标签:
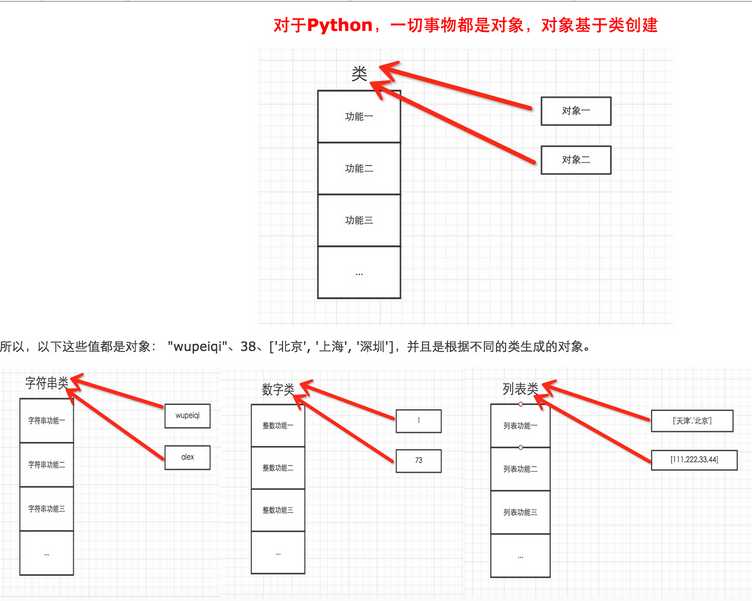
注:查看对象相关成员 var,type,dir
一、整数
如: 18、73、84
每一个整数都具备如下功能

1 bit_length(self): 2 """ 返回表示该数字的时占用的二进制最少位数 """ 3 a = 18 4 print(bin(a)) 5 print(a.bit_length()) 6 0b10010 7 5 8 最少占用5位二进制数 9 可以通过 bin(a) 查看二进制 10 11 例: 12 arg = 18 13 print(arg.bit_length()) 14 print(bin(arg)) 15 输出; 16 5 17 0b10010 18 0b 表示二进制 19 20

1 conjugate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 2 """ 返回该复数的共轭复数 """ 3 pass 4

1 __abs__(self): 2 """ 返回绝对值 """ 3 """ x.__abs__() <==> abs(x) """ 4 pass 5 a = -18 6 print(a.__abs__()) 7 打印:18 8 python 会把常用的功能放在内置函数里 9 也可以通过abs(-19)来调用__abs__()来拿到绝对值

1 __add__(self, y): 2 """ x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """ 3 pass 4 两个值相加 5 a = -18 6 print(a.__add__(100)) 7 打印:82

1 __and__(self, y): 2 """ x.__and__(y) <==> x&y """ 3 pass 4 与运算 5 1 且 2 6

1 __cmp__(self, y): 2 """ 比较两个数大小 """ 3 """ x.__cmp__(y) <==> cmp(x,y) """ 4 pass 5 6 在 Python3 中 已经没有了

1 def __bool__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 2 """ self != 0 """ 3 pass 4 布尔值的转换

1 def __divmod__(self, y): 2 """ 相除,得到商和余数组成的元组 """ 3 """ x.__divmod__(y) <==> divmod(x, y) """ 4 pass 5 6 a = 18 7 print(a.__divmod__(10)) 8 9 (1, 8) 10 -------------------- 11 例如: 12 all_item = 95 13 pager = 10 14 resual = all_item.__divmod__(10) 15 print(resual) 16 输出: 17 (9, 5) 18 ------------------------------ 19 a = 18 20 b = a.__divmod__(10) 21 if b[1] >0: 22 print("da le ") 23 else: 24 print("xiaole") 25 print(b[0])

1 _eq__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 2 """ Return self==value. """ 3 pass 4 #两个 字符串做对比如果相等 输出 True 否则 输出 Fales 5 age = 1 6 agr = 2 7 ww = age.__eq__(1) 8 print(ww) 9 10 True 11 -------------------------- 12 age = 1 13 agr = 2 14 ww = age.__eq__(2) 15 print(ww) 16 17 False

