标签:
本篇主要通过分析Tony Parisi的sim.js库(原版代码托管于:https://github.com/tparisi/WebGLBook/tree/master/sim),总结基础Web3D框架的编写方法。在上一篇的基础上,要求读者具有简短英文阅读或者查字典的能力。
限于水平和时间,本文难免出现错误与遗漏,您在阅读过程中如果遇到错误或者疑问请在评论区中指出,我将尽快回复。
为提高JavaScript编程效率,建议使用WebStorm工具进行网页程序编写,WebStorm官网:http://www.jetbrains.com/webstorm/。
上一篇中,我们把程序的所有文件放在同一个目录下,这种文件组织方式适用于简单的功能测试,但当文件数量更多时则会变得混乱不堪,我们在编写一般规模的Web3D程序时可参考下图进行文件组织:
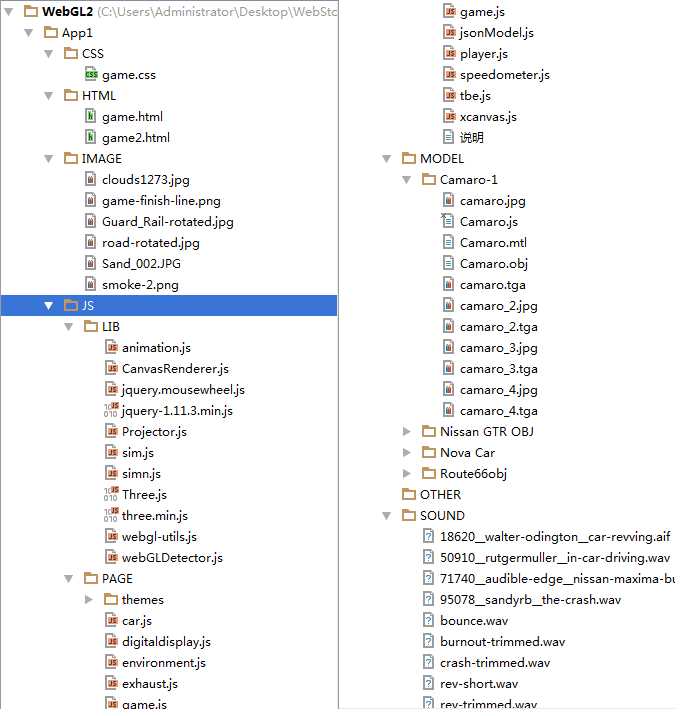
该组织方式把JavaScript文件分为LIB和PAGE两部分,LIB保存一般不做修改的库文件,PAGE保存为特定页面编写的js文件,如果页面js较多可在PAGE中再分离出子文件夹。
MODEL下的每个文件夹都是一个JSON类型的模型,可以看到其中有保存纹理信息的jpg文件和保存顶点数组、法线向量、纹理坐标的文本文件。
上一篇的代码中,我们把所有需要多次调用的对象设为了全局变量和全局函数,当代码量增多时这种“全局管理”方式将面临巨大的挑战,随然我们可以用规范的变量命名或者变量数组来尽可能避免变量名重复,但全局管理方式仍缺少对变量间关系的描述方法,这时使用“面向对象”的变量管理方法似乎是唯一的选择。
下面进入正题:
1 //代码截取自https://github.com/tparisi/WebGLBook/tree/master/sim,在那里Tony Parisi的Sim库依照旧版Three.js库编写,为了使用新版本Three.js库我对Sim.js进行了部分修改,修改点附近以“@@”标记 2 // Sim.js - A Simple Simulator for WebGL (based on Three.js) 3 //Sim.js是一个基于Three.js的WebGL简单框架 4 Sim = {};//Sim是一个自包含对象,库中的其他变量和函数都是这个自包含对象的属性,可以在库的外部通过“Sim.”的方式调用库内的方法。 5 6 // Sim.Publisher - base class for event publishers 7 //Publish/Subscribe消息通信,用来优化多个对象之间的消息传递,事实上Tony Parisi的WebGL著作里并没有真正使用这种消息传递方法,关于Publish/Subscribe的简单例程可以参考:http://www.mamicode.com/info-detail-502782.html 8 Sim.Publisher = function() { 9 this.messageTypes = {}; 10 } 11 12 Sim.Publisher.prototype.subscribe = function(message, subscriber, callback) { 13 var subscribers = this.messageTypes[message]; 14 if (subscribers) 15 { 16 if (this.findSubscriber(subscribers, subscriber) != -1) 17 { 18 return; 19 } 20 } 21 else 22 { 23 subscribers = []; 24 this.messageTypes[message] = subscribers; 25 } 26 27 subscribers.push({ subscriber : subscriber, callback : callback }); 28 } 29 30 Sim.Publisher.prototype.unsubscribe = function(message, subscriber, callback) { 31 if (subscriber) 32 { 33 var subscribers = this.messageTypes[message]; 34 35 if (subscribers) 36 { 37 var i = this.findSubscriber(subscribers, subscriber, callback); 38 if (i != -1) 39 { 40 this.messageTypes[message].splice(i, 1); 41 } 42 } 43 } 44 else 45 { 46 delete this.messageTypes[message]; 47 } 48 } 49 50 Sim.Publisher.prototype.publish = function(message) { 51 var subscribers = this.messageTypes[message]; 52 53 if (subscribers) 54 { 55 for (var i = 0; i < subscribers.length; i++) 56 { 57 var args = []; 58 for (var j = 0; j < arguments.length - 1; j++) 59 { 60 args.push(arguments[j + 1]); 61 } 62 subscribers[i].callback.apply(subscribers[i].subscriber, args); 63 } 64 } 65 } 66 67 Sim.Publisher.prototype.findSubscriber = function (subscribers, subscriber) { 68 for (var i = 0; i < subscribers.length; i++) 69 { 70 if (subscribers[i] == subscriber) 71 { 72 return i; 73 } 74 } 75 76 return -1; 77 } 78 79 // Sim.App - application class (singleton) 80 //Sim.App属性对“绘制环境”的封装(这里认为一个canvas里只有一个绘制环境) 81 Sim.App = function() 82 { 83 Sim.Publisher.call(this); 84 //call表示this(Sim.App)继承自Sim.Publisher,意指在Sim.App的上下文环境使用Sim.Publisher的“构造方法”,也就是使用Sim.App与Sim.Publisher重叠的属性(这里没有)执行了this.messageTypes = {};语句,为App对象建立了消息一个队列。 85 86 this.renderer = null; 87 this.scene = null; 88 this.camera = null; 89 this.objects = []; 90 //可见App对象包含了canvas的上下文、与显卡的交互接口、相机设置、物体数组 91 } 92 93 Sim.App.prototype = new Sim.Publisher; 94 //prototype表示Sim.App扩展自new Sim.Publisher,当调用Sim.App中的某个未定义的方法时,编译器会尝试到prototype中去寻找,如App.subscribe 95 //prototype.init表示使用init方法对Sim.App进行原型拓展,这样所有的var myApp=new Sim.App都会自动具有init方法(找不到时去prototype中找);这与"Sim.App.init"是不同的,如果后着的init不在App的“构造方法”中定义,myApp是不会具有init方法的。 