标签:
分类:C#、Android、VS2015;
创建日期:2016-03-13
Android提供的Camera有两个典型的版本,一个是在Android 5.0以前提供的,称为Camera;另一个是从Android 5.0开始提供的,称为Camera2。
这里仅演示使用系统Camera程序实现拍照的基本用法。
用Camera实现拍照和摄像功能时,有以下两种实现办法:
一是直接利用Intent启动系统自带的Camera App打开相机实现拍照和摄像功能,然后通过Android.Provider命名空间下的.MediaStore类获取拍照或摄像结果保存的文件路径。这是最简单的实现办法,对于一般的需求基本上就能满足要求了。
二是使用Camera API自定义相机,实现专用的拍照和摄像功能。
1、确定是否需要在AndroidMainfest.xml中声明使用照相机.
(1)Camera权限和Camera特性
如果你是调用系统Camera程序,不必声明该权限和特性。
如果你是构造自定义的Camera程序,则必须在AndroidMainfest.xml中声明使用照相机的权限,例如:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" />
你还必须在AndroidMainfest.xml中声明照相机特性,例如:
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera" />
如果你的程序可能需要使用照相机,但并不是一定要使用,那么可以设置android:required属性,比如:
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera" android:required="false" />
(2)存储权限
如果需要在扩展存储设备上(如sd卡)存储你的照片或者拍摄的视频,那么必须声明如下权限:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
(3)音频录制权限
如果需要录制音频或者视频,必须在AndroidMainfest.xml文件中设置如下权限:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECORD_AUDIO" />
2、使用系统Camera程序
这是一种可以让你的程序以最少的编码,然后可以快速使用照相机的方法,此方式通过一个Intent来调用系统的Camera程序,让系统的Camera应用程序去拍摄照片或者录制视频,而且可以返回拍摄或者录制的结果给你自己的应用程序。
(1)基本用法
(a)构造一个Camera Intent -- 创建一个拍摄照片或者视频的Intent,可以使用如下两种方法:
向系统Camera程序请求拍摄图片。例如:
Intent intent = new Intent(MediaStore.ActionImageCapture);
向系统Camera程序请求录制视频。例如:
Intent intent = new Intent(MediaStore.ActionVideoCapture);
(b)开启Camera intent -- 通过调用startActivityForResult()来执行Camera intent, 在你调用这个方法之后,系统Camera程序就是出现在用户界面,然后用户就可以拍摄照片或者视频了。
(c)接收Intent 结果 -- 在你的应用程序里面建立一个OnActivityResult()方法来接收来自系统Camera程序的执行结果。当用户拍摄了照片或者视频(也许取消了拍摄操作),系统就会调用这个方法。
(2)图片拍摄Intent
使用系统Camera来拍摄图片,是一种以最快的速度,最少的代码,让你的程序能够拍照的方法。一个图片拍摄的intent可以包含如下扩展信息:
(a)MediaStore.ExtraOutput -- 指定一个Uri对象,系统Camera程序会把拍摄的图片存储到指定位置。这个设置一般是强烈推荐的。如果你不指定这个Uri路径,那么系统Camera程序会把图片以一个默认的名字存储在一个默认的位置。我们可以通过返回的intent,然后用Intent.GetData()方法来获取这个值。
例如:
private File file;
string dirPath;
string filePath;
……
Intent imageIntent = new Intent(MediaStore.ActionImageCapture);
filePath = dirPath + $"/PP{System.DateTime.Now:yyyyMMdd_hhmmss}.jpg";
file = new File(filePath);
imageIntent.PutExtra(MediaStore.ExtraOutput, Uri.FromFile(file));
StartActivityForResult(imageIntent, 100, savedInstanceState);
当StartActivityForResult()方法执行之后,用户就会看到系统的Camera界面。当用户完成拍摄照片(或者取消拍摄)之后,用户界面就会返回你自己的应用程序。那么你必须拦截OnActivityResult方法,以便接收执行结果和继续你自己代码的逻辑。
(3)视频录制intent
使用系统Camera来录制视频,是一种以最快的速度,最少的代码,让你的程序能够录制视频的方法。一个视频录制的intent可以包含如下扩展信息:
