标签:
------------------------------------------LinearLayout---------------------------------------------------
LinearLayout又称作线性布局,是一种非常常用的布局。
正如名字所描述的一样,这个布局会将它所包含的控件在线性方向上依次排列。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!--水平布局--><!--android:orientation="vertical"--> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical"> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> </LinearLayout>
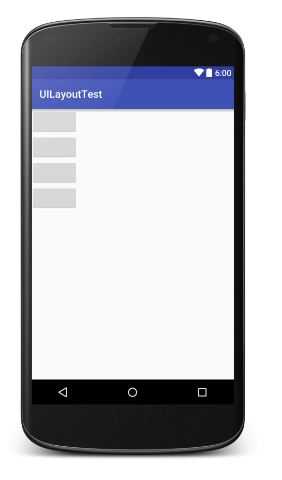
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!--垂直布局--><!--android:orientation="horizontal"--> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="horizontal"> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> </LinearLayout>
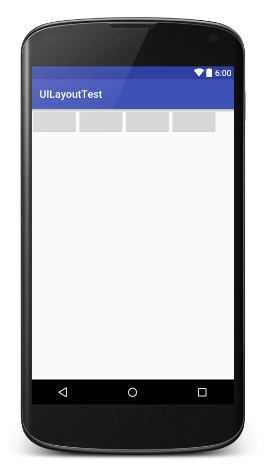
提示:如果LinearLayout的排列方式是horizontal,内部控件就绝不能将宽度指定为imatch_parent,因为这样的话单独一个控件就会将整个水平方向占满,其他控件就没有可放置的位置了。同样的道理,如果LinearLayout的排列方向是vertical,内部的控件就不能将高度指定为match_parent。
Layout_gravity属性:
注意:android:gravity是用于指定文字在控件中的对齐方式,而android:layout_gravity是用于指定控件在布局中的对齐方式。
android:layout_gravity的限制:
当LinearLayout的排了方式是horizontal时,只有垂直方向上的对齐方式才会生效,因为此时水平方向上的长度是不固定的,每添加一个控件,水平方向的长度都会发生改变,因此无法指定该方向上的对齐方式。
同样的道理,当LinearLayout的排列方向是vertical时,只有水平方向上的对齐方式才会生效。
horizontal: top bottom center_vertical
vertical: left right center_horizontal
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!--layout_gravity的示例--> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="horizontal"> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="top" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="center_vertical" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="bottom" /> </LinearLayout>

Layout_weight属性:
android:layout_weight 这个属性允许我们使用比例的方式来指定控件的大小,它在手机屏幕的适配性方面可以起到非常重要的作用。
Layout_weight表示屏占比。系统会根据layout_weight的数值大小为控件分配空间。调节layout_weight数值,也就是调整各个控件所占空间的比例。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="horizontal"> <!--EditText占5/6--> <EditText android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="5" /> <!--Button占1/6--> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" /> </LinearLayout>
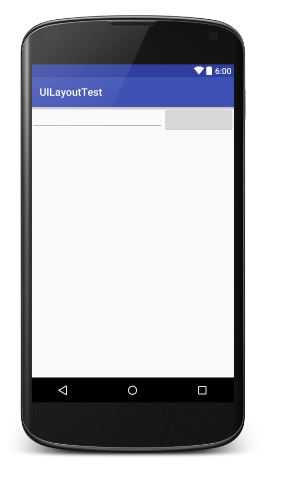
------------------------------------------------RelativeLayout--------------------------------------------------------
RelativeLayout又称为相对布局,也是一种非常常用的布局。它可以通过相对定位的方式让控件出现在布局的任何位置。
父元素定位属性:
android:layout_alignParentTop="true" 对齐父类顶端
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" 对齐父类底端
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" 对齐父类左端
android:layout_alignParentRight="true" 对齐父类右端
android:layout_centerInParent="true" 居于父类中间
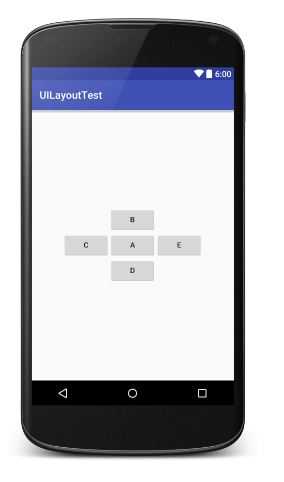
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:layout_alignParentTop="true" android:text="A" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" android:layout_alignParentTop="true" android:text="B" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerInParent="true" android:text="C" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:text="D" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" android:text="E" /> </RelativeLayout>
相对控件ID定位:
android:layout_above="@+id/A" 居于A元素顶端
android:layout_below="@+id/A" 居于A元素底端
android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/A" 居于A元素左端
