标签:
线性表的结构简单,长度允许动态增长或搜索;可以对线性表中的任何数据元素进行访问和查找;允许进行数据的插入和删除操作;求线性表中的指定数据的前驱和后继;合并线性表以及拆分线性表中。
Java JDK中有ArrayList和LinkedList两个类很好的实现了顺序存储和链式存储。因此学习数据结构的最好方式是去研究JDK源码。
这里的代码个人作为练习,为了便于理解,很多地方处理的并非十分严谨,仅供参考。转载注明出处,技术讨论 email: <yaoyao0777@Gmail.com>
1 package org.yohhan.data_structure.api; 2 3 /** 4 * @author yohhan <yaoyao0777@Gmail.com> 5 * @date create:2016年1月10日 下午4:05:35 6 * 7 * 线性表的抽象数据类型 8 * 9 */ 10 public interface MyList { 11 public void clear(); 12 13 public boolean isEmpty(); 14 15 public int length(); 16 17 public Object get(int i) throws Exception; 18 19 public void insert(int i, Object obj) throws Exception; 20 21 public void remove(int i) throws Exception; 22 23 public int indexOf(Object obj); 24 25 public void display(); 26 }
顺序存储采用一组地址连续的存储单元依次存储线性表占用的各个数据元素的存储结构。
1)逻辑上相邻的数据元素,在物理存储位置上也是相邻的。
2)存储密度高,事先需要分配足够应用的存储空间。
3)随机存取,查询速度快,直接访问地址单元中的数据。时间复杂度 O(1)
4)插入删除操作会引起大量的数据移动,时间复杂度O(n)
1 package org.yohhan.data_structure.linear; 2 3 import org.yohhan.data_structure.api.MyList; 4 5 /** 6 * @author yohhan <yaoyao0777@Gmail.com> 7 * @date create:2016年1月10日 下午4:09:15 8 * 9 * 线性表的顺序存储实现 10 */ 11 public class SqList implements MyList { 12 13 private Object[] listElem; // 数组作为线性表的存储空间 14 private int curLen; // 线性表的当前长度 15 16 public SqList(int maxSize) { 17 curLen = 0; 18 listElem = new Object[maxSize]; 19 } 20 21 @Override 22 public void clear() { 23 curLen = 0; 24 } 25 26 @Override 27 public boolean isEmpty() { 28 return curLen == 0; 29 } 30 31 @Override 32 public int length() { 33 return curLen; 34 } 35 36 @Override 37 public Object get(int i) throws Exception { 38 if (i < 0 || i > curLen - 1) 39 throw new Exception("元素不存在"); 40 return listElem[i]; 41 } 42 43 @Override 44 public void insert(int i, Object obj) throws Exception { 45 if (curLen == listElem.length) 46 throw new Exception("存储空间已满"); 47 if (i < 0 || i > curLen) 48 throw new Exception("插入位置不合法"); 49 for (int j = curLen; j > i; j--) 50 listElem[j] = listElem[j - 1]; 51 listElem[i] = obj; 52 ++curLen; 53 } 54 55 @Override 56 public void remove(int i) throws Exception { 57 if (i < 0 || i > curLen - 1) 58 throw new Exception("删除位置不合法"); 59 for (int j = i; j < curLen; j++) 60 listElem[j] = listElem[j + 1]; 61 --curLen; 62 } 63 64 @Override 65 public int indexOf(Object obj) { 66 int j = 0; 67 while (j < curLen && !listElem[j].equals(obj)) 68 j++; 69 if (j < curLen) 70 return j; 71 return -1; 72 } 73 74 @Override 75 public void display() { 76 for (int j = 0; j < curLen; j++) 77 System.out.print(listElem[j] + ", "); 78 } 79 80 @Override 81 public String toString() { 82 StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); 83 sb.append("["); 84 for (Object obj : listElem) { 85 if (null != obj) 86 sb.append(obj.toString() + ", "); 87 } 88 sb.delete(sb.length() - 2, sb.length()); 89 sb.append("]"); 90 return sb.toString(); 91 } 92 93 }
