标签:
一、Android四大组件
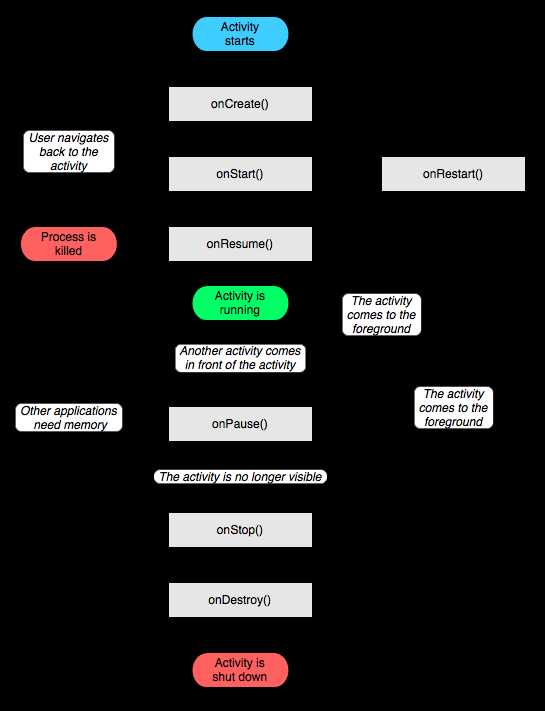
1. Activity
生命周期:
2. Service
生命周期:
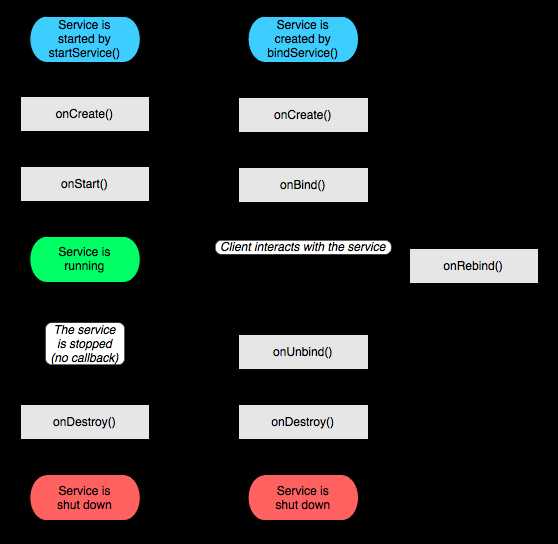
Service的生命周期长,没有用户界面,可以用来开发监控程序。
Service有两种调用方式:
通过Context.startService()调用Service,当调用者关闭时,Service不会关闭,只用通过Context.stopService()才能关闭。
通过Context.bindService()调用Service,当调用者关闭时,Service也会关闭,关闭Service需要使用Context.unbindService()
3. Broadcast Receiver
Broadcast Receiver的生命周期只有十几秒,所以不能在onReceive()中做耗时操作,否则会报ANR。也不能开子线程,因为可能子线程还没运行完Broadcast Receiver就结束了。应该通过发送Intent给Service来处理。
动态注册广播接收器会随着注册的Activity关闭后关闭;静态的广播接收器即便app关闭,只要设备是开启的,接收到广播后仍能够触发。
4. Content Provider
二、Android 异步
1. Handler负责线程间通信
Handler处于构建它的主线程中,可以在子线程中通过post(Runnalbe)或者sendMessage(msg)来通知主线程更新UI。
Runnable: 执行handler.post(Runnalble),Handler将Runnable放入MessageQueue中,一旦从MessageQueue中取出,Runnable可以自动运行它的Run方法来进行主线程的UI更新。
主要方法:
boolean post(Runnable r) :从消息队列中取出runnable后立即执行
boolean postAtTime(Runnable r, long uptimeMillis):从消息队列中取出runnable后,指定时间执行
boolean postDelayed(Runnable r, long delayMillis):从消息队列中取出runnable后,延迟一定时间执行
void removeCallbacks(Runnable r):从消息队列中删除runnable
Message: 执行handler.sendMessage()或者msg.sendToTarget(),Handler会将msg放入MessageQueue中,不过msg不能自动执行,需要重写Handler的handleMessage方法,通过获取msg中的信息进行UI更新。可以用setData(Bundle),其中Bundle可以通过putParcelable(String key, Parcelable value)和putSerializable(String key, Serializable value)传递对象。Message是一个final类不能继承。有四个参数arg1,arg2,obj,what。
主要方法:
Message obtainMessage:从消息池中获取一个msg
boolean sendMessage:发送一个消息到消息队列,从消息队列中取出后立即执行
boolean sendMessageDelayed:发送一个消息到消息队列,从消息队列中取出后延迟执行
boolean removeMessage:从消息队列中移除一个未响应到消息
Handler用法,开一个子线程,然后在Handler.post(Runnable)的run方法里面更新UI
public class MainActivity extends Activity { ProgressDialog progressDialog; Handler handler; Button btn; TextView tv; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); btn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.load_pic); tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv); progressDialog = new ProgressDialog(this); progressDialog.setTitle("提示"); progressDialog.setMessage("正在加载,请稍后..."); progressDialog.setCancelable(false); handler = new Handler(); btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { progressDialog.show(); new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(3000); System.out.println("执行完耗时操作"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } handler.post(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { tv.setText("执行完毕"); progressDialog.dismiss(); } }); } }).start(); } }); } }
Message用法
写法1 message.obtain()不传参数,需要调用handler.sendMessage(msg)发送msg
