标签:
本文主要讲述C++ new运算符和operator new, placement new之间的种种关联,new的底层实现,以及operator new的重载和一些在内存池,STL中的应用。
operator new can be called explicitly as a regular function, but in C++, new is an operator with a very specific behavior: An expression with the new operator, first calls function operator new (i.e., this function) with the size of its type specifier as first argument, and if this is successful, it then automatically initializes or constructs the object (if needed). Finally, the expression evaluates as a pointer to the appropriate type.//平台:Visual Stdio 2008 #include<iostream> class A { public: A() { std::cout<<"call A constructor"<<std::endl; } ~A() { std::cout<<"call A destructor"<<std::endl; } } int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { A* a = new A; delete a; system("pause"); return 0; }
A* a = new A; 01301022 push 1 ;不含数据成员的类占用一字节空间,此处压入sizeof(A) 01301024 call operator new (13013C2h) ;调用operator new(size_t size) 01301029 mov esi,eax ;返回值保存到esi 0130102B add esp,4 ;平衡栈 0130102E mov dword ptr [esp+8],esi ; 01301032 mov dword ptr [esp+14h],0 0130103A test esi,esi ;在operator new之后,检查其返回值,如果为空(分配失败),则不调用A()构造函数 0130103C je wmain+62h (1301062h) ;为空 跳过构造函数部分 0130103E mov eax,dword ptr [__imp_std::endl (1302038h)] ;构造函数内部,输出字符串 01301043 mov ecx,dword ptr [__imp_std::cout (1302050h)] 01301049 push eax 0130104A push offset string "call A constructor" (1302134h) 0130104F push ecx 01301050 call std::operator<<<std::char_traits<char> > (13011F0h) 01301055 add esp,8 01301058 mov ecx,eax 0130105A call dword ptr [__imp_std::basic_ostream<char,std::char_traits<char> >::operator<< (1302040h)] 01301060 jmp wmain+64h (1301064h) ;构造完成,跳过下一句 01301062 xor esi,esi ;将esi置空,这里的esi即为new A的返回值 01301064 mov dword ptr [esp+14h],0FFFFFFFFh delete a; 0130106C test esi,esi ;检查a是否为空 0130106E je wmain+9Bh (130109Bh) ;如果为空,跳过析构函数和operator delete 01301070 mov edx,dword ptr [__imp_std::endl (1302038h)] ;析构函数 输出字符串 01301076 mov eax,dword ptr [__imp_std::cout (1302050h)] 0130107B push edx 0130107C push offset string "call A destructor" (1302148h) 01301081 push eax 01301082 call std::operator<<<std::char_traits<char> > (13011F0h) 01301087 add esp,8 0130108A mov ecx,eax 0130108C call dword ptr [__imp_std::basic_ostream<char,std::char_traits<char> >::operator<< (1302040h)] 01301092 push esi ;压入a 01301093 call operator delete (13013BCh) ;调用operator delete 01301098 add esp,4
通过反汇编可以看出A* = new A包含了operator new(sizeof(A))和A()两个步骤(当然,最后还要将值返回到a)
delete a包含了~A()和operator delete(a)两个步骤。
| throwing (1) |
void* operator new (std::size_t size) throw (std::bad_alloc); |
|---|---|
| nothrow (2) |
void* operator new (std::size_t size, const std::nothrow_t& nothrow_value) throw(); |
| placement (3) |
void* operator new (std::size_t size, void* ptr) throw(); |
#ifndef __PLACEMENT_NEW_INLINE #define __PLACEMENT_NEW_INLINE inline void *__cdecl operator new(size_t, void *_P) {return (_P); } #if _MSC_VER >= 1200 inline void __cdecl operator delete(void *, void *) {return; } #endif #endif
#include <iostream> class A { public: A() { std::cout<<"call A constructor"<<std::endl; } ~A() { std::cout<<"call A destructor"<<std::endl; } }; int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { A* p = (A*)::operator new(sizeof(A)); //分配 new(p) A(); //构造 p->~A(); //析构 ::operator delete(p); //释放 system("pause"); return 0; }
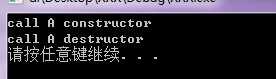
A* a = (A*)::operator new(sizeof(A)); //分配 00F9151D push 1 00F9151F call operator new (0F91208h) ;调用::operator new(size_t size)也就是throwing(1)版本 00F91524 add esp,4 00F91527 mov dword ptr [ebp-14h],eax ;返回地址放入[ebp-14h] 即为p new(a) A(); //构造 00F9152A mov eax,dword ptr [ebp-14h] 00F9152D push eax 00F9152E push 1 ;压入p 00F91530 call operator new (0F91280h);调用operator new(size_t, void* p)即placement(3)版本 只是简单返回p 00F91535 add esp,8 00F91538 mov dword ptr [ebp-0E0h],eax ;将p放入[ebp-0E0h] 00F9153E mov dword ptr [ebp-4],0 00F91545 cmp dword ptr [ebp-0E0h],0 ;判断p是否为空 00F9154C je wmain+81h (0F91561h) ;如果为空 跳过构造函数 00F9154E mov ecx,dword ptr [ebp-0E0h] ;取出p到ecx 00F91554 call A::A (0F91285h) ;调用构造函数 根据_thiscall调用约定 this指针通过ecx寄存器传递 00F91559 mov dword ptr [ebp-0F4h],eax ;将返回值(this指针)放入[ebp-0F4h]中 00F9155F jmp wmain+8Bh (0F9156Bh) ;跳过下一句 00F91561 mov dword ptr [ebp-0F4h],0 ;将[ebp-0F4h]置空 当前面判断p为空时执行此语句 00F9156B mov ecx,dword ptr [ebp-0F4h] ;[ebp-0F4h]为最终构造完成后的this指针(或者为空) 放入ecx 00F91571 mov dword ptr [ebp-0ECh],ecx ;又将this放入[ebp-0ECh] 这些都是调试所用 00F91577 mov dword ptr [ebp-4],0FFFFFFFFh a->~A(); //析构 00F9157E push 0 00F91580 mov ecx,dword ptr [ebp-14h] ;从[ebp-14h]中取出p 00F91583 call A::`scalar deleting destructor‘ (0F91041h) ;调用析构函数(跟踪进去比较复杂 如果在Release下,构造析构函数都是直接展开的) ::operator delete(a); //释放 00F91588 mov eax,dword ptr [ebp-14h] ;将p放入eax 00F9158B push eax ;压入p 00F9158C call operator delete (0F910B9h);调用operator delete(void* ) 00F91591 add esp,4