采用链式存储方式存储的线性表,链表中每一个结点中包含存放数据元素值的数据域和存放逻辑上相邻结点的指针域。(示例中的结点只包含一个指针域,称为单链表(Single Linked List))
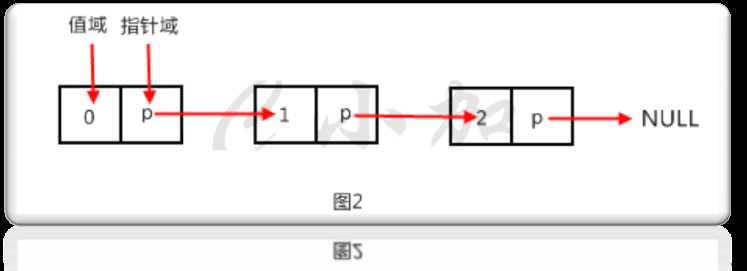
(图片摘自网上)
单链表通过指向后继结点的指针将结点串联成一条链。
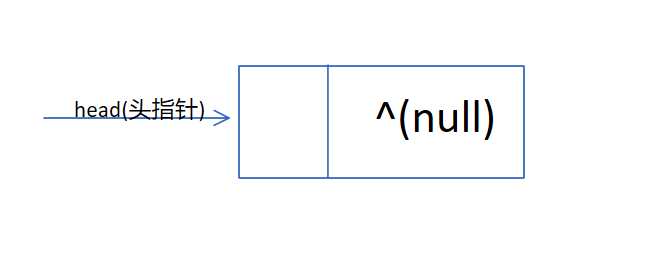
以线性表中的第一个数据元素的存储地址作为线性表的起始地址,称为线性表的头指针。通过头指针(head)来唯一标识一个链表。
单链表中的最后一个节点没有后继,指针域为空指针(null),称为尾结点。
示例中采用一个“虚头结点”数据域不存放具体值,指针域中的指针指向单链表的第一个结点(首结点)。即当头结点中的指针域为空时,链表为空
1)不需要预先分配存储空间,动态分配存储空间,存储密度较低、
2) 无法随机查询,需要从头遍历来查找元素。时间复杂度O(n)
3)便于进行数据的插入和删除。时间复杂度O(1)
结点类结构:
1 package org.yohhan.data_structure.node; 2 3 /** 4 * @author yohhan <yaoyao0777@Gmail.com> 5 * @date create:2016年1月10日 下午4:39:15 6 * 7 * 链表的结点类描述 8 * 9 */ 10 public class Node { 11 12 private Object data; 13 private Node next; 14 15 public Node() { 16 this(null, null); 17 } 18 19 public Node(Object data) { 20 this(data, null); 21 } 22 23 public Node(Object data, Node next) { 24 super(); 25 this.data = data; 26 this.next = next; 27 } 28 29 public Object getData() { 30 return data; 31 } 32 33 public void setData(Object data) { 34 this.data = data; 35 } 36 37 public Node getNext() { 38 return next; 39 } 40 41 public void setNext(Node next) { 42 this.next = next; 43 } 44 45 }
单链表类的描述:
1 package org.yohhan.data_structure.linear; 2 3 import org.yohhan.data_structure.api.MyList; 4 import org.yohhan.data_structure.node.Node; 5 6 /** 7 * @author yohhan <yaoyao0777@Gmail.com> 8 * @date create:2016年1月10日 下午4:51:58 9 * 10 * 带头结点的单链表实现 11 * 12 */ 13 public class LinkList implements MyList { 14 15 private Node head; 16 17 public LinkList() { 18 head = new Node(); 19 } 20 21 public LinkList(int n, boolean order) throws Exception { 22 this(); 23 if (order) 24 createFromTail(n); 25 else 26 createFromHead(n); 27 } 28 29 private void createFromTail(int n) throws Exception { 30 // 可在此添加输入流,传入数据 31 32 for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) 33 insert(length(), j + 1); 34 } 35 36 private void createFromHead(int n) throws Exception { 37 // 可在此添加输入流,传入数据 38 39 for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) 40 insert(0, j + 1); 41 } 42 43 @Override 44 public void clear() { 45 head.setData(null); 46 head.setNext(null); 47 } 48 49 @Override 50 public boolean isEmpty() { 51 return head.getNext() == null; 52 } 53 54 @Override 55 public int length() { 56 Node node = head.getNext(); 57 int length = 0; 58 while (node != null) { 59 node = node.getNext(); 60 ++length; 61 } 62 return length; 63 } 64 65 /** 66 * 按位序号查找算法 67 */ 68 @Override 69 public Object get(int i) throws Exception { 70 Node node = head.getNext(); 71 int j = 0; 72 while (node != null && j < i) { 73 node = node.getNext(); 74 ++j; 75 } 76 if (j > i || node == null) 77 throw new Exception("元素不存在"); 78 return node.getData(); 79 } 80 81 /** 82 * 在index前插入新结点 83 */ 84 @Override 85 public void insert(int i, Object obj) throws Exception { 86 Node node = head; 87 int j = -1; 88 while (node != null && j < i - 1) { 89 node = node.getNext(); 90 ++j; 91 } 92 if (j > i - 1 || node == null) 93 throw new Exception("插入位置不合法"); 94 Node newNode = new Node(obj); 95 newNode.setNext(node.getNext()); 96 node.setNext(newNode); 97 } 98 99 @Override 100 public void remove(int i) throws Exception { 101 Node node = head; 102 int j = -1; 103 while (node.getNext() != null && j < i - 1) { // 链表不能为空 104 node = node.getNext(); 105 ++j; 106 } 107 if (j > i - 1 || node == null) 108 throw new Exception("删除位置不合法"); 109 node.setNext(node.getNext().getNext()); 110 } 111 112 /** 113 * 按值查找算法 114 */ 115 @Override 116 public int indexOf(Object obj) { 117 Node node = head.getNext(); 118 int j = 0; 119 while (node != null && !node.getData().equals(obj)) { 120 node = node.getNext(); 121 ++j; 122 } 123 if (node != null) 124 return j; 125 return -1; 126 } 127 128 @Override 129 public void display() { 130 Node node = head.getNext(); 131 while (node != null) { 132 System.out.print(node.getData() + ""); 133 node = node.getNext(); 134 } 135 System.out.println(); 136 } 137 138 @Override 139 public String toString() { 140 StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); 141 sb.append("["); 142 Node node = head.getNext(); 143 while (node != null) { 144 sb.append(node.getData().toString() + ", "); 145 node = node.getNext(); 146 } 147 sb.delete(sb.length() - 2, sb.length()); 148 sb.append("]"); 149 return sb.toString(); 150 } 151 152 }
附:线性表的单元测试类:
1 package org.yohhan.data_structure.test; 2 3 import static org.junit.Assert.*; 4 import org.junit.Test; 5 import org.yohhan.data_structure.linear.LinkList; 6 import org.yohhan.data_structure.linear.SqList; 7 8 /** 9 * @author yohhan <yaoyao0777@Gmail.com> 10 * @date create:2016年1月10日 下午4:25:12 11 * 12 * 线性表单元测试类 13 * 14 */ 15 public class LinearTest { 16 17 @Test 18 public void sqListTest() throws Exception { 19 SqList sqList = new SqList(10); 20 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) 21 sqList.insert(i, i + 1); 22 System.out.println(sqList); 23 assertTrue(sqList.toString().equals("[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]")); 24 assertTrue(sqList.length() == 5); 25 assertTrue(sqList.indexOf(2) == 1); 26 assertTrue(sqList.get(0).equals(1)); 27 sqList.remove(1); 28 assertTrue(sqList.length() == 4); 29 assertTrue(sqList.indexOf(1) == 0); 30 } 31 32 @Test 33 public void linkListTest() throws Exception { 34 LinkList linkList = new LinkList(5, true); 35 System.out.println(linkList); 36 assertTrue(new LinkList(5, false).toString().equals("[5, 4, 3, 2, 1]")); 37 assertTrue(linkList.toString().equals("[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]")); 38 assertTrue(linkList.length() == 5); 39 assertTrue(linkList.indexOf(2) == 1); 40 assertTrue(linkList.get(0).equals(1)); 41 linkList.remove(1); 42 assertTrue(linkList.length() == 4); 43 assertTrue(linkList.indexOf(1) == 0); 44 45 } 46 47 }
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/yaoyao-start/p/5122537.html