标签:
11.进程控制理论
进程:进程是一个具有一定独立功能的应用程序的运行。一个没有运行起来的程序不能叫做一个进程,只有运行起来的程序才会产生一个进程。
进程的特点:
进程的状态:
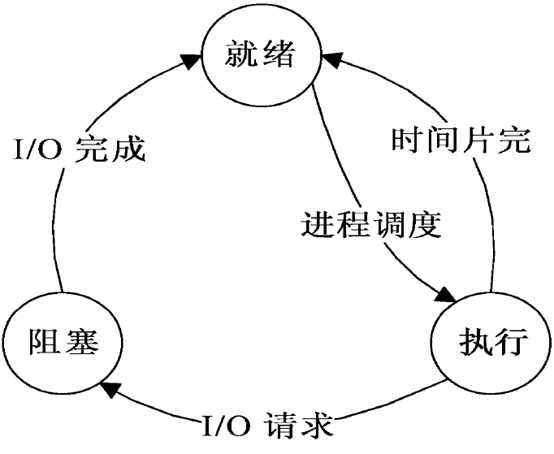
当我们运行一个程序的时候,该程序就处于就绪状态。由于程序的运行需要资源,例如内存、硬盘的空间等。所以cpu会发出I/O请求。如果此时正有程序在运行,正在使用这些资源。就会得不到满足,会导致进程进入阻塞状态。当资源请求满足的时候,再次进入就绪状态。等待cpu的调度,在执行的过程中,如果一个进程在系统规定的一个时间片内没能执行完,他会再次进入就绪状态,再次等待cpu调度。如此循环,知道程序运行完。
?
进程ID:
进程的ID(PID):系统给每一个进程的唯一标识,是一个数字。
父进程的ID(PPID)。
启动进程的用户ID(UID)。
?
?
进程的互斥:
进程互斥是指当有若干进程都要使用某一资源时,但该资源在同一时刻最多允许一个进程使
用,这时其他进程必须等待,直到占用该资源者释放了该资源为止。
?
临界资源:
在操作系统中,在某一时刻,只允许一个进程访问的资源叫临界资源。
?
临界区:
进程中访问临界资源的那段程序代码称为临界区。为实现对临界资源的互斥访问,应保证诸进程互斥地进入各自的临界区。
?
进程的同步:
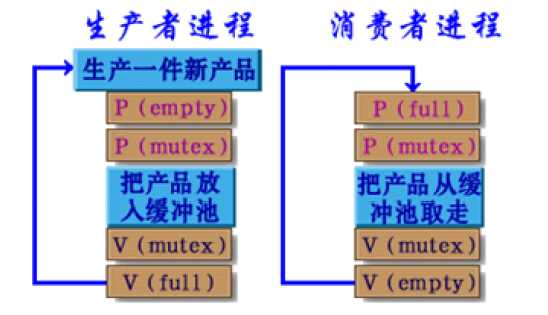
一组进程按一定的顺序执行的过程称为进程间的同步.具有同步关系的这组进程称为合作进程,最为有名的是生产者和消费者进程.
?
进程的调度:
按一定算法,从一组待运行的进程中选出一个来占有cpu运行。
?
常见的调度算法:
调度的时机:
?
?
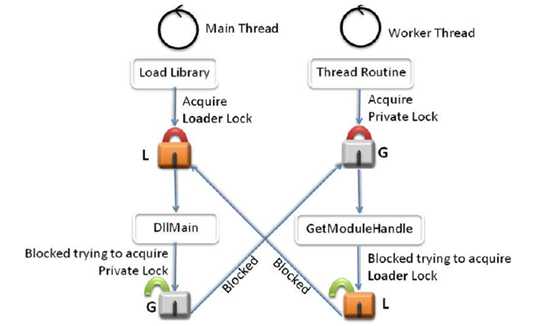
死锁:
多个进程因竞争资源而形成一种僵局,导致这些进程都无法继续往前执行。
?
下面我们来看获取进程的函数:
获取进程ID的函数是:getpid。
查看该函数的信息:man 2 getpid:
NAME
getpid, getppid - get process identification
?
SYNOPSIS
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
?
pid_t getpid(void);
pid_t getppid(void);
?
DESCRIPTION
getpid() returns the process ID of the calling process. (This is often
used by routines that generate unique temporary filenames.)
?
getppid() returns the process ID of the parent of the calling process.
?
ERRORS
These functions are always successful.
?
CONFORMING TO
POSIX.1-2001, 4.3BSD, SVr4.
?
NOTES
Since glibc version 2.3.4, the glibc wrapper function for getpid()
caches PIDs, so as to avoid additional system calls when a process
calls getpid() repeatedly. Normally this caching is invisible, but its
correct operation relies on support in the wrapper functions for
fork(2), vfork(2), and clone(2): if an application bypasses the glibc
wrappers for these system calls by using syscall(2), then a call to
getpid() in the child will return the wrong value (to be precise: it
will return the PID of the parent process). See also clone(2) for dis-
cussion of a case where getpid() may return the wrong value even when
invoking clone(2) via the glibc wrapper function.
?
SEE ALSO
clone(2), fork(2), kill(2), exec(3), mkstemp(3), tempnam(3), tmp-
file(3), tmpnam(3), credentials(7)
?
COLOPHON
This page is part of release 3.22 of the Linux man-pages project. A
description of the project, and information about reporting bugs, can
be found at http://www.kernel.org/doc/man-pages/.
获取进程ID的函数getpid。该函数的返回值是调用该函数的进程的ID。需要的头文件:
<sys/types.h> <unistd.h>
该函数没有参数。返回值是调用该函数的进程的ID。
实例getpid.c:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
?
void main(){
????int id = 0;
????id = getpid();
????printf("process‘s ID %d\n",id);
}
?
运行的结果:
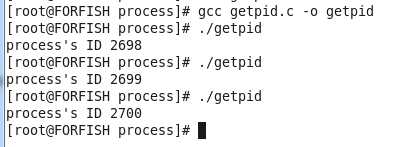
上面中,生成的getpid就是一个程序,当我们没有去运行的时候,他就是一个程序。当我们运行起来的时候他就变成了一个进程。进程的ID时时刻刻都在发生变化。
?
?
?
?
?
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/FORFISH/p/5188653.html