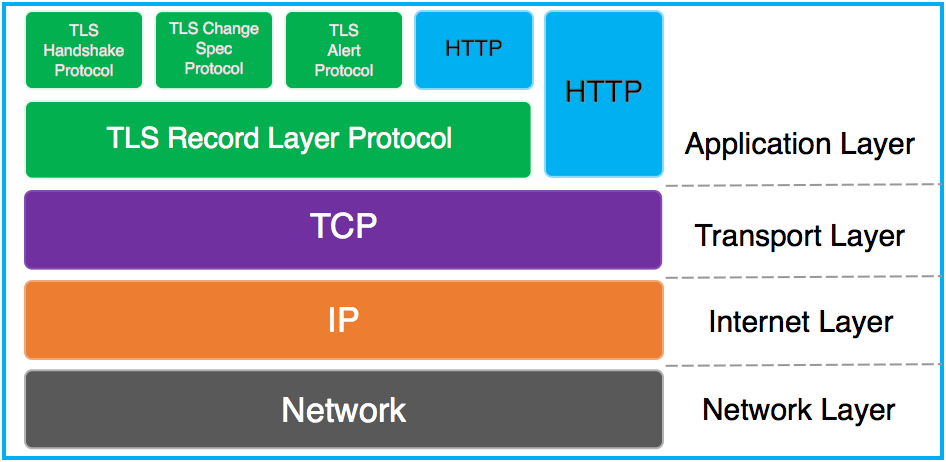
Credit: Kaushal Kumar Panday From: SSL Handshake and HTTPS Bindings on IIS
其中Handshake protocol,Change Ciper Spec protocol和Alert protocol组成了SSL Handshaking Protocols。
HTTPS和HTTP协议相比提供了
其中,数据完整性和隐私性由TLS Record Protocol保证,身份认证由TLS Handshaking Protocols实现。
使用RSA算法的SSL握手过程是这样的
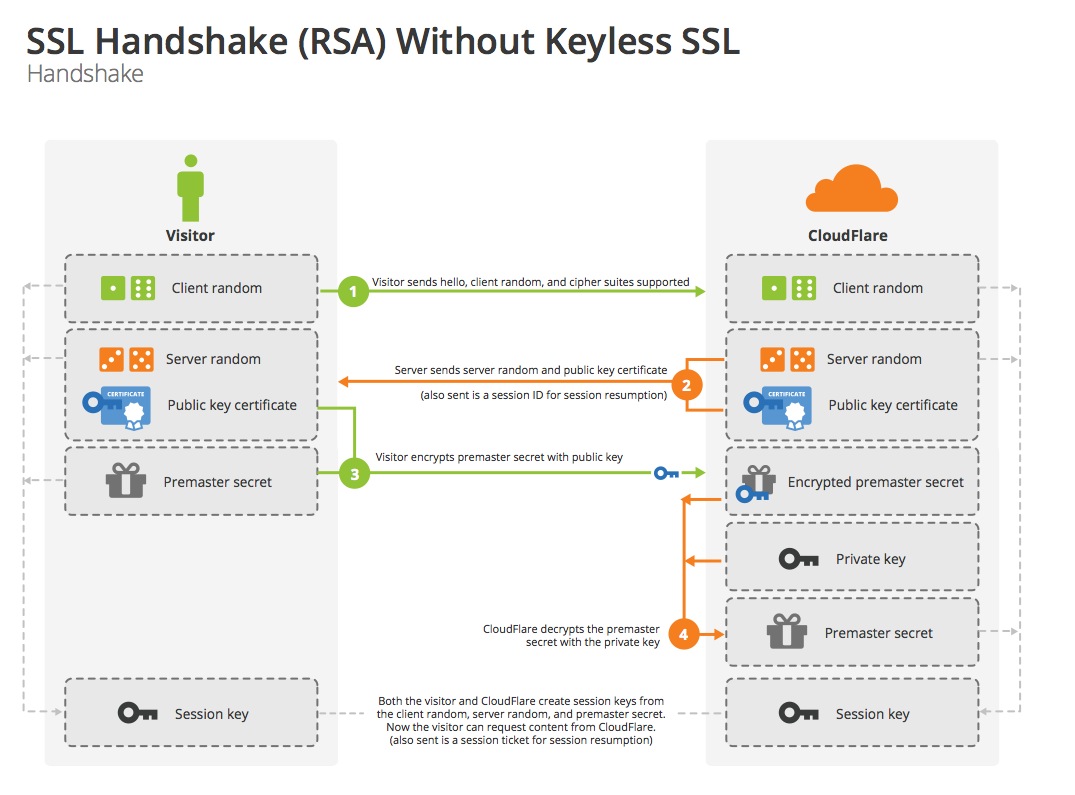
client_random和支持的加密方式列表server_random,选择的加密方式和服务器证书链premaster secret发送给服务端premaster secretclient_random,server_random和premaster secret生成master secret,用于对称加密后续通信内容那么什么是证书呢?
