标签:
HLS(HTTP Live Streaming)是Apple的动态码率自适应技术。主要用于PC和Apple终端的音视频服务。包括一个m3u(8)的索引文件,TS媒体分片文件和key加密串文件。
HLS的关键其实是生成m3u8索引文件和TS媒体分片,下面我将通过以下几个步骤讲述m3u8及TS媒体分片的生成:
第一步---获取TS文件:
TS(Transport Stream)既传输流,标准制定于mpeg2文档协议中,当时TS格式主要是为了数字电视传输而制定,制定的年限相当早,在网上能找到很完备的mpeg2文档介绍。大家可以参考mpege-2文档标准中TS流介绍学习该格式。
现在的我们下载的高清电影以mkv格式居多,早期的的电影可能一rmvb和avi居多,更早的甚至还有mpg格式,现在流行的视频网站下载的视频基本都是flv格式。这些格式都是非TS格式,不过不要紧,现在视频转码的软件也非常多,我们可以通过以下两种方式进行转码。
1,通过格式工厂软件,这是一个比较成熟的软件,网上百度下载即可,不过只有软件,不利于后期源码的直接开发;
下载地址:http://www.pcfreetime.com/CN/index.html
2,通过ffmpeg进行格式转换,该工程为开源项目,我们在实际开发的过程中可以直接集成该源码,(具体的集成方式该篇文章不讲解,后期将对怎么封装调用ffmpeg做出相应介绍)。目前我们只是想获取TS文件用于生产m3u8索引文件和TS分片而已,直接下载ffmpeg的可执行程序,通过ffmpeg.exe转换即可:
下载地址:http://ffmpeg.org/
通过命令行模式进入到ffmpeg.exe所在的目录,在命令行中输入:ffmpeg.exe -i XXX.flv xxx.ts 即可,如下图:
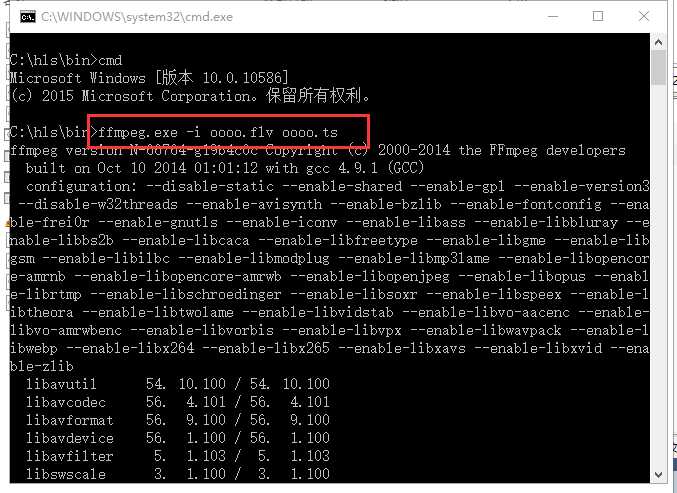
图1
第二步--生成m3u8索引文件和TS媒体分片
1, m3u8 源码下,
下载地址:
https://github.com/johnf/m3u8-segmenter/archive/master.zip 该地址的源码主要是在linux系统编译,不过也能修改成在windows下编译。
windows的源码下载 :
官网: http://www.espend.de/artikel/iphone-ipad-ipod-http-streaming-segmenter-and-m3u8-windows.html 源码地址http://code.google.com/p/httpsegmenter/ 不过也要依赖ffmpeg库,稍微修改下即可。
其实以上两个路径的源码其实是一样滴,下面那个是德国人修改写的,看后缀de就知道了,可能需要FQ才能打开。
下面是截取segmenter.c中的代码分片片段:
do { double segment_time = 0.0; AVPacket packet; double packetStartTime = 0.0; double packetDuration = 0.0; if (!decode_done) { decode_done = av_read_frame(ic, &packet); if (!decode_done) { if (packet.stream_index != video_index && packet.stream_index != audio_index) { av_free_packet(&packet); continue; } timeStamp = (double)(packet.pts) * (double)(ic->streams[packet.stream_index]->time_base.num) / (double)(ic->streams[packet.stream_index]->time_base.den); if (av_dup_packet(&packet) < 0) { fprintf(stderr, "Could not duplicate packet\n"); av_free_packet(&packet); break; } insertPacket(streamLace, &packet, timeStamp); } } if (countPackets(streamLace) < 50 && !decode_done) { /* allow the queue to fill up so that the packets can be sorted properly */ continue; } if (!removePacket(streamLace, &packet)) { if (decode_done) { /* the queue is empty, we are done */ break; } assert(decode_done); continue; } packetStartTime = (double)(packet.pts) * (double)(ic->streams[packet.stream_index]->time_base.num) / (double)(ic->streams[packet.stream_index]->time_base.den); packetDuration = (double)(packet.duration) * (double)(ic->streams[packet.stream_index]->time_base.num) / (double)(ic->streams[packet.stream_index]->time_base.den); #if !defined(NDEBUG) && (defined(DEBUG) || defined(_DEBUG)) if (av_log_get_level() >= AV_LOG_VERBOSE) fprintf(stderr, "stream %i, packet [%f, %f)\n", packet.stream_index, packetStartTime, packetStartTime + packetDuration); #endif segment_duration = packetStartTime + packetDuration - prev_segment_time; // NOTE: segments are supposed to start on a keyframe. // If the keyframe interval and segment duration do not match // forcing the segment creation for "better seeking behavior" // will result in decoding artifacts after seeking or stream switching. if (packet.stream_index == video_index && (packet.flags & AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY || strict_segment_duration)) { segment_time = packetStartTime; } else if (video_index < 0) { segment_time = packetStartTime; } else { segment_time = prev_segment_time; } if (segment_time - prev_segment_time + segment_duration_error_tolerance > target_segment_duration + extra_duration_needed) { avio_flush(oc->pb); avio_close(oc->pb); // Keep track of accumulated rounding error to account for it in later chunks. segment_duration = segment_time - prev_segment_time; rounded_segment_duration = (int)(segment_duration + 0.5); extra_duration_needed += (double)rounded_segment_duration - segment_duration; updatePlaylist(playlist, playlist_filename, output_filename, output_index, rounded_segment_duration); _snprintf(output_filename, strlen(output_prefix) + 15, "%s-%u.ts", output_prefix, ++output_index); if (avio_open(&oc->pb, output_filename, AVIO_FLAG_WRITE) < 0) { fprintf(stderr, "Could not open ‘%s‘\n", output_filename); break; } // close when we find the ‘kill‘ file if (kill_file) { FILE* fp = fopen("kill", "rb"); if (fp) { fprintf(stderr, "user abort: found kill file\n"); fclose(fp); remove("kill"); decode_done = 1; removeAllPackets(streamLace); } } prev_segment_time = segment_time; } ret = av_interleaved_write_frame(oc, &packet); if (ret < 0) { fprintf(stderr, "Warning: Could not write frame of stream\n"); } else if (ret > 0) { fprintf(stderr, "End of stream requested\n"); av_free_packet(&packet); break; } av_free_packet(&packet); } while (!decode_done || countPackets(streamLace) > 0);
2, 把下载下来的源码直接在vs中编译生成exe即可, 如我生成的exe为m3u8.exe:
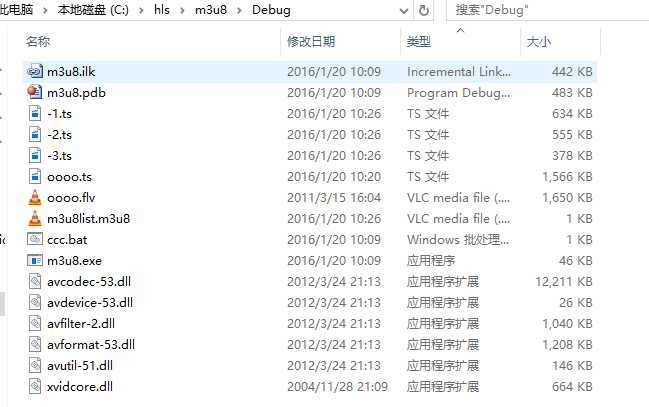
图2
3, 通过命令行进入该目录,并在命令行中输入: m3u8.exe -d 10 -x m3u8list.m3u8 即可生成.m3u8文件和ts分片文件,如图2目录文件的m3u8list.m3u8 和-1.ts、-2.ts和-3.ts文件。
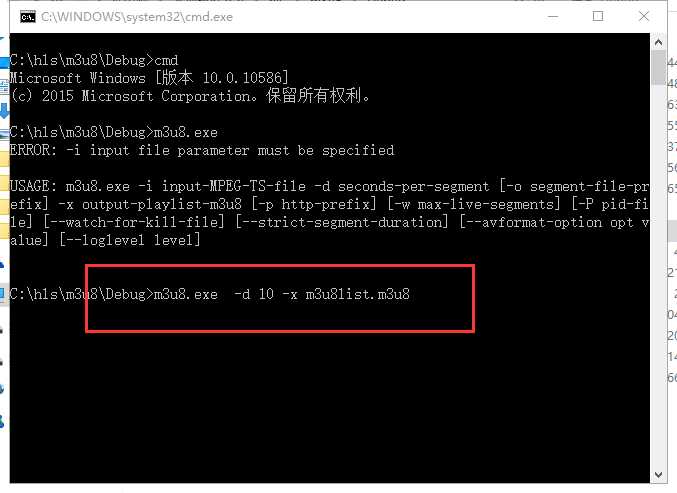
图3
4, 如以图2的目录列表,直接用VLC播放器就可以播放m3u8list.m3u8文件, 用写字板查看m3u8文件内容为:
#EXTM3U
#EXT-X-TARGETDURATION:10
#EXTINF:10,
-1.ts
#EXTINF:10,
-2.ts
#EXTINF:9,
-3.ts
#EXT-X-ENDLIST
好了,大功告成! 我们可以直接播放m3u8list.m3u8 和-1.ts、-2.ts、-3.ts文件 , 也可以直接用http协议传输这些文件,就成了hls协议了
HLS(HTTP Live Streaming)协议之m3u8文件生成方式
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/qazwsxwtc/p/5144604.html