1 浮点型 把一个数字转换成浮点型 2 age = 1 3 #执行了一个age.__float__() 是吧age 转换成浮点型可以通过print 类型来查看 4 eee = age.__float__() 5 print(type(age)) 6 print(type(eee)) 7 8 <class ‘int‘> 9 <class ‘float‘>

1 __floordiv__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 2 """ Return self//value. """ 3 pass 4 5 地板除 6 7 age = 5 8 #表示打印age 地板出 6 得出的结果是 0 9 print(age.__floordiv__(6)) 10 #也可以用 print(a//6) 11 12 0

1 def __ge__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 2 """ Return self>=value. """ 3 pass 4 #如果age = 18 那么 age.__ge__(99),self(表示age,18)>=value(value表示 传进来的99) 5 #如果age 大于等于等于 17 则 显示True,如果age小于99则显示Fale 6 7 age = 18 8 9 ww = age.__ge__(99) 10 print(ww) 11 输出:Fasle 12 ------------------------- 13 age = 18 14 15 ww = age.__ge__(17) 16 print(ww) 17 输出:True

1 def __gt__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 2 """ Return self>value. """ 3 pass 4 #如果age = 18 那么 age.__gt__(99),self(表示age,18)>value(value表示 传进来的99) 5 #如果age 大于等于 17 则 显示True,如果age小于99则显示Fale 6 agr = 18 7 8 ww = agr.__gt__(17) 9 print(ww) 10 输出: True 11 ----------------------------- 12 agr = 18 13 14 ww = agr.__gt__(99) 15 print(ww) 16 输出: False

1 def __hash__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 2 """ Return hash(self). """ 3 pass 4 #哈希值 系统创建对象的时候自动生成的哈希值

1 def __index__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 2 """ Return self converted to an integer, if self is suitable for use as an index into a list. """ 3 pass 4 #索引

1 def __init__(self, x, base=10): # known special case of int.__init__ 2 """ 3 int(x=0) -> integer 4 int(x, base=10) -> integer 5 6 Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments 7 are given. If x is a number, return x.__int__(). For floating point 8 numbers, this truncates towards zero. 9 10 If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string, 11 bytes, or bytearray instance representing an integer literal in the 12 given base. The literal can be preceded by ‘+‘ or ‘-‘ and be surrounded 13 by whitespace. The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. 14 Base 0 means to interpret the base from the string as an integer literal. 15 >>> int(‘0b100‘, base=0) 16 4 17 # (copied from class doc) 18 """ 19 pass 20 # 一个类里面有__init__叫做构造方法, 21 如果; 22 age = 19 23 age = int(19) 24 #在python 解释器里 执行int类的时候回自动触发__init__ 方法

1 def __invert__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 2 """ ~self """ 3 pass 4 #位运算 5 def __le__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 6 """ Return self<=value. """ 7 pass 8 9 def __lshift__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 10 """ Return self<<value. """ 11 pass 12 13 def __lt__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 14 """ Return self<value. """ 15 pass 16 17 def __mod__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 18 """ Return self%value. """ 19 pass 20 21 def __mul__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 22 """ Return self*value. """ 23 pass 24 25 def __neg__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 26 """ -self """ 27 pass 28 29 @staticmethod # known case of __new__ 30 def __new__(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 31 """ Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature. """ 32 pass 33 34 def __ne__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 35 """ Return self!=value. """ 36 pass

1 #或 or 相等的 2 def __or__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 3 """ Return self|value. """ 4 pass

1 def __pos__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 2 """ +self """ 3 pass 4

1 #幂 2 def __pow__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 3 """ Return pow(self, value, mod). """ 4 pass 5 例; 6 agr = 2 7 print(agr.__pow__(8)) 8 #等同于 2**8
上面举例写了一些,详细地全面地请看下面