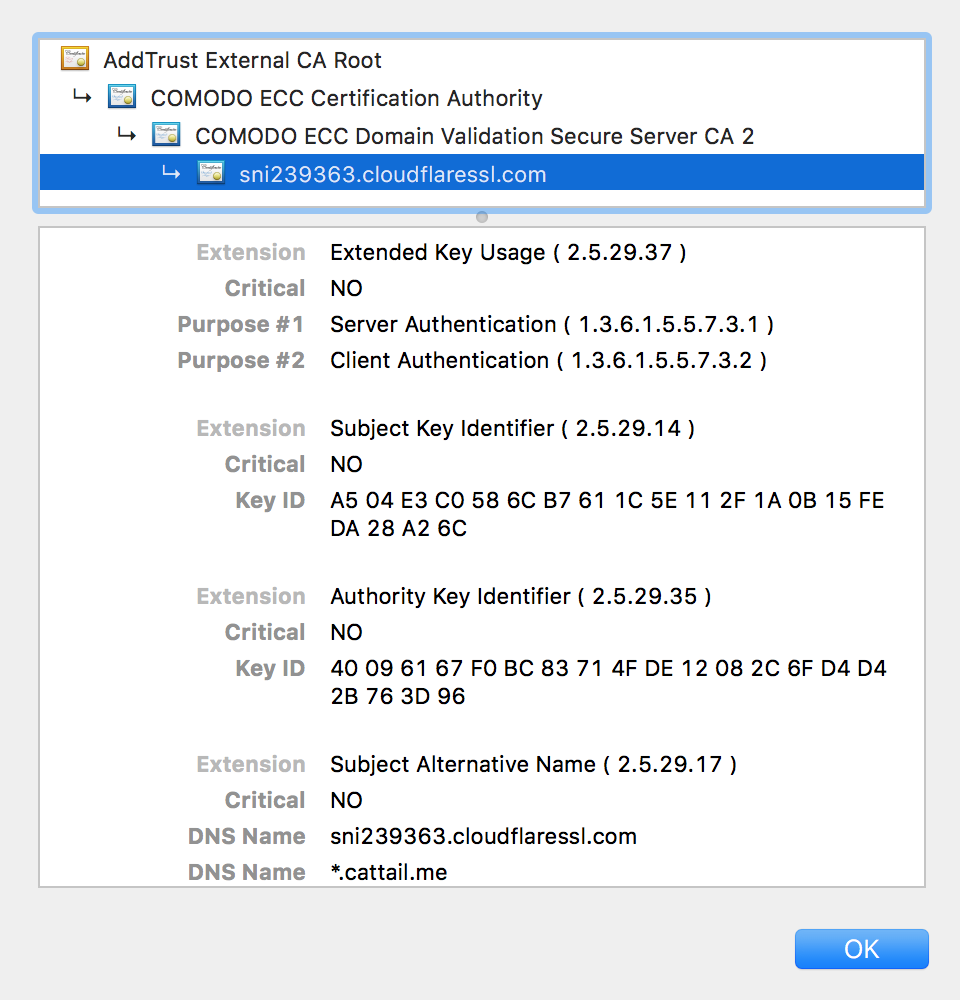
证书中包含什么信息
为什么服务端要发送证书给客户端
互联网有太多的服务需要使用证书来验证身份,以至于客户端(操作系统或浏览器等)无法内置所有证书,需要通过服务端将证书发送给客户端。
客户端为什么要验证接收到的证书
中间人攻击
客户端<------------攻击者<------------服务端
伪造证书 拦截请求
客户端如何验证接收到的证书
为了回答这个问题,需要引入数字签名(Digital Signature)。
+---------------------+
| A digital signature |
|(not to be confused |
|with a digital |
|certificate) | +---------+ +--------+
| is a mathematical |----哈希--->| 消息摘要 |---私钥加密--->| 数字签名 |
|technique used | +---------+ +--------+
|to validate the |
|authenticity and |
|integrity of a |
|message, software |
|or digital document. |
+---------------------+
将一段文本通过哈希(hash)和私钥加密处理后生成数字签名。
假设消息传递在Bob,Susan和Pat三人之间发生。Susan将消息连同数字签名一起发送给Bob,Bob接收到消息后,可以这样验证接收到的消息就是Susan发送的
+---------------------+
| A digital signature |
|(not to be confused |
|with a digital |
|certificate) | +---------+
| is a mathematical |----哈希--->| 消息摘要 |
|technique used | +---------+
|to validate the | |
|authenticity and | |
|integrity of a | |
|message, software | 对
|or digital document. | 比
+---------------------+ |
|
|
+--------+ +---------+
| 数字签名 |---公钥解密--->| 消息摘要 |
+--------+ +---------+
当然,这个前提是Bob知道Susan的公钥。更重要的是,和消息本身一样,公钥不能在不安全的网络中直接发送给Bob。
此时就引入了证书颁发机构(Certificate Authority,简称CA),CA数量并不多,Bob客户端内置了所有受信任CA的证书。CA对Susan的公钥(和其他信息)数字签名后生成证书。