96 Sim.App.prototype.init = function(param)//绘图环境初始化 97 { 98 param = param || {}; 99 var container = param.container; 100 var canvas = param.canvas; 101 102 // Create the Three.js renderer, add it to our div 103 //@@这一段是我自己改的,加入了没有显卡时的软件渲染选择,可惜CanvasRenderer只支持部分的Three.js功能,并且没有找到去除图元边线的方法。 104 105 function webglAvailable()//是否可用webgl 106 { 107 try{ 108 var canvas=document.createElement("canvas"); 109 return !!(window.WebGLRenderingContext 110 &&(canvas.getContext("webgl")||canvas.getContext("experimental-webgl")) 111 ); 112 }catch(e){ 113 return false; 114 } 115 } 116 if(webglAvailable()){ 117 var renderer=new THREE.WebGLRenderer({ antialias: true, canvas: canvas }); 118 }else{ 119 var renderer=new THREE.CanvasRenderer({ antialias: true, canvas: canvas });//对于支持html5但不支持webgl的情况,使用更慢一些的2Dcanvas来软件实现webgl的效果 120 } 121 //var renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer( { antialias: true, canvas: canvas } ); 122 //@@ 123 124 renderer.setClearColor( 0xffffff );//@@旧版本中这个是默认的 125 renderer.setSize(container.offsetWidth, container.offsetHeight); 126 container.appendChild( renderer.domElement ); 127 container.onfocus=function(){ 128 renderer.domElement.focus();//@@保持焦点!! 129 } 130 //在部分浏览器中canvas不具备保持焦点的能力,点击canvas时焦点会被设置在外面的container上,影响交互效果 131 132 // Create a new Three.js scene 133 var scene = new THREE.Scene(); 134 scene.add( new THREE.AmbientLight( 0x505050 ) ); 135 scene.data = this; 136 137 // Put in a camera at a good default location 138 camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera( 45, container.offsetWidth / container.offsetHeight, 1, 10000 ); 139 camera.position.set( 0, 0, 3.3333 ); 140 141 scene.add(camera); 142 143 // Create a root object to contain all other scene objects 144 //建立了一个“根物体”,来存放场景中的其他物体,也就是根物体移动时所有其他物体会和它一同移动 145 var root = new THREE.Object3D(); 146 scene.add(root); 147 148 // Create a projector to handle picking 149 //建立一个“投影器”来处理三维空间中的点选,@@新版本中去掉了这个属性,这里的定义是多余的 150 var projector = new THREE.Projector(); 151 152 // Save away a few things 153 //把上面的属性设为App对象的“公有”属性,var则是App对象的“私有”属性 154 this.container = container; 155 this.renderer = renderer; 156 this.scene = scene; 157 this.camera = camera; 158 this.projector = projector; 159 this.root = root; 160 161 // Set up event handlers 162 //启动事件响应功能 163 this.initMouse(); 164 this.initKeyboard(); 165 this.addDomHandlers(); 166 } 167 168 //Core run loop 169 //核心循环 170 Sim.App.prototype.run = function() 171 { 172 this.update(); 173 this.renderer.render( this.scene, this.camera ); 174 var that = this;//之所以使用that是为了保存此时的this状态,requestAnimationFrame会在“浏览器认为合适”的时候重调,而那时的“this”可能已经发生变化了。 175 //requestAnimationFrame(function() { that.run(); }); 176 requestAnimFrame(function() { that.run(); });//@@换用了另一个帧动画库 177 } 178 179 // Update method - called once per tick 180 //场景更新方法,这里的代码逻辑运行在浏览器端,是CPU资源的主要消耗者 181 Sim.App.prototype.update = function() 182 { 183 var i, len; 184 len = this.objects.length; 185 for (i = 0; i < len; i++) 186 {//将App的update转化为其所包含的objects的update 187 this.objects[i].update(); 188 } 189 } 190 191 // Add/remove objects 192 //在场景中添加或删除一个物体 193 //添加 194 Sim.App.prototype.addObject = function(obj) 195 { 196 this.objects.push(obj);//将物体对象添加到前面建立的物体数组里 197 198 // If this is a renderable object, add it to the root scene 199 //Three.js对于场景中object3D类型的对象提供了“parent/children ”式的关联链,Sim.js封装了这一关联 200 if (obj.object3D) 201 { 202 this.root.add(obj.object3D); 203 } 204 } 205 //删除 206 Sim.App.prototype.removeObject = function(obj) 207 { 208 var index = this.objects.indexOf(obj); 209 if (index != -1) 210 { 211 this.objects.splice(index, 1); 212 // If this is a renderable object, remove it from the root scene 213 214 if (obj.object3D) 215 { 216 this.root.remove(obj.object3D); 217 } 218 } 219 } 220 221 // Event handling 222 //事件处理 223 //初始化鼠标响应 224 Sim.App.prototype.initMouse = function() 225 { 226 var dom = this.renderer.domElement;//取得canvas 227 228 //添加监听 229 var that = this; 230 dom.addEventListener( ‘mousemove‘, 231 function(e) { that.onDocumentMouseMove(e); }, false ); 232 dom.addEventListener( ‘mousedown‘, 233 function(e) { that.onDocumentMouseDown(e); }, false ); 234 dom.addEventListener( ‘mouseup‘, 235 function(e) { that.onDocumentMouseUp(e); }, false ); 236 237 //中键滚动 238 $(dom).mousewheel( 239 function(e, delta) { 240 that.onDocumentMouseScroll(e, delta); 241 } 242 ); 243 244 //鼠标悬停的物体 245 this.overObject = null; 246 //被点击到的物体 247 this.clickedObject = null; 248 } 249 //初始化键盘响应 250 Sim.App.prototype.initKeyboard = function() 251 { 252 var dom = this.renderer.domElement; 253 254 var that = this; 255 dom.addEventListener( ‘keydown‘, 256 function(e) { that.onKeyDown(e); }, false ); 257 dom.addEventListener( ‘keyup‘, 258 function(e) { that.onKeyUp(e); }, false ); 259 dom.addEventListener( ‘keypress‘, 260 function(e) { that.onKeyPress(e); }, false ); 261 262 // so it can take focus 263 //这样设置之后canvas可以通过Tab键获得焦点,@@但这个设置并不完美,仍需要修改 264 dom.setAttribute("tabindex", 1); 265 dom.style.outline=‘none‘; 266 dom.focus(); 267 } 268 269 Sim.App.prototype.addDomHandlers = function() 270 { 271 var that = this; 272 //监听浏览器窗口大小的变化 273 window.addEventListener( ‘resize‘, function(event) { that.onWindowResize(event); }, false ); 274 } 275 276 //如果监听到鼠标移动 277 Sim.App.prototype.onDocumentMouseMove = function(event) 278 { 279 event.preventDefault();//阻止浏览器的默认响应 280 281 if (this.clickedObject && this.clickedObject.handleMouseMove) 282 {//如果已经有选中的物体,并且被选中的物体具有自己的handleMouseMove方法 283 var hitpoint = null, hitnormal = null;//三维空间中的“点击点”和“点击法线”(鼠标在3D物体上的点击方向)设为空 284 var intersected = this.objectFromMouse(event.pageX, event.pageY); 285 //在三维空间中通过浏览器中的二维坐标,找到鼠标所在的物体,稍后详细分析该方法 286 if (intersected.object == this.clickedObject) 287 {//如果鼠标所在的物体确实是被选中的物体, 288 hitpoint = intersected.point; 289 hitnormal = intersected.normal; 290 } 291 this.clickedObject.handleMouseMove(event.pageX, event.pageY, hitpoint, hitnormal); 292 //执行这个被选中的物体的鼠标移动方法,比如拖拽变形之类 293 } 294 else 295 {//如果没有被选中的物体 296 var handled = false; 297 298 var oldObj = this.overObject;//暂存旧的“悬停物体” 299 var intersected = this.objectFromMouse(event.pageX, event.pageY); 300 this.overObject = intersected.object;//将悬停物体设为鼠标所在的物体 301 302 if (this.overObject != oldObj)//如果这是一个新物体,也就是说鼠标从一个物体上移到另一物体上 303 { 304 if (oldObj) 305 {//如果存在旧的物体,则要触发旧物体的“鼠标移出”事件 306 this.container.style.cursor = ‘auto‘;//取巧用CSS来处理光标变化,是2D网页和3Dcanvas的结合运用 307 308 if (oldObj.handleMouseOut) 309 { 310 oldObj.handleMouseOut(event.pageX, event.pageY); 311 } 312 } 313 314 if (this.overObject) 315 { 316 if (this.overObject.overCursor) 317 { 318 this.container.style.cursor = this.overObject.overCursor;//光标设置 319 } 320 321 if (this.overObject.handleMouseOver) 322 { 323 this.overObject.handleMouseOver(event.pageX, event.pageY); 324 } 325 } 326 327 handled = true;//表示物体的handleMouseOver执行完毕 328 } 329 330 if (!handled && this.handleMouseMove) 331 { 332 this.handleMouseMove(event.pageX, event.pageY); 333 //如果物体没有执行handleMouseOver,且环境(App)能够响应handleMouseOver,则执行环境的鼠标移动响应,在应用中可体现为移动视角之类 334 } 335 } 336 } 337 //鼠标按下 338 Sim.App.prototype.onDocumentMouseDown = function(event) 339 { 340 event.preventDefault(); 341 342 var handled = false; 343 344 var intersected = this.objectFromMouse(event.pageX, event.pageY); 345 if (intersected.object) 346 { 347 if (intersected.object.handleMouseDown) 348 { 349 intersected.object.handleMouseDown(event.pageX, event.pageY, intersected.point, intersected.normal); 