1 class int(object): 2 """ 3 int(x=0) -> int or long 4 int(x, base=10) -> int or long 5 6 Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments 7 are given. If x is floating point, the conversion truncates towards zero. 8 If x is outside the integer range, the function returns a long instead. 9 10 If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string or 11 Unicode object representing an integer literal in the given base. The 12 literal can be preceded by ‘+‘ or ‘-‘ and be surrounded by whitespace. 13 The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. Base 0 means to 14 interpret the base from the string as an integer literal. 15 >>> int(‘0b100‘, base=0) 16 """ 17 def bit_length(self): 18 """ 返回表示该数字的时占用的最少位数 """ 19 """ 20 int.bit_length() -> int 21 22 Number of bits necessary to represent self in binary. 23 >>> bin(37) 24 ‘0b100101‘ 25 >>> (37).bit_length() 26 """ 27 return 0 28 29 def conjugate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 30 """ 返回该复数的共轭复数 """ 31 """ Returns self, the complex conjugate of any int. """ 32 pass 33 34 def __abs__(self): 35 """ 返回绝对值 """ 36 """ x.__abs__() <==> abs(x) """ 37 pass 38 39 def __add__(self, y): 40 """ x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """ 41 pass 42 43 def __and__(self, y): 44 """ x.__and__(y) <==> x&y """ 45 pass 46 47 def __cmp__(self, y): 48 """ 比较两个数大小 """ 49 """ x.__cmp__(y) <==> cmp(x,y) """ 50 pass 51 52 def __coerce__(self, y): 53 """ 强制生成一个元组 """ 54 """ x.__coerce__(y) <==> coerce(x, y) """ 55 pass 56 57 def __divmod__(self, y): 58 """ 相除,得到商和余数组成的元组 """ 59 """ x.__divmod__(y) <==> divmod(x, y) """ 60 pass 61 62 def __div__(self, y): 63 """ x.__div__(y) <==> x/y """ 64 pass 65 66 def __float__(self): 67 """ 转换为浮点类型 """ 68 """ x.__float__() <==> float(x) """ 69 pass 70 71 def __floordiv__(self, y): 72 """ x.__floordiv__(y) <==> x//y """ 73 pass 74 75 def __format__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 76 pass 77 78 def __getattribute__(self, name): 79 """ x.__getattribute__(‘name‘) <==> x.name """ 80 pass 81 82 def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 83 """ 内部调用 __new__方法或创建对象时传入参数使用 """ 84 pass 85 86 def __hash__(self): 87 """如果对象object为哈希表类型,返回对象object的哈希值。哈希值为整数。在字典查找中,哈希值用于快速比较字典的键。两个数值如果相等,则哈希值也相等。""" 88 """ x.__hash__() <==> hash(x) """ 89 pass 90 91 def __hex__(self): 92 """ 返回当前数的 十六进制 表示 """ 93 """ x.__hex__() <==> hex(x) """ 94 pass 95 96 def __index__(self): 97 """ 用于切片,数字无意义 """ 98 """ x[y:z] <==> x[y.__index__():z.__index__()] """ 99 pass 100 101 def __init__(self, x, base=10): # known special case of int.__init__ 102 """ 构造方法,执行 x = 123 或 x = int(10) 时,自动调用,暂时忽略 """ 103 """ 104 int(x=0) -> int or long 105 int(x, base=10) -> int or long 106 107 Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments 108 are given. If x is floating point, the conversion truncates towards zero. 109 If x is outside the integer range, the function returns a long instead. 110 111 If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string or 112 Unicode object representing an integer literal in the given base. The 113 literal can be preceded by ‘+‘ or ‘-‘ and be surrounded by whitespace. 114 The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. Base 0 means to 115 interpret the base from the string as an integer literal. 116 >>> int(‘0b100‘, base=0) 117 # (copied from class doc) 118 """ 119 pass 120 121 def __int__(self): 122 """ 转换为整数 """ 123 """ x.__int__() <==> int(x) """ 124 pass 125 126 def __invert__(self): 127 """ x.