public class MainActivity extends Activity { ProgressDialog progressDialog; Handler handler; Button btn; TextView tv; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); btn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.load_pic); tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv); progressDialog = new ProgressDialog(this); progressDialog.setTitle("提示"); progressDialog.setMessage("正在加载,请稍后..."); progressDialog.setCancelable(false); handler = new Handler() { @Override public void handleMessage(Message msg) { Bundle bundle = msg.getData(); tv.setText(bundle.getString("tv")); progressDialog.dismiss(); } }; btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { progressDialog.show(); new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(3000); System.out.println("执行完耗时操作"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } Message msg = Message.obtain(); Bundle bundle = new Bundle(); bundle.putString("tv", "执行完毕"); msg.setData(bundle); handler.sendMessage(msg); } }).start(); } }); } }
写法2 Message.obtain(handler)传一个handler参数,这样可以直接调用msg.sendToTarget()方法,因为在message内部有一个Handler属性的Target,相当于给target赋值为Handler。
public class MainActivity extends Activity { ProgressDialog progressDialog; Handler handler; Button btn; TextView tv; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); btn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.load_pic); tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv); progressDialog = new ProgressDialog(this); progressDialog.setTitle("提示"); progressDialog.setMessage("正在加载,请稍后..."); progressDialog.setCancelable(false); handler = new Handler() { @Override public void handleMessage(Message msg) { Bundle bundle = msg.getData(); tv.setText(bundle.getString("tv")); progressDialog.dismiss(); } }; btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { progressDialog.show(); new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(3000); System.out.println("执行完耗时操作"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } Message msg = Message.obtain(handler); Bundle bundle = new Bundle(); bundle.putString("tv", "执行完毕"); msg.setData(bundle); msg.sendToTarget(); } }).start(); } }); } }
2. AsyncTask类
简单单一的异步操作
主要方法:
1. onPreExecute():由UI线程调用,异步操作开始执行之前调用
2. doInBackground():后台线程执行,处理耗时操作
3. onProgressUpdate():更新UI线程,在doInBackground中调用publicProgress()即可进行执行此方法
4. onPostExecute():UI线程调用,doInBackground()执行完之后调用
三、Android跨进程通信
利用四大组件实现:
1. Activity可以启动其他进程的Activity
在调用者Activity中使用Intent来启动被调用Activity,在被调用Activity中需要在AndroidManifest里面配置该Activity的action和data,action表示被调用Activity的字符串ID,data表示被调用Activity的访问协议Uri比如ok://abc。调用者Activity使用Intent(被调用Activity.Action, 被调用Activity.Uri)来启动其他进程中的Activity。被调用Activity中getIntent().getData()获得整体Uri, getIntent().getData().getHost()获取Uri主体也就是ok://后面的abc,可以借助intent发送数据。当然如果在被调用Activity中setResult可以返回给调用者Activity数据,也就是数据通信可以是双向的。