MediaStore.ExtraOutput -- 指定一个Uri对象,系统Camera程序会把录制的视频存储到指定位置。这个设置一般是强烈推荐的。如果你不指定这个Uri路径,那么系统Camera程序会把视频以一个默认的名字存储在默认的位置。可以通过返回的intent,然后用Intent.GetData()方法来获取这个值。
MediaStore.ExtraVideoQuality -- 视频质量,0(低质量,比较小的文件来存储视频), 1(高质量,比较大的文件来存储视频)
MediaStore.ExtraDurationLimit -- 设置一个值来限制视频的录制时间,单位为秒。
MediaStore.ExtraSizeLimit -- 设置一个值来限制视频大小,byte为单位。
当StartActivityForResult()方法执行之后,用户就会看到系统的Camera界面。当用户完成录制视频(或者取消拍摄)之后,用户界面就会返回你自己的应用程序,接下来你就通过重写的OnActivityResult()方法接收执行结果。
(4)接收Camera返回的结果
一旦你执行了拍摄图片或者视频的intent之后,就可以重写OnActivityResult()方法接收执行结果了。得到结果后,存储在指定位置的图片或者视频就能被我们的程序使用了。
3、构造自定义的Camera程序
调用系统Camera App实现拍照和摄像功能虽然能够满足我们的简单需求,但是毕竟自由度降低了,而且拍照的界面就是系统提供的样子。
如果你希望自定义比较漂亮的界面,可以自己定制Camera应用程序制自定义的Camera程序可能比调用系统的Camera需要更多的代码,但是这能给你的用户带来不一样的用户体验。比如Camera 360软件等,就需要根据SDK提供的Camera API来编写自己的程序。
注意:Android已经弃用了5.0之前的版本中提供的Android.Hardware.Camera类,而是改为用Camera2实现,具体用法请参看相关资料。
由于手机自带摄像头,因此可直接使用相机功能。但是,如果你希望在模拟器中测试你的程序,在模拟器中可利用前置相机(Front Camera)来模拟。
下图是Android 4.4.2(Api 19)的模拟器参数设置界面:
将此界面中的【Front Camera】设置为“Emulated”以后,模拟器就会用一个随机移动的矩形来模拟相机的拍照和摄像效果。
下图是Android 6.0(Api 23)的模拟器参数设置界面:
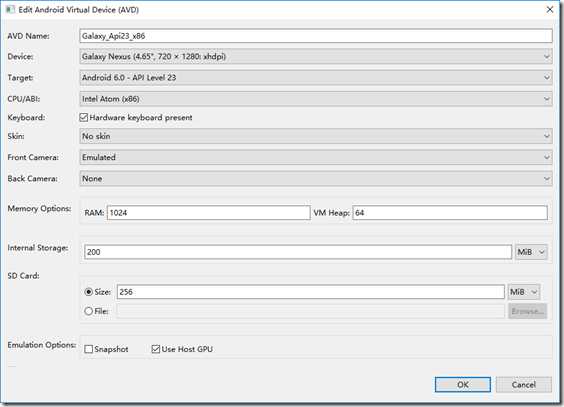
在模拟器中运行时,打开相机后,单击下方的圆形按钮即可拍照,拍照的结果保存到SD卡中指定的文件夹下,所拍的图片也会立即在ImageView控件中显示出来,而且还能单独通过Android系统自带的【图库】程序查看拍照的结果。
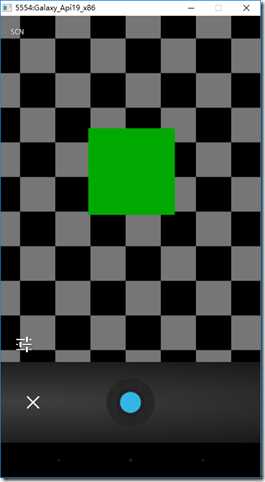
1、运行截图
下图左侧为初始界面,右侧为单击【拍照】后的拍照界面。

下图左侧为单击圆形拍照按钮后的结果,右侧为对号后显示的文件保存位置。
下面左图为单击【视频录制】后的结果,右图为录制完成后的结果。
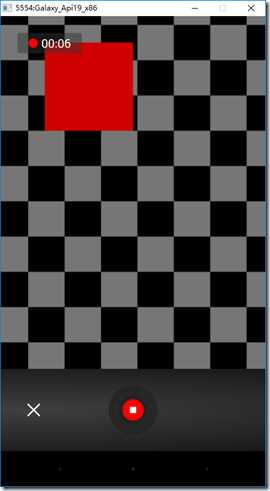
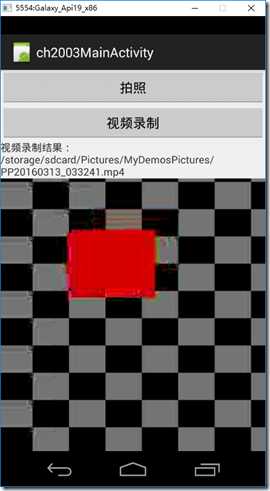
2、设计步骤
(1)权限要求
本例子需要在AndroidManifest.xml中添加下面的权限:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
如果已经有对应的权限就不用再添加了,如果没有就双击Properties文件夹勾选这个权限,让系统自动将其添加到AndroidManifest.xml文件中,或者自己直接将其添加到AndroidManifest.xml文件中。
(2)添加ch2003Main.axml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"> <Button android:id="@+id/ch2003_btn1" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="拍照" /> <Button android:id="@+id/ch2003_btn2" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="视频录制" /> <TextView android:text="" android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceSmall" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/ch2003_textView1" /> <ImageView android:src="@android:drawable/ic_menu_gallery" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="300dp" android:id="@+id/ch2003_imageView1" android:adjustViewBounds="true" /> <VideoView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/ch2003_videoView1" /> </LinearLayout>
(3)添加ch2003BitmapHelpers.cs
该文件会自动缩放图片以适应屏幕大小,这是为了解决内存不够时直接加载大图片可能会导致应用程序崩溃的情况。