__invert__() <==> ~x """ 128 pass 129 130 def __long__(self): 131 """ 转换为长整数 """ 132 """ x.__long__() <==> long(x) """ 133 pass 134 135 def __lshift__(self, y): 136 """ x.__lshift__(y) <==> x<<y """ 137 pass 138 139 def __mod__(self, y): 140 """ x.__mod__(y) <==> x%y """ 141 pass 142 143 def __mul__(self, y): 144 """ x.__mul__(y) <==> x*y """ 145 pass 146 147 def __neg__(self): 148 """ x.__neg__() <==> -x """ 149 pass 150 151 @staticmethod # known case of __new__ 152 def __new__(S, *more): 153 """ T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """ 154 pass 155 156 def __nonzero__(self): 157 """ x.__nonzero__() <==> x != 0 """ 158 pass 159 160 def __oct__(self): 161 """ 返回改值的 八进制 表示 """ 162 """ x.__oct__() <==> oct(x) """ 163 pass 164 165 def __or__(self, y): 166 """ x.__or__(y) <==> x|y """ 167 pass 168 169 def __pos__(self): 170 """ x.__pos__() <==> +x """ 171 pass 172 173 def __pow__(self, y, z=None): 174 """ 幂,次方 """ 175 """ x.__pow__(y[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """ 176 pass 177 178 def __radd__(self, y): 179 """ x.__radd__(y) <==> y+x """ 180 pass 181 182 def __rand__(self, y): 183 """ x.__rand__(y) <==> y&x """ 184 pass 185 186 def __rdivmod__(self, y): 187 """ x.__rdivmod__(y) <==> divmod(y, x) """ 188 pass 189 190 def __rdiv__(self, y): 191 """ x.__rdiv__(y) <==> y/x """ 192 pass 193 194 def __repr__(self): 195 """转化为解释器可读取的形式 """ 196 """ x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """ 197 pass 198 199 def __str__(self): 200 """转换为人阅读的形式,如果没有适于人阅读的解释形式的话,则返回解释器课阅读的形式""" 201 """ x.__str__() <==> str(x) """ 202 pass 203 204 def __rfloordiv__(self, y): 205 """ x.__rfloordiv__(y) <==> y//x """ 206 pass 207 208 def __rlshift__(self, y): 209 """ x.__rlshift__(y) <==> y<<x """ 210 pass 211 212 def __rmod__(self, y): 213 """ x.__rmod__(y) <==> y%x """ 214 pass 215 216 def __rmul__(self, y): 217 """ x.__rmul__(y) <==> y*x """ 218 pass 219 220 def __ror__(self, y): 221 """ x.__ror__(y) <==> y|x """ 222 pass 223 224 def __rpow__(self, x, z=None): 225 """ y.__rpow__(x[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """ 226 pass 227 228 def __rrshift__(self, y): 229 """ x.__rrshift__(y) <==> y>>x """ 230 pass 231 232 def __rshift__(self, y): 233 """ x.__rshift__(y) <==> x>>y """ 234 pass 235 236 def __rsub__(self, y): 237 """ x.__rsub__(y) <==> y-x """ 238 pass 239 240 def __rtruediv__(self, y): 241 """ x.__rtruediv__(y) <==> y/x """ 242 pass 243 244 def __rxor__(self, y): 245 """ x.__rxor__(y) <==> y^x """ 246 pass 247 248 def __sub__(self, y): 249 """ x.__sub__(y) <==> x-y """ 250 pass 251 252 def __truediv__(self, y): 253 """ x.__truediv__(y) <==> x/y """ 254 pass 255 256 def __trunc__(self, *args, **kwargs): 257 """ 返回数值被截取为整形的值,在整形中无意义 """ 258 pass 259 260 def __xor__(self, y): 261 """ x.__xor__(y) <==> x^y """ 262 pass 263 264 denominator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default 265 """ 分母 = 1 """ 266 """the denominator of a rational number in lowest terms""" 267 268 imag = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default 269 """ 虚数,无意义 """ 270 """the imaginary part of a complex number""" 271 272 numerator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default 273 """ 分子 = 数字大小 """ 274 """the numerator of a rational number in lowest terms""" 275 276 real = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default 277 """ 实属,无意义 """ 278 """the real part of a complex number""" 279 280 int
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/nb-blog/p/5144616.html