350 this.clickedObject = intersected.object; 351 handled = true; 352 } 353 } 354 355 if (!handled && this.handleMouseDown) 356 { 357 this.handleMouseDown(event.pageX, event.pageY); 358 } 359 } 360 361 Sim.App.prototype.onDocumentMouseUp = function(event) 362 { 363 event.preventDefault(); 364 365 var handled = false; 366 367 var intersected = this.objectFromMouse(event.pageX, event.pageY); 368 if (intersected.object) 369 { 370 if (intersected.object.handleMouseUp) 371 { 372 intersected.object.handleMouseUp(event.pageX, event.pageY, intersected.point, intersected.normal); 373 handled = true; 374 } 375 } 376 377 if (!handled && this.handleMouseUp) 378 { 379 this.handleMouseUp(event.pageX, event.pageY); 380 } 381 382 this.clickedObject = null; 383 } 384 385 Sim.App.prototype.onDocumentMouseScroll = function(event, delta) 386 { 387 event.preventDefault(); 388 389 if (this.handleMouseScroll) 390 { 391 this.handleMouseScroll(delta); 392 } 393 } 394 395 Sim.App.prototype.objectFromMouse = function(pagex, pagey) 396 { 397 // Translate page coords to element coords 398 //把浏览器页面中的位置转化为canvas中的坐标 399 var offset = $(this.renderer.domElement).offset(); 400 var eltx = pagex - offset.left; 401 var elty = pagey - offset.top; 402 403 // Translate client coords into viewport x,y 404 //把canvas中的坐标转化为3D场景中的坐标 405 var vpx = ( eltx / this.container.offsetWidth ) * 2 - 1; 406 var vpy = - ( elty / this.container.offsetHeight ) * 2 + 1; 407 408 var vector = new THREE.Vector3( vpx, vpy, 0.5 );//补充一个z轴坐标,形成三维空间中靠原点外侧的一个点(在Three.js中“点”分为Points和Vector两种,前者具有颜色、大小、材质是真正可以被显示出来的物体,后着是数学意义上的点或者向量) 409 410 //this.projector.unprojectVector( vector, this.camera ); 411 vector.unproject(this.camera);//@@新版本中去掉投影矩阵影响的方法,不要忘记3D场景中看到的东西都是经过投影矩阵变形过的,所以要先把“看到的位置”转化为“实际的位置”再进行位置计算 412 413 //@@这里是Sim.js中版本差异最大的地方 414 //在三维空间中取得物体的原理:从相机到“鼠标所在的点”画一条射线,通过Three.js封装的方法取得这条射线穿过的所有物体,第一个穿过的物体被认为是“鼠标所在的物体” 415 416 //var ray = new THREE.Ray( this.camera.position, vector.subSelf( this.camera.position ).normalize() ); 417 //var intersects = ray.intersectScene( this.scene ); 418 var raycaster = new THREE.Raycaster(this.camera.position,vector.subVectors(vector,this.camera.position).normalize()); 419 //@@Raycaster是新版Three.js专门为“穿过检测”定义的一种对象,与Ray分别开来,第一个参数是射线的端点,第二个参数是一个标准化(长度为一)的向量 420 var intersects = raycaster.intersectObjects(this.scene.children,true); 421 //true表示考虑物体的子物体,这里必须加上,被“穿过到”的物体被存入了一个数组 422 423 if ( intersects.length > 0 ) { 424 425 /*var i = 0; 426 while(!intersects[i].object.visible) 427 { 428 i++; 429 } 430 431 var intersected = intersects[i]; 432 var mat = new THREE.Matrix4().getInverse(intersected.object.matrixWorld); 433 var point = mat.multiplyVector3(intersected.point); 434 435 return (this.findObjectFromIntersected(intersected.object, intersected.point, intersected.face.normal)); */ 436 //@@ 437 for(var i=0;i<intersects.length;i++) 438 { 439 if(intersects[i].object.visible&&intersects[i].face) 440 {//物体可见并且”有面“(剔除了穿过线物体和点物体的情况) 441 var intersected = intersects[i]; 442 var mat = new THREE.Matrix4().getInverse(intersected.object.matrixWorld); 443 var point=intersected.point.applyMatrix4( mat );//可见intersected.point是相对坐标,加上物体所在的姿态矩阵之后变成了3D空间中的绝对坐标 444 return (this.findObjectFromIntersected(intersected.object, intersected.point, intersected.face.normal)); 445 } 446 } 447 return { object : null, point : null, normal : null };//没有找到符合条件的物体 448 } 449 else 450 { 451 return { object : null, point : null, normal : null }; 452 } 453 } 454 455 Sim.App.prototype.findObjectFromIntersected = function(object, point, normal) 456 {//回溯子物体的parent/children链,找到距它最近的具有data属性的父物体,这样的物体是使用Sim.Object定义的。