using Android.Widget; using Android.Graphics.Drawables; using Android.Graphics; namespace MyDemos.SrcDemos { public static class ch2003BitmapHelpers { public static void RecycleBitmap(ImageView imageView) { if (imageView == null) { return; } Drawable toRecycle = imageView.Drawable; if (toRecycle != null) { ((BitmapDrawable)toRecycle).Bitmap.Recycle(); } } public static Bitmap LoadAndResizeBitmap(string fileName, int width, int height) { BitmapFactory.Options options = new BitmapFactory.Options { InPurgeable = true, InJustDecodeBounds = true }; BitmapFactory.DecodeFile(fileName, options); int outHeight = options.OutHeight; int outWidth = options.OutWidth; int inSampleSize = 1; if (outHeight > height || outWidth > width) { if(outWidth > outHeight) { inSampleSize = outHeight / height; } else { inSampleSize = outWidth / width; } } options.InSampleSize = inSampleSize; options.InJustDecodeBounds = false; Bitmap resizedBitmap = BitmapFactory.DecodeFile(fileName, options); return resizedBitmap; } } }
(4)添加ch2003MainActivity.cs
using System.Collections.Generic; using Android.App; using Android.Content; using Android.OS; using Android.Runtime; using Android.Widget; using Android.Provider; using Android.Content.PM; using Android.Graphics; using Android.Net; using Java.IO; namespace MyDemos.SrcDemos { [Activity(Label = "ch2003MainActivity")] [IntentFilter(new[] { Intent.ActionMain }, Categories = new[] { Intent.CategoryDefault, ch.MyDemosCategory })] public class ch2003MainActivity : Activity { private File file; string dirPath; string filePath; private ImageView imageView1; private VideoView videoView1; private TextView textView1; private MediaType mediaType; protected override void OnCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { base.OnCreate(savedInstanceState); SetContentView(Resource.Layout.ch2003Main); textView1 = FindViewById<TextView>(Resource.Id.ch2003_textView1); imageView1 = FindViewById<ImageView>(Resource.Id.ch2003_imageView1); videoView1 = FindViewById<VideoView>(Resource.Id.ch2003_videoView1); Button btn1 = FindViewById<Button>(Resource.Id.ch2003_btn1); Button btn2 = FindViewById<Button>(Resource.Id.ch2003_btn2); //判断相机是否可用(是否有一个App正在准备拍照) if (IsThereAnAppToTakePictures()) { dirPath = $"{Environment.ExternalStorageDirectory.Path}/{Environment.DirectoryPictures}/MyDemosPictures"; if (!System.IO.Directory.Exists(dirPath)) { System.IO.Directory.CreateDirectory(dirPath); } btn1.Click += delegate { //拍照 mediaType = MediaType.Image; Intent imageIntent = new Intent(MediaStore.ActionImageCapture); filePath = dirPath + $"/PP{System.DateTime.Now:yyyyMMdd_hhmmss}.jpg"; file = new File(filePath); imageIntent.PutExtra(MediaStore.ExtraOutput, Uri.FromFile(file)); StartActivityForResult(imageIntent, 100); }; btn2.Click += delegate { //视频录制 mediaType = MediaType.Video; Intent videoIntent = new Intent(MediaStore.ActionVideoCapture); filePath = dirPath + $"/PP{System.DateTime.Now:yyyyMMdd_hhmmss}.mp4"; file = new File(filePath); videoIntent.PutExtra(MediaStore.ExtraOutput, Uri.FromFile(file)); videoIntent.PutExtra(MediaStore.ExtraVideoQuality, 1); StartActivityForResult(videoIntent, 200); }; } else { //如果相机不可用,禁用按钮 btn1.Text = "相机不可用,无法拍照"; btn2.Text = "相机不可用,无法录制视频"; btn1.Enabled = btn2.Enabled = false; } } /// <summary> /// 判断相机是否可用(是否有一个App正在准备拍照) /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> private bool IsThereAnAppToTakePictures() { Intent intent = new Intent(MediaStore.ActionImageCapture); IList<ResolveInfo> availableActivities = PackageManager.QueryIntentActivities(intent, PackageInfoFlags.MatchDefaultOnly); return availableActivities != null && availableActivities.Count > 0; } protected override void OnActivityResult(int requestCode, [GeneratedEnum] Result resultCode, Intent data) { base.OnActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data); // 使其可以在图库中可用,即浏览图库时能看到相机拍摄的照片 Intent mediaScanIntent = new Intent(Intent.ActionMediaScannerScanFile); Uri contentUri = Uri.FromFile(file); mediaScanIntent.SetData(contentUri); SendBroadcast(mediaScanIntent); if(mediaType== MediaType.Image) { imageView1.Visibility = Android.Views.ViewStates.Visible; videoView1.Visibility = Android.Views.ViewStates.Gone; //辅助程序(ch2003BitmapHelpers.cs)会自动缩放该图片以适应屏幕大小。 int width = Resources.DisplayMetrics.WidthPixels; int height = imageView1.Height; using (Bitmap bitmap = ch2003BitmapHelpers.LoadAndResizeBitmap(filePath, width, height)) { ch2003BitmapHelpers.RecycleBitmap(imageView1); imageView1.SetImageBitmap(bitmap); imageView1.RefreshDrawableState(); } textView1.Text = "拍照结果:\n" + filePath; } else { imageView1.Visibility = Android.Views.ViewStates.Gone; videoView1.Visibility = Android.Views.ViewStates.Visible; videoView1.SetVideoURI(Uri.Parse(filePath)); videoView1.SetMediaController(new MediaController(this)); videoView1.Start(); textView1.Text = "视频录制结果:\n" + filePath; } } } }
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/rainmj/p/5271167.html