A* a = (A*)::operator new(sizeof(A)); //分配 010614FE push 1 01061500 call operator new (1061208h) 01061505 add esp,4 01061508 mov dword ptr [a],eax //new(a) A(); //构造 a->A::A(); 0106150B mov ecx,dword ptr [a] 0106150E call operator new (1061285h) a->~A(); //析构 01061513 push 0 01061515 mov ecx,dword ptr [a] 01061518 call A::`scalar deleting destructor‘ (1061041h) ::operator delete(a); //释放 0106151D mov eax,dword ptr [a] 01061520 push eax 01061521 call operator delete (10610B9h) 01061526 add esp,4
#include <iostream> class A { public: A() { std::cout<<"call A constructor"<<std::endl; } ~A() { std::cout<<"call A destructor"<<std::endl; } void* operator new(size_t size) { std::cout<<"call A::operator new"<<std::endl; return malloc(size); } void* operator new(size_t size, const std::nothrow_t& nothrow_value) { std::cout<<"call A::operator new nothrow"<<std::endl; return malloc(size); } }; int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { A* p1 = new A; delete p1; A* p2 = new(std::nothrow) A; delete p2; system("pause"); return 0; }
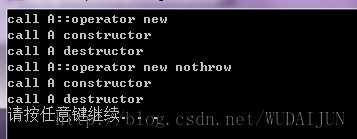
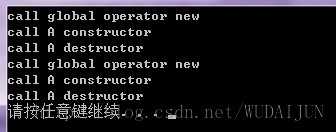
如果类A中没有对operator new的重载,那么new A和new(std::nothrow) A;都将会使用全局operator new(size_t size)。可将A中两个operator new注释掉,并且在A外添加一个全局operator new重载:
void* ::operator new(size_t size) { std::cout<<"call global operator new"<<std::endl; return malloc(size); }
程序输出:
void* operator new(size_t size, int x, int y, int z) { std::cout<<"X="<<x<<" Y="<<y<<" Z="<<z<<std::endl; return malloc(size); }
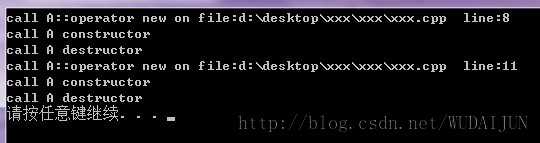
//A.h class A { public: A() { std::cout<<"call A constructor"<<std::endl; } ~A() { std::cout<<"call A destructor"<<std::endl; } void* operator new(size_t size, const char* file, int line) { std::cout<<"call A::operator new on file:"<<file<<" line:"<<line<<std::endl; return malloc(size); return NULL; } }; //Test.cpp #include <iostream> #include "A.h" #define new new(__FILE__, __LINE__) int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { A* p1 = new A; delete p1; A* p2 = new A; delete p2; system("pause"); return 0; }
输出:
void* operator new(size_t size, int x) { cout<<" x = "<<x<<endl; return malloc(size); } void operator delete(void* p, int x) { cout<<" x = "<<x<<endl; free(p); }
#include <iostream> #include <new.h>// 使用_set_new_mode和set_new_handler void nomem_handler() { std::cout<<"call nomem_handler"<<std::endl; } int main() { _set_new_mode(1); //使new_handler有效 set_new_handler(nomem_handler);//指定入口函数 函数原型void f(); std::cout<<"try to alloc 2GB memory...."<<std::endl; char* a = (char*)malloc(2*1024*1024*1024); if(a) std::cout<<"ok...I got it"<<std::endl; free(a); system("pause"); }
//A.h class A { public: A() { std::cout<<"call A constructor"<<std::endl; } ~A() { std::cout<<"call A destructor"<<std::endl; } void* operator new(size_t size) { std::cout<<"call A::operator new[] size:"<<size<<std::endl; return malloc(size); } void operator delete[](void* p) { std::cout<<"call A::operator delete[]"<<std::endl; free(p); } void operator delete(void* p) { free(p); } };
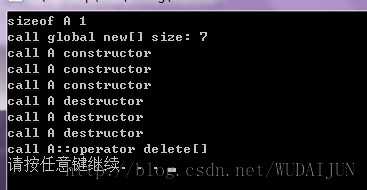
//Test.cpp #include <iostream> #include "A.h" void* operator new[](size_t size) { std::cout<<"call global new[] size: "<<size<<std::endl; return malloc(size); } void operator delete[](void* p) { std::cout<<"call global delete[] "<<std::endl; } int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { std::cout<<"sizeof A "<<sizeof(A)<<std::endl; A* p1 = new A[3]; delete []p1; system("pause"); return 0; }
输出:
【转】C++ 内存分配(new,operator new)详解
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/budapeng/p/5237972.html