Susan将证书发送给Bob后,Bob通过CA证书的公钥验证证书签名。
Bob信任CA,CA信任Susan 使得 Bob信任Susan,信任链(Chain Of Trust)就是这样形成的。
事实上,Bob客户端内置的是CA的根证书(Root Certificate),HTTPS协议中服务器会发送证书链(Certificate Chain)给客户端。
TLS协议包括TLS Record Protocol和TLS Handshake Protocol。总览中的流程图仅涉及到TLS Handshake Protocol。
在TLS协议中,有四种子协议运行于Record protocol之上
Record protocol起到了这样的作用
值得一提的是,Record protocol提供了数据完整性和隐私性保证,但Record类型(type)和长度(length)是公开传输的
Record Protocol有三个连接状态(Connection State),连接状态定义了压缩,加密和MAC算法。所有的Record都是被当前状态(Current State)确定的算法处理的。
TLS Handshake Protocol和Change Ciper Spec Protocol会导致Record Protocol状态切换。
empty state -------------------> pending state ------------------> current state
Handshake Protocol Change Cipher Spec
初始当前状态(Current State)没有指定加密,压缩和MAC算法,因而在完成TLS Handshaking Protocols一系列动作之前,客户端和服务端的数据都是明文传输的;当TLS完成握手过程后,客户端和服务端确定了加密,压缩和MAC算法及其参数,数据(Record)会通过指定算法处理。
其中,Record首先被加密,然后添加MAC(message authentication code)以保证数据完整性。
Handshakeing protocols包括Alert Protocol,Change Ciper Spec Protocol和Handshake protocol。本文不会详细介绍Alert Protocol和Change Ciper Spec Protocol。
使用RSA算法的握手过程是这样的(已在总览中提到)

客户端和服务端在握手hello消息中明文交换了client_random和server_random,使用RSA公钥加密传输premaster secret,最后通过算法,客户端和服务端分别计算master secret。其中,不直接使用premaster secret的原因是:保证secret的随机性不受任意一方的影响。