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/A" 居于A元素右端
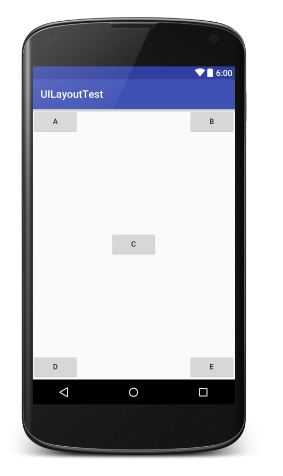
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <Button android:id="@+id/A" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerInParent="true" android:text="A" /> <Button android:id="@+id/B" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_above="@+id/A" android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/A" android:text="B" /> <Button android:id="@+id/C" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_above="@+id/A" android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/A" android:text="C" /> <Button android:id="@+id/D" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@+id/A" android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/A" android:text="D" /> <Button android:id="@+id/E" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@+id/A" android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/A" android:text="E" /> </RelativeLayout>
居中对齐:
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" 水平居中
android:layout_centerVertical="true" 垂直居中
提示:居中属性可能会有点难以理解,尝试着这样去想象,指定垂直或水平表示该方向有界,居中就是找到这个界限的中间位置。
尝试去做下面这个RelativeLayout:
---------------------------------------------------FrameLayout----------------------------------------------------
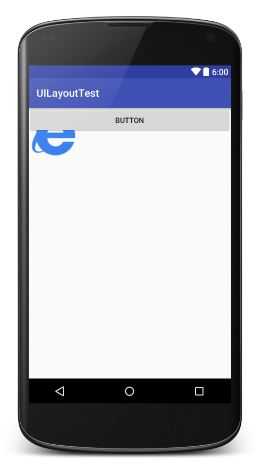
FrameLayout相比前面两种布局就简单太多了。这种布局没有任何定位方式,所有的控件都会摆放在布局的左上角。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:src="@drawable/ie" /> <Button android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Button" /> </FrameLayout>
-----------------------------------------------------TableLayout-----------------------------------------------------------
TableLayout允许我们使用表格的方式来排列控件,这种布局也不是很常用,只需要了解一下它的基本用法就可以了。
既然是表格,那就一定会有行和列,在设计表格时我们尽量让每一行都拥有相同的列数,这样的表格也是最简单的。
不过有时候事情并非总会顺从我们的心意,当表格的某行一定要有不相等的列数时,就需要通过合并单元格的方式来应对。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <TableRow> <TextView android:text=" 账号:" /> <EditText android:hint=" 输入账户名" /> </TableRow> <TableRow> <TextView android:text=" 密码:" /> <EditText android:hint=" 输入密码" /> </TableRow> <TableRow> <Button android:text="登录" /> </TableRow> </TableLayout>
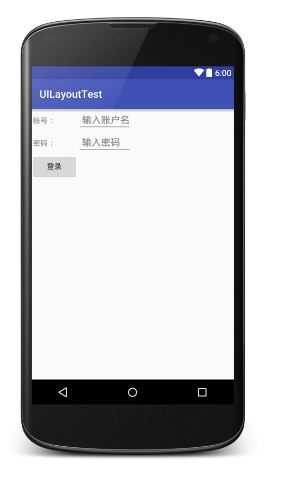
在TableLayout中每添加一个TableRow就表示在表格中添加了一行,然后再TableRow中每添加一个控件,就表示在该列中加入了一列。
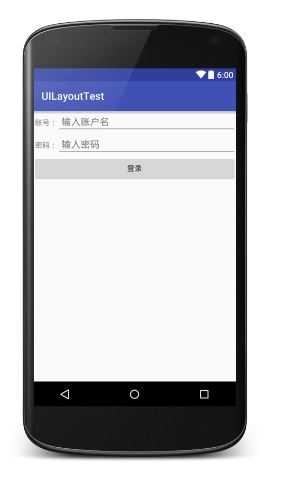
TableRow中的控件是不能指定宽度的。这时就需要通过对单元格进行合并来解决这个问题,使用android:layout_span="2"让登录按钮占据两列的空间,以保证表格结构的合理性。
因为TableRow中无法指定控件的宽度,所以当前的登录界面并没有充分利用屏幕的宽度。这时使用android:strechColumns属性将TableLayout的某一列进行拉伸,以达到自动适应屏幕宽度的作用。
注意:android:stretchColumns的值是从0开始,表示第一行。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:stretchColumns="1"> <TableRow> <TextView android:text=" 账号:" /> <EditText android:hint=" 输入账户名" /> </TableRow> <TableRow> <TextView android:text=" 密码:" /> <EditText android:hint=" 输入密码" /> </TableRow> <TableRow> <Button android:layout_span="2" android:text="登录" /> </TableRow> </TableLayout>
Android中其实还有一个AbsoluteLayout,不过这个布局已经被GridLayout替代了。官方已经不推荐使用这种布局了,因此直接将它忽略就好。
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/woider/p/5118742.html
Android四种基本布局(LinearLayout \ RelativeLayout \ FrameLayout \ TableLayout)
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/woider/p/5118742.html