这种回溯保持了复杂物体的整体性:拉一个人的手使得整个人移动,而非手脱离了人自己移动。 457 458 if (object.data) 459 { 460 return { object: object.data, point: point, normal: normal }; 461 } 462 else if (object.parent) 463 { 464 return this.findObjectFromIntersected(object.parent, point, normal); 465 } 466 else 467 { 468 return { object : null, point : null, normal : null }; 469 } 470 } 471 472 //键盘按键被按下 473 Sim.App.prototype.onKeyDown = function(event) 474 { 475 // N.B.: Chrome doesn‘t deliver keyPress if we don‘t bubble... keep an eye on this 476 //作者说的是浏览器兼容性的问题,是否可用JQuery弥补? 477 event.preventDefault(); 478 479 if (this.handleKeyDown) 480 { 481 this.handleKeyDown(event.keyCode, event.charCode); 482 } 483 } 484 485 Sim.App.prototype.onKeyUp = function(event) 486 { 487 // N.B.: Chrome doesn‘t deliver keyPress if we don‘t bubble... keep an eye on this 488 event.preventDefault(); 489 490 if (this.handleKeyUp) 491 { 492 this.handleKeyUp(event.keyCode, event.charCode); 493 } 494 } 495 496 Sim.App.prototype.onKeyPress = function(event) 497 { 498 // N.B.: Chrome doesn‘t deliver keyPress if we don‘t bubble... keep an eye on this 499 event.preventDefault(); 500 501 if (this.handleKeyPress) 502 { 503 this.handleKeyPress(event.keyCode, event.charCode); 504 } 505 } 506 507 //浏览器窗口大小变化 508 Sim.App.prototype.onWindowResize = function(event) { 509 510 this.renderer.setSize(this.container.offsetWidth, this.container.offsetHeight); 511 512 this.camera.aspect = this.container.offsetWidth / this.container.offsetHeight;//宽高比 513 this.camera.updateProjectionMatrix();//投影矩阵 514 515 } 516 //给环境定义了一个取得焦点的方法 517 Sim.App.prototype.focus = function() 518 { 519 if (this.renderer && this.renderer.domElement) 520 { 521 this.renderer.domElement.focus(); 522 } 523 } 524 525 526 // Sim.Object - base class for all objects in our simulation 527 //物体的“基类” 528 Sim.Object = function() 529 { 530 Sim.Publisher.call(this); 531 532 this.object3D = null; 533 this.children = []; 534 } 535 536 Sim.Object.prototype = new Sim.Publisher; 537 538 Sim.Object.prototype.init = function()//物体本身没有init时,才会到“基类”里找 539 { 540 } 541 542 Sim.Object.prototype.update = function() 543 { 544 this.updateChildren();//驱动子物体的update 545 } 546 547 // setPosition - move the object to a new position 548 //把物体移到到另一个位置 549 Sim.Object.prototype.setPosition = function(x, y, z) 550 { 551 if (this.object3D) 552 { 553 this.object3D.position.set(x, y, z); 554 } 555 } 556 557 //setScale - scale the object 558 //成比例的放大缩小这个物体 559 Sim.Object.prototype.setScale = function(x, y, z) 560 { 561 if (this.object3D) 562 { 563 this.object3D.scale.set(x, y, z); 564 } 565 } 566 567 //setScale - scale the object 568 //用递归的方式设置物体及其子物体的可见性 569 Sim.Object.prototype.setVisible = function(visible) 570 { 571 function setVisible(obj, visible) 572 { 573 obj.visible = visible; 574 var i, len = obj.children.length; 575 for (i = 0; i < len; i++) 576 { 577 setVisible(obj.children[i], visible); 578 } 579 } 580 581 if (this.object3D) 582 { 583 setVisible(this.object3D, visible); 584 } 585 } 586 //@@写到这里作者也累了,所以附近出现了错误代码 587 // updateChildren - update all child objects 588 Sim.Object.prototype.updateChildren = function() 589 { 590 var i, len; 591 len = this.children.length; 592 for (i = 0; i < len; i++) 593 { 594 this.children[i].update(); 595 } 596 } 597 598 Sim.Object.prototype.setObject3D = function(object3D) 599 { 600 object3D.data = this;//建立双向链表,可以相互调用 601 this.object3D = object3D;//将这个我们自己定义的Sim.Object和Three.js的object3D对象关联在一起 602 } 603 604 //Add/remove children 605 //添加/删除子物体 606 Sim.Object.prototype.addChild = function(child) 607 { 608 this.children.push(child);//Sim.js设置 609 610 // If this is a renderable