标签:
JAVA从J2SE5开始提供名为annotation(注释,标注)的功能。Java的annotation,可以附加在package, class, method, field等上面,相当于给它们添加了额外的辅助信息。附加在package, class, method, field等上的Annotation,如果没有外部解析工具等对其加以解析和处理的情况,本身不会对Java的源代码或class等产生任何影响,也不会对它们的执行产生任何影响。 但借助外部工具,比如javac,EJB容器等,可以对附加在package, class, method, field的annotation进行解析,可以根据annotation而做出相应的处理,比如运行时改变对象/方法的行为。 Java标准Annotation @Deprecated 相当于Javadoc的@deprecated,被@Deprecated标注的对象class, method等被注明为不推荐使用。主要用于javac等编译工具。 @Override 注明对象method重载了父类的方法。javac等编译工具编译时会根据此Annotation判断重载方法是否正确。 @SuppressWarnings 告诉javac等编译器忽略所指定的特定的警告信息。 @Target 被定义的annotation可以附加在那些对象上。 @Retention annotation的作用期间。 Java标准Annotation的使用 @Deprecated: @Deprecated public class TestBean { … } @SuppressWarnings: @SuppressWarnings("serial ") public class TestBean implements java.io.Serializable { … } @SuppressWarnings(value = {"serial ", "unchecked "}) public String doSth() { … } @Override: @Override public String doSth() { … } Annotation的定义 定义方法: @interface Annotation名 {定义体} 定义例1: public @interface MyAnnotation {} 该例定义了一个无任何属性/方法的Annotation。 定义例2: public @interface MyAnnotation { public String value(); } 该例定义了只有一个方法为value()的Annotation。一般来说,只有一个方法的Annotation,方法名一定定义为value。 定义例3: @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.METHOD) public @interface MyAnnotation { public String value(); public String [] multiValues(); int number() default 0; } 该例定义了一个具有多方法的Annotation。并设置其中一个方法number的默认值为0。multiValues 方法定义为数组类型。Annotation定义可以用MetaAnnotation(元注释)修饰。MetaAnnotation有以下2个: @Retention @Target 我们将在以下对@Retention与@Target加以说明。 @Retention @Retention 可以设置为RetentionPolicy类型的值。 例: @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)

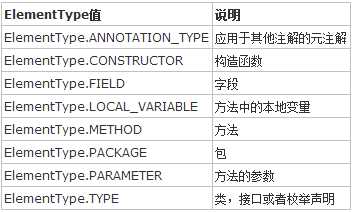
@Target @Target表明Annotation可以附加在哪种JAVA元素之上,可以设置为java.lang.annotation.ElementType数组类型的值。 使用例1: @Target(ElementType.METHOD) 使用例2: @Target(value={ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE, ElementType.METHOD}) ElementType是一个枚举类型,它具有以下定义:
自定义 Java Annotation Annotation是一种特殊的interface。所以可以在annotation里定义方法,属性;也可以让某个类从annotation继承(implements)。 下面从简单地范例开始,让我们一步步加深对annotation的了解。 无任何方法/属性Annotation范例: MyAnnotation0.java package com.test.annotation; public @interface MyAnnotation0 { } MyAnnotation0为一个无任何方法和属性的annotation。 使用MyAnnotation0: TestMyAnnotation0.java @MyAnnotation0 public class TestMyAnnotation0 { @MyAnnotation0 public void testMethod() { } } 具有一个value方法Annotation范例: MyAnnotation1.java public @interface MyAnnotation1 { /** * value method * @return value */ public String value(); } MyAnnotation1具有一个名为value的方法。 MyAnnotation1使用: TestMyAnnotation1.java @MyAnnotation1("hello ") public class TestMyAnnotation1 { @MyAnnotation1(value="world ") public void testMethod() { } } 可以通过@Annotation名(方法名1=值1, 方法名2=值2, …)的形式给annotation赋值。只有一个方法的时候,可以直接省略为:@Annotation名(值1) 的赋值形式。当方法返回一个数组时,可以用 方法名={值1, 值2, …}给其赋值。 具有一个value方法和一个属性Annotation范例: 如果必要,还可以在annotation里为其定义属性。如下: MyAnnotation2.java @interface MyAnnotation2 { public String value(); public String myProperty = "hello world "; } 其中,myProperty只能申明为public或无public修饰(无public修饰时也默认为public)为static, final属性(即使不写也默认为static, final)。 使用例: TestMyAnnotation2 class TestMyAnnotation2 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(MyAnnotation2.myProperty); } @MyAnnotation2("") public void testMethod1() { } } 上例会打印出: hello world 复杂型annotation的定义与使用 本节介绍较为复杂的annotation定义与使用。 先看代码: MyAnnotation3.java public @interface MyAnnotation3 { public String value(); public String[] multiValues(); int number() default 0; } MyAnnotation3具有一个返回String的value方法,返回String[]的multiValues 方法;还有一个返回int 的number方法。其中number方法具有默认值0。 使用例: TestMyAnnotation3.java class TestMyAnnotation3 { @MyAnnotation3(value = "call testMethod1 ", multiValues={"1 ", "2 "}, number = 1) public void testMethod1() { } @MyAnnotation3(value = "call testMethod2 ", multiValues={"1 ", "2 "}) public void testMethod2() { } } number具有默认值,所以标注时可以不为其赋值。其余方法则必须通过上面介绍的方法赋值。multiValues返回一个String[]数组,所以可以通过multiValues={"1", "2"}为其赋值。 这样说来,annotation到底能起什么作用呢? 1,编译工具或其他工具可以根据被附加在代码里的annotation信息自动生成配置文件或文档等外部文件。 比如,sun公司就提供了apt(Annotation Processing Tool) 工具,apt工具是一个可以处理annotation的命令行工具,apt提供了在编译期针对源代码级别的解析,并可以在解析时生成新的源代码和其他文件,同时还可以对生成的源代码进行编译。 2,其他程序可以在运行时动态解析将要被执行的程序里的annotation信息,并根据被附加的annotation信息来执行不同的操作。 比如,EJB3规范就比较广泛地使用了annotation特性。比如只要在POJO为class注明@Stateless注释,EJB容器便会根据此annotation把该POJO注册为无状态的Session Bean。EJB3使用了annotation大大地简化了EJB的开发和配置过程。我们会在其他文章里专门介绍EJB Annotation的原理与使用方法,这里不做详述。 本文通过一个简单地例子来说明怎么在运行期动态解析annotation。