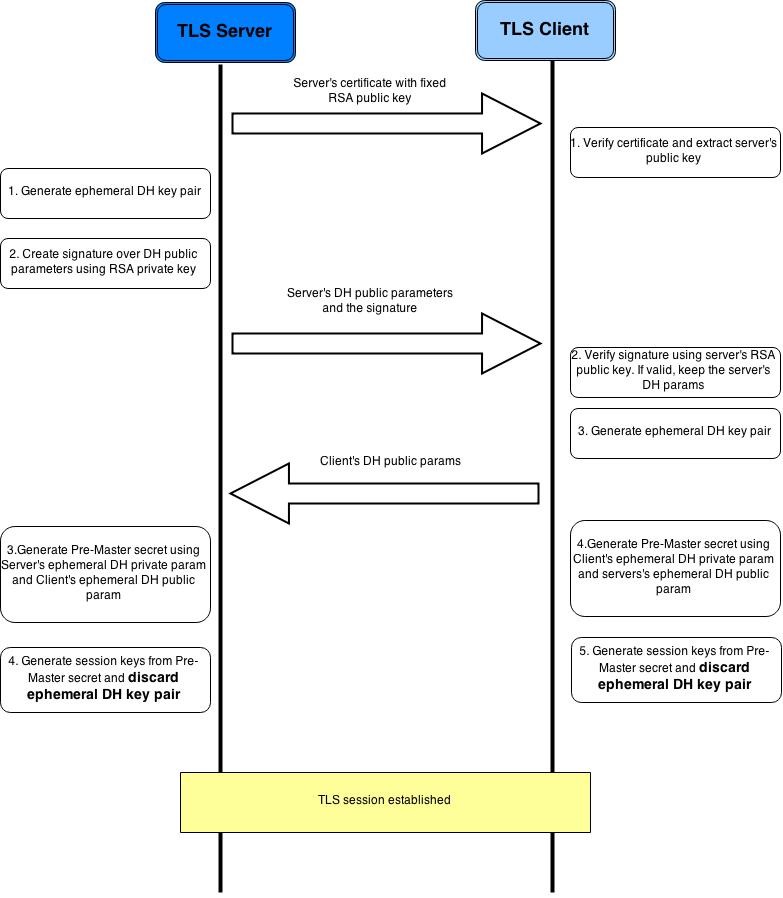
除了使用RSA算法在公共信道交换密钥,还可以通过Diffie–Hellman算法。Diffie–Hellman算法的原理是这样的
By Original schema: A.J. Han Vinck, University of Duisburg-Essen SVG version: Flugaal [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons
使用Diffie–Hellman算法交换premaster secret的流程
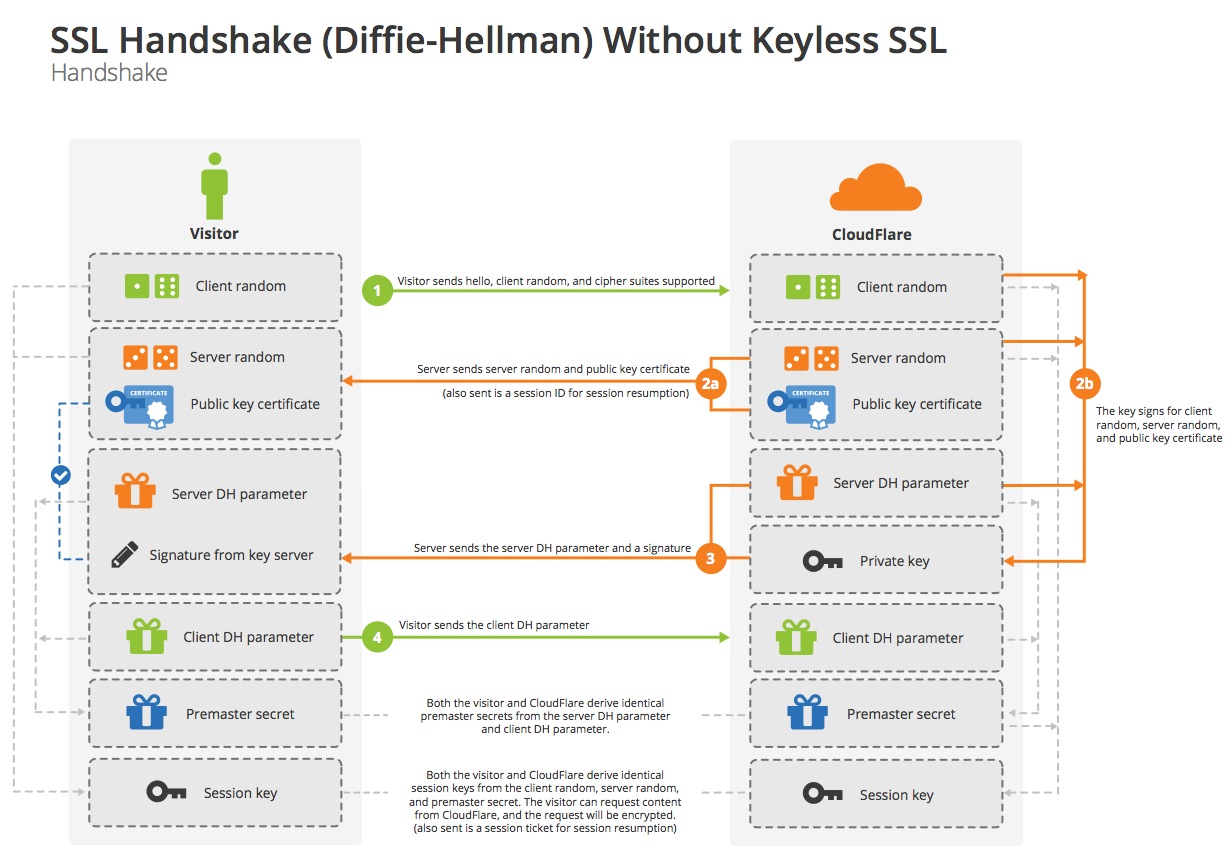
TLS Handshaking Protocols协商了TLS Record Protocol使用的算法和所需参数,并验证了服务端身份;TLS Record Protocol在协商后保证应用层数据的完整性和隐私性。
TLS Handshaking Protocol的核心是在公开信道上传递premaster secret。
性能
no
There are a number of ways in which a man-in-the-middle attacker can attempt to make two entities drop down to the least secure method they support.
攻击者甚至可以直接丢弃双方的数据包
通过Client Certificate
This message conveys the client‘s certificate chain to the server; the server will use it when verifying the CertificateVerify message (when the client authentication is based on signing) or calculating the
premaster secret(for non-ephemeral Diffie- Hellman). The certificate MUST be appropriate for the negotiated cipher suite‘s key exchange algorithm, and any negotiated extensions.
Closure Alerts:防止Truncation Attack