object, add its object3D as a child of mine 611 if (child.object3D)//Three.js设置 612 { 613 this.object3D.add(child.object3D); 614 } 615 } 616 617 Sim.Object.prototype.removeChild = function(child) 618 { 619 var index = this.children.indexOf(child); 620 if (index != -1) 621 { 622 this.children.splice(index, 1); 623 // If this is a renderable object, remove its object3D as a child of mine 624 if (child.object3D) 625 { 626 this.object3D.remove(child.object3D); 627 } 628 } 629 } 630 631 // Some utility methods 632 //从物体返回到场景,如果没有这个方法就只能用全局变量去引用camera了 633 Sim.Object.prototype.getScene = function() 634 { 635 var scene = null; 636 if (this.object3D) 637 { 638 var obj = this.object3D; 639 while (obj.parent) 640 { 641 obj = obj.parent; 642 } 643 644 scene = obj; 645 } 646 647 return scene; 648 } 649 650 Sim.Object.prototype.getApp = function() 651 { 652 var scene = this.getScene(); 653 return scene ? scene.data : null;//如果scene不具备data属性,说明scene不对应App 654 } 655 656 // Some constants 657 658 /* key codes 659 37: left 660 38: up 661 39: right 662 40: down 663 */ 664 Sim.KeyCodes = {}; 665 Sim.KeyCodes.KEY_LEFT = 37; 666 Sim.KeyCodes.KEY_UP = 38; 667 Sim.KeyCodes.KEY_RIGHT = 39; 668 Sim.KeyCodes.KEY_DOWN = 40; 669 //几个常用按键的键值
下面通过部分示例代码演示Sim框架的使用方法。原始示例引用自(T)的第三章,时间有限,我并没有对全部代码进行Three.js新版本修改,选取的两个JS文件主要用来体现这种面向对象的调用方法。如果需要旧版本的完整示例代码请到(T)的github下载(https://github.com/tparisi/WebGLBook),如果想研究新版本方法请到Three.js官网阅读官方文档(http://threejs.org/docs/index.html#Manual/Introduction/Creating_a_scene)。
Sim.App的示例代码:
1 //这是一个模拟太阳系的3D场景,这里是solarSystem2.js文件 2 // Constructor 3 SolarSystemApp = function() 4 { 5 Sim.App.call(this);//用Sim.App构造SolarSystemApp 6 } 7 8 // Subclass Sim.App 9 SolarSystemApp.prototype = new Sim.App();//原型扩展 10 11 // Our custom initializer 12 //“太阳系对象”的初始化方法(“构造”是“初始化”的基础) 13 SolarSystemApp.prototype.init = function(container) 14 { 15 // Call superclass init code to set up scene, renderer, default camera 16 //在this的情况下调用Sim.js库中的Sim.App.prototype.init方法,实现了代码重用,container是init方法的参数 17 Sim.App.prototype.init.call(this, container); 18 //除了调用库中的init,初始化还要做这些: 19 this.planets = [];//行星数组 20 this.orbits = [];//行星轨道 21 this.lastX = 0; 22 this.lastY = 0; 23 this.mouseDown = false; 24 this.lastTime = 0;//上次渲染时间 25 this.currentlyPressedKeys=[];//当前键盘数组 26 27 // Let there be light! 28 var sun = new Sun();//建立Sun对象 29 sun.init();//sun对象的初始化方法 30 this.addObject(sun);//很自然的把Sun对象添加到SolarSystemApp的objects数组中 31 32 // Are the stars out tonight...? 33 var stars = new Stars();//太阳系外的遥远恒星 34 // Push the stars out past Pluto 35 //括号里是到太阳的最小距离 36 stars.init(Sun.SIZE_IN_EARTHS + SolarSystemApp.EARTH_DISTANCE * SolarSystemApp.PLUTO_DISTANCE_IN_EARTHS); 37 this.addObject(stars); 38 39 // And on the third day... 40 this.createPlanets();//建立行星 41 42 // Move the camera back so we can see our Solar System 43 this.camera.position.set(0, 0, Sun.SIZE_IN_EARTHS * 8);//将相机向外移动一些,看到太阳系的全貌 44 45 var amb = new THREE.AmbientLight(0x676767);//环境光 46 this.scene.add(amb); 47 48 // Tilt the whole solar system toward the camera a bit 49 //将整个太阳系绕x轴旋转一些 50 this.root.rotation.x = Math.PI / 8; 51 52 53 } 54 55 //下面是对鼠标键盘的响应,其中的监听配置由Sim库完成 56 //SolarSystemApp对象的鼠标移动处理 57 SolarSystemApp.prototype.handleMouseMove = function(x, y) 58 { 59 if (this.mouseDown)//如果现在鼠标是按下的状态 60 { 61 var dx = x - this.lastX;//鼠标在x轴上相对于原位置的位移 62 if (Math.abs(dx) > SolarSystemApp.MOUSE_MOVE_TOLERANCE)//这个位移大于一定程度才能够生效,避免了鼠标微小震动的影响 63 { 64 this.root.rotation.y -= (dx * 0.01);//太阳系绕y轴旋转一定角度 65 } 66 this.lastX = x;//更新x轴原位置 67 68 //return; 69 70 var dy = y - this.lastY; 71 if (Math.abs(dy) > SolarSystemApp.MOUSE_MOVE_TOLERANCE) 72 { 73 