Apt工具的使用我们会在近期其他文章里对其加以介绍。 比如,我们定义了MyAnnotation3注释: MyAnnotation3.java package com.test.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.Annotation; import java.lang.annotation.Inherited; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface MyAnnotation3 { public String value(); public String[] multiValues(); int number() default 0; } 上面定义了一个名为MyAnnotation3的注释。 我们再定义一个GetMyAnnotation类,该类使用了MyAnnotation3注释: GetMyAnnotation.java: package com.test.annotation.test; import java.lang.annotation.Annotation; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import javax.ejb.EJB; import javax.naming.InitialContext; import javax.naming.NamingException; import com.test.annotation.MyAnnotation3; // 为GetMyAnnotation类附加MyAnnotation3 注释 @MyAnnotation3(value = "Class GetMyAnnotation ", multiValues = {"1 ","2 "}) public class GetMyAnnotation { // 为testField1属性附加MyAnnotation3 注释 @MyAnnotation3(value = "call testField1 ", multiValues={"1 "}, number = 1) private String testField1; // 为testMethod1方法附加MyAnnotation3 注释 @MyAnnotation3(value = "call testMethod1 ", multiValues={"1 ", "2 "}, number = 1) public void testMethod1() { } @Deprecated @MyAnnotation3(value = "call testMethod2 ", multiValues={"3 ", "4 ", "5 "}) public void testMethod2() { } } 上面的例子GetMyAnnotation非常简单,里面没有任何功能,但是分别为类(class),属性(field),方法(method)申明(附加)了MyAnnotation3 注释。 下面我们用程序TestMyAnnotation3对GetMyAnnotation里MyAnnotation3注释进行解析。 运行时解析annotation TestMyAnnotation3.java public class TestMyAnnotation3 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("--Class Annotations-- "); if (GetMyAnnotation.class.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation3.class )) { System.out.println("[GetMyAnnotation].annotation: "); MyAnnotation3 classAnnotation = GetMyAnnotation.class.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation3.class ); printMyAnnotation3(classAnnotation); } System.out.println("--Fields Annotations-- "); Field [] fields = GetMyAnnotation.class.getDeclaredFields(); for (Field field : fields) { if (field.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation3.class )) { System.out.println("[GetMyAnnotation. " + field.getName() + "].annotation: "); MyAnnotation3 fieldAnnotation = field.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation3.class ); printMyAnnotation3(fieldAnnotation); } } System.out.println("--Methods Annotations-- "); Method[] methods = GetMyAnnotation.class.getDeclaredMethods(); for (Method method : methods) { System.out.println("[GetMyAnnotation. " + method.getName() + "].annotation: "); if (method.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation3.class )) { MyAnnotation3 methodAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation3.class ); printMyAnnotation3(methodAnnotation); } } } private static void printMyAnnotation3(MyAnnotation3 annotation3) { if (annotation3 == null ) { return; } System.out.println("{value= " + annotation3.value()); String multiValues = ""; for (String value: annotation3.multiValues()) { multiValues += ", " + value; } System.out.println("multiValues= " + multiValues); System.out.println("number= " + annotation3.number() + "} "); } } 输出: --Class Annotations-- [GetMyAnnotation].annotation: {value=Class GetMyAnnotation multiValues=,1,2 number=0} --Fields Annotations-- [GetMyAnnotation.testField1].annotation: {value=call testField1 multiValues=,1 number=1} --Methods Annotations-- [GetMyAnnotation.testMethod1].annotation: {value=call testMethod1 multiValues=,1,2 number=1} [GetMyAnnotation.testMethod2].annotation: {value=call testMethod2 multiValues=,3,4,5 number=0} JDK1.5以后的版本提供的跟annotation有关的接口: interface java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement { boolean isAnnotationPresent(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass); <T extends Annotation> T getAnnotation(Class<T> annotationClass); Annotation[] getAnnotations(); Annotation[] getDeclaredAnnotations(); } 该接口主要用来取得附加在类(class),构造方法(constructor),属性(field),方法(method),包(package)上的annotation信息。 JDK1.5与此有关的几个类都实现了AnnotatedElement接口: java.lang.reflect.AccessibleObject, java.lang.reflect.Class, java.lang.reflect.Constructor, java.lang.reflect.Field, java.lang.reflect.Method, java.lang.reflect.Package 所以可以利用反射(reflection)功能在程序里动态解析附加的annotation信息。 总结: 本文通过举例简单地说明了怎么动态解析annotation,大家可以举一反三,利用Java的annotation特性,完成更复杂功能等。
http://www.cnblogs.com/ansen/articles/2100335.html
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/leijiangtao/p/5157542.html