In a truncation attack, an attacker inserts into a message a TCP code indicating the message has finished, thus preventing the recipient picking up the rest of the message. To prevent this, SSL from version v3 onward has a closing handshake, so the recipient knows the message has not ended until this has been performed.
Error Alerts:错误处理
master_secret = PRF(pre_master_secret, "master secret",
ClientHello.random + ServerHello.random)
[0..47];
Handshaking Protocols使得客户端和服务端交换了三个参数:client_random,server_random和master_secret,通过以下算法生成算法所需要的参数
To generate the key material, compute
key_block = PRF(SecurityParameters.master_secret,
"key expansion",
SecurityParameters.`server_random ` +
SecurityParameters.`client_random`);
until enough output has been generated. Then, the key_block is
partitioned as follows:
client_write_MAC_key[SecurityParameters.mac_key_length]
server_write_MAC_key[SecurityParameters.mac_key_length]
client_write_key[SecurityParameters.enc_key_length]
server_write_key[SecurityParameters.enc_key_length]
client_write_IV[SecurityParameters.fixed_iv_length]
server_write_IV[SecurityParameters.fixed_iv_length]
The master secret is expanded into a sequence of secure bytes, which is then split to a client write MAC key, a server write MAC key, a client write encryption key, and a server write encryption key
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/svan/p/5090201.html