this.root.rotation.x += (dy * 0.01); 74 75 // Clamp to some outer boundary values 76 if (this.root.rotation.x < 0) 77 this.root.rotation.x = 0; 78 79 if (this.root.rotation.x > SolarSystemApp.MAX_ROTATION_X)//达到一定角度之后禁止继续旋转 80 this.root.rotation.x = SolarSystemApp.MAX_ROTATION_X; 81 82 } 83 this.lastY = y; 84 85 } 86 } 87 88 SolarSystemApp.prototype.handleMouseDown = function(x, y) 89 { 90 this.lastX = x; 91 this.lastY = y; 92 this.mouseDown = true; 93 } 94 95 SolarSystemApp.prototype.handleMouseUp = function(x, y) 96 { 97 this.lastX = x; 98 this.lastY = y; 99 this.mouseDown = false; 100 } 101 102 SolarSystemApp.prototype.handleMouseScroll = function(delta) 103 {//鼠标滚轮控制相机远近 104 var dx = delta; 105 106 this.camera.position.z -= dx*10; 107 108 // Clamp to some boundary values 109 if (this.camera.position.z < SolarSystemApp.MIN_CAMERA_Z) 110 this.camera.position.z = SolarSystemApp.MIN_CAMERA_Z; 111 if (this.camera.position.z > SolarSystemApp.MAX_CAMERA_Z) 112 this.camera.position.z = SolarSystemApp.MAX_CAMERA_Z; 113 } 114 //用currentlyPressedKeys数组保存键盘所有按键的状态 115 SolarSystemApp.prototype.handleKeyDown= function(keyCode,charCode) 116 { 117 this.currentlyPressedKeys[keyCode] = true; 118 } 119 SolarSystemApp.prototype.handleKeyUp= function(keyCode,charCode) 120 { 121 this.currentlyPressedKeys[keyCode] = false; 122 } 123 124 SolarSystemApp.prototype.update = function() 125 { 126 showFocus(); 127 var speed=0//前后速度 128 var adspeed=0//左右速度 129 if (this.currentlyPressedKeys[65]) { 130 // A键-横向左 131 adspeed = -0.009; 132 } else if ( this.currentlyPressedKeys[68]) { 133 // D键-横向右 134 adspeed = +0.009; 135 } 136 137 if (this.currentlyPressedKeys[87]) { 138 // W键-纵向上 139 speed = 0.003; 140 } else if ( this.currentlyPressedKeys[83]) { 141 // S键-纵向下 142 speed = -0.003; 143 } 144 var timeNow = new Date().getTime(); 145 if (this.lastTime != 0) { 146 var elapsed = timeNow - this.lastTime; 147 148 if (speed != 0||adspeed!=0) { 149 this.camera.position.x+=adspeed* elapsed; 150 this.camera.position.y+=speed* elapsed; 151 } 152 153 // adjust yaw and pitch by their respective rates of change 154 } 155 this.lastTime = timeNow; 156 157 Sim.App.prototype.update.call(this);//驱动Sim中的“this.objects[i].update();” 158 } 159 //按照planet_specs数组批量生成行星 160 SolarSystemApp.prototype.createPlanets = function () 161 { 162 var i, len = SolarSystemApp.planet_specs.length; 163 for (i = 0; i < len; i++) 164 { 165 var spec = SolarSystemApp.planet_specs[i];//这个行星的参数 166 var planet = spec.type ? new spec.type : new Planet;//除了地球和土星比较特殊,其他星球都创建为Planet对象,Planet继承自Sim.Object 167 168 planet.init({animateOrbit:true, animateRotation: true, showOrbit:true, 169 distance:spec.distance * SolarSystemApp.EARTH_DISTANCE + Sun.SIZE_IN_EARTHS, 170 size:spec.size * SolarSystemApp.EXAGGERATED_PLANET_SCALE, 171 period : spec.period, 172 revolutionSpeed : 0.002, 173 map : spec.map}); 174 this.addObject(planet); 175 this.planets.push(planet); 176 177 var orbit = new Orbit();//行星轨道 178 orbit.init(spec.distance * SolarSystemApp.EARTH_DISTANCE + Sun.SIZE_IN_EARTHS); 179 this.addObject(orbit); 180 this.orbits.push(orbit); 181 } 182 } 183 184 SolarSystemApp.MOUSE_MOVE_TOLERANCE = 4; 185 SolarSystemApp.MAX_ROTATION_X = Math.PI / 2; 186 SolarSystemApp.MAX_CAMERA_Z = Sun.SIZE_IN_EARTHS * 50; 187 SolarSystemApp.MIN_CAMERA_Z = Sun.SIZE_IN_EARTHS * 2;//镜头最小z值 188 SolarSystemApp.EARTH_DISTANCE = 50; 189 SolarSystemApp.PLUTO_DISTANCE_IN_EARTHS = 77.2; 190 SolarSystemApp.EARTH_DISTANCE_SQUARED = 45000; 191 SolarSystemApp.EXAGGERATED_PLANET_SCALE = 5.55; 192 SolarSystemApp.planet_specs = [ 193 //大小,距离,周期,纹理图片 194 // Mercury 195 { size : 1 / 2.54, distance : 0.4, period : 0.24, map : "../IMAGE/SOLAR/Mercury.jpg" }, 196 // Venus 197 { size : 1 / 1.05, distance : 0.7, period : 0.62, map : "../IMAGE/SOLAR/venus.jpg" }, 198 // Earth 199 { type : Earth, size : 1 , distance : 1, period : 1, map : "../IMAGE/SOLAR/earth_surface_2048.jpg" }, 200 // Mars 201 { size : 1 / 1.88, distance : 1.6, period : 1.88, map : "../IMAGE/SOLAR/MarsV3-Shaded-2k.jpg" }, 202 // Jupiter 203 { size : 11.1, distance : 5.2, period : 11.86, map : "../IMAGE/SOLAR/realj2k.jpg" }, 204 // Saturn 205 { type : Saturn, size : 9.41, distance : 10, period : 29.46, map : "../IMAGE/SOLAR/saturn_bjoernjonsson.jpg" }, 206 // Uranus 207 { size : 4, distance : 19.6, period : 84.01, map : "../IMAGE/SOLAR/uranus.jpg" }, 208 // Neptune 209 { size : 3.88, distance : 38.8, period : 164.8, map : "../IMAGE/SOLAR/neptune.jpg" }, 210 // Pluto - have to exaggerate his size or we‘ll never see the little guy 211 { size : 10 / 5.55, distance : 77.2, period : 247.7, map : "../IMAGE/SOLAR/pluto.jpg" }, 212 ];
接下来是Sim.Object的示例代码:
1 //Sim.Object的使用方式 2 // Custom Planet class 3 Planet = function() 4 { 5 Sim.Object.call(this); 6 } 7 8 Planet.prototype = new Sim.Object(); 9 10 Planet.prototype.init = function(param) 11 { 12 param = param || {}; 13 14 // Create an orbit group to simulate the orbit - this is the top-level Planet group 15 var planetOrbitGroup = new THREE.Object3D();//planetOrbitGroup是一个Three.js中的3D对象,Three.js为它准备了各种相关的方法和属性 16 17 // Tell the framework about our object 18 this.setObject3D(planetOrbitGroup);//将Sim.js定义的Sim.object与Three.js定义的Object3D关联起来 19 20 // Create a group to contain Planet and Clouds meshes 21 var planetGroup = new THREE.Object3D(); 22 var distance = param.distance || 0; 23 var distsquared = distance * distance; 24 planetGroup.position.set(Math.sqrt(distsquared/2), 0, -Math.sqrt(distsquared/2));//设置行星位置 25 planetOrbitGroup.add(planetGroup);//planetGroup是planetOrbitGroup在Three.js层面的子物体 26 27 this.planetGroup = planetGroup; 28 var size = param.size || 1; 29 this.planetGroup.scale.set(size, size, size);//设置大小比例 30 31 var map = param.map;//纹理图片 32 this.createGlobe(map);//使用纹理图片建立行星 33 34 this.animateOrbit = param.animateOrbit;//行星是否沿着轨道运动 35 this.period = param.period;//公转周期 36 this.revolutionSpeed = param.revolutionSpeed ? param.revolutionSpeed : Planet.REVOLUTION_Y;//公转速度 37 } 38 39 Planet.prototype.createGlobe = function(map) 40 { 41 // Create our Planet with nice texture 42 var geometry = new THREE.SphereGeometry(1, 32, 32);//建立一个多面体(球) 43 //var texture = THREE.ImageUtils.loadTexture(map); 44 //@@新版加载纹理方法 45 var texture = new THREE.TextureLoader().load(map); 46 //var material = new THREE.MeshPhongMaterial( {map: texture, ambient: 0x333333} ); 47 //@@ 48 var material = new THREE.MeshPhongMaterial( {map: texture} ); 49 var globeMesh = new THREE.Mesh( geometry, material ); 50 51 // Add it to our group 52 this.planetGroup.add(globeMesh);//globeMesh是planetGroup的子物体 53 54 // Save it away so we can rotate it 55 this.globeMesh = globeMesh; 56 } 57 58 59 Planet.prototype.update = function() //物体的update 60 { 61 // Simulate the orbit 62 if (this.animateOrbit) 63 { 64 this.object3D.rotation.y += this.revolutionSpeed / this.period; 65 } 66 67 Sim.Object.prototype.update.call(this); 68 } 69 70 Planet.REVOLUTION_Y = 0.003;
最终效果:
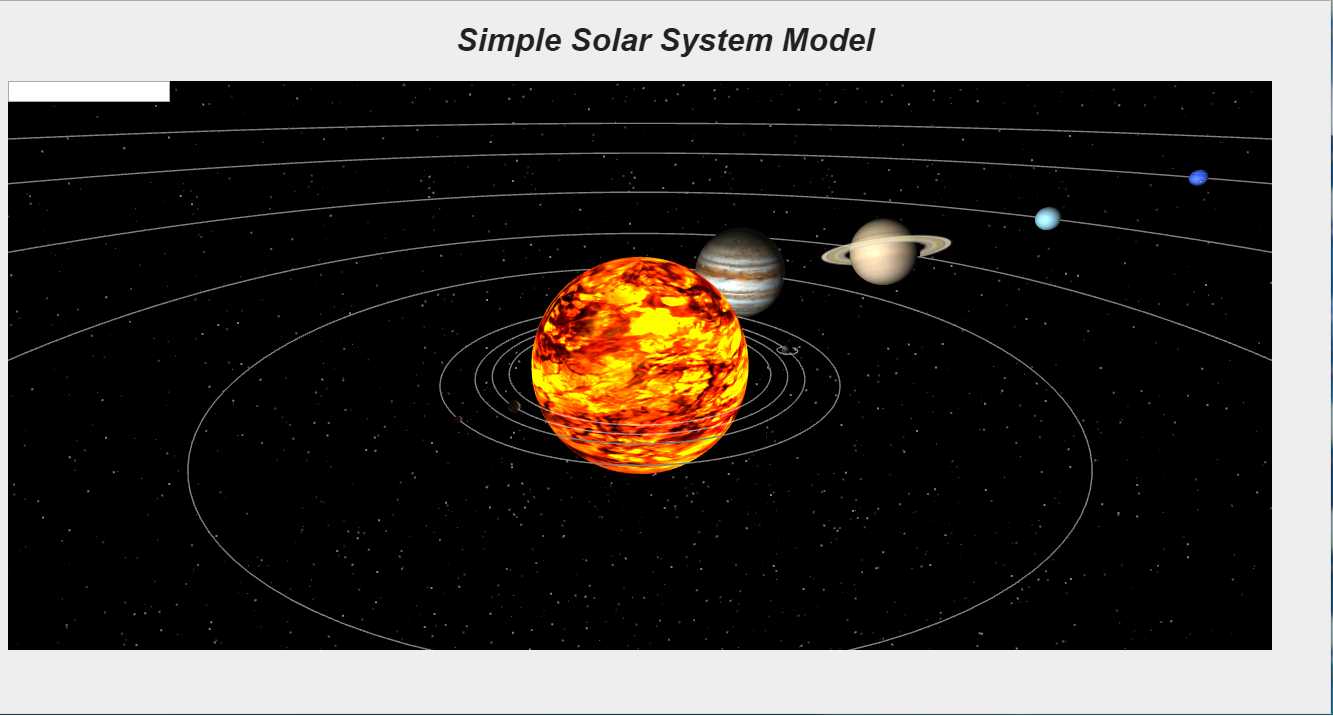
上面的代码简单演示了基于Three.js的面向对象框架使用方法,在使用过程中我们发现Three.js的更倾向于3D场景构建,其本身并不具备作为“游戏引擎”的完整功能,很多功能需要用户自己编写。与其相对babylon.js是一个面向3D游戏应用编写的WebGL封装(http://www.babylonjs.com/),具有碰撞检测、物理模拟等功能,但渲染性能较Three.js略低。
下一步准备编写基于Three.js的3D碰撞检测功能。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/ljzc002/p/5156850.html