标签:
1. 基本思想
将待排序记录Key=A[i+1]插入到已排序序列A[1…i]中。Key由后向前依次与A[1…i]中的元素进行比较,若A[x]<=Key,将Key插入到A[x]的后面,即A[x+1]=Key,否则将元素A[x]后移。
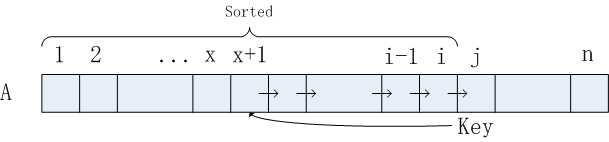
S0:从无序序列A[n]的第一个元素A[1]开始,该元素可被认定已完成排序。
S1:取出下一个元素并记录为Key,在已排序序列中倒序遍历。
S2:若已排序序列中的元素A[x]<=Key,将Key插入到A[x]的后面,否则将元素A[x]后移。
S3:重复步骤S2,直到找到适合Key插入的位置。
S4:重复步骤S1,完成排序。
2. 时间复杂度
正序有序:仅需比较n次,无需元素移动,时间复杂度为O(n)。
逆序有序:需比较1+2+…+n-1+n=n*(n+1)/2≈n^2/2次,时间复杂度为O(n^2)。
3. 稳定性
排序算法的稳定性是指,两个相同元素,排序前后的位置关系是否发生变化。
若序列A[n]中的两个元素K1=K2(K1位于K2前面),在直接插入排序算法中,K2与K1进行比较时,K2直接插入到K1后面,无需做元素移动,K1与K2的位置关系不会发生变化。因此,直接插入排序算法是稳定的。
4. 算法程序
function sortArray = straightInsertionSort(array, number, sortKind)
% Straight insertion sort.
%
% input - array : disordered array.
% number : the number of array elements.
% sortKind : kind of sort (1 - positive and 0 - negative).
%
% output - sortArray : sorted array.
if (number <= 0)
error(‘The disordered array empty.‘);
end
if (number > 1)
% the number of disordered array is more than 2.
for index = 2 : number
% insert the element to the correct position of sorted array.
i = index - 1;
key = array(index);
if (sortKind == 1)
% positive
while ((i > 0) && (array(i) > key))
array(i + 1) = array(i);
i = i - 1;
end
end
if (sortKind == 0)
% negative
while ((i > 0) && (array(i) < key))
array(i + 1) = array(i);
i = i - 1;
end
end
array(i + 1) = key;
end
end
sortArray = array;
5. 视觉直观感受

标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/liekkas0626/p/5212603.html