//调用者Activity里面实现 Intent intent = new Intent("com.wwwsealss.action.another", Uri.parse("ok://go and fight!")); intent.putExtra("value", "Hello world!"); startActivity(intent); finish(); //被调用者AndroidManifest里面注册 <activity android:name=".Main2Activity" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="com.wwwsealss.action.another" /> <data android:scheme="ok" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" /> </intent-filter> </activity> //被调用者Activity里面实现 if (getIntent().getData() != null) { //获取Uri主体部分和intent中传递的数据 tv.setText(getIntent().getData().getHost() + getIntent().getStringExtra("value")); }
2. Content Provider向其他应用共享数据,并且允许其他应用对数据的增删改查
3. BroadCast 一个应用作为电台发送广播,其他应用作为收音机接收广播,但不能和电台进行通信,只能被动接收。
//通过intent发送广播,需要加Action Intent intent = new Intent("com.wwwsealss.receivebroadcast"); intent.putExtra("value", "Hello World!"); sendBroadcast(intent); //注册广播接收器 public class MyReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver { public MyReceiver() { } @Override public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) { String get = intent.getStringExtra("value"); Toast.makeText(context, get, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); Intent it = new Intent(context, MainActivity.class); //如果没有传入Activity的上下文需要加个标志 it.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK); context.startActivity(it); } } //在AndroidManifest中注册Receiver <receiver android:name=".MyReceiver" android:enabled="true" android:exported="true" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="com.wwwsealss.receivebroadcast" /> </intent-filter> </receiver>
4. AIDL是进程间通信的服务,首先需要在服务端创建AIDL文件(是一个接口,里面的抽象方法就是共享给客户端的),编译后会生成对应的java文件。然后定义一个service,在其中完成AIDL接口的实现类(实现其内部的抽象方法),然后重写service的onbind方法,让其返回该AIDL实现类的实例化对象,这样一来就完成了服务端。然后将AIDL文件放到客户端工程中,注意AIDL所在文件的包名必须和服务端中的包名一致,然后定义serviceConnecton用于在绑定服务端后获取其onbind方法返回的AIDL实现类的实例化对象(共享对象)。
//创建AIDL文件 interface IMyAidlInterface { String getValue(); } //定义服务端 public class MyService extends Service { //实现AIDL接口中的方法 public class MyAidlInterface extends IMyAidlInterface.Stub { @Override public String getValue() throws RemoteException { return "从AIDL服务获取的值"; } } public MyService() { } //绑定该服务后返回AIDL接口的实现类的实例 @Override public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { return new MyAidlInterface(); } } //在客户端中实现 btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) {
//通过intent Action绑定服务端 bindService(new Intent("com.example.administrator.findjob.IMyAidlInterface"), serviceConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE); } }); //定义AIDL接口用于获取发送过来的接口实现类 private IMyAidlInterface myAidlInterface = null; //建立一个服务连接对象用于获取服务端onbind返回值 private ServiceConnection serviceConnection = new ServiceConnection() { @Override public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
//获取AIDL接口实现类对象 myAidlInterface = IMyAidlInterface.Stub.asInterface(service); //调用AIDL接口实现类对象中的方法 try { Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, myAidlInterface.getValue(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } catch (RemoteException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) { } };
三、Android自定义控件
三、Android系统框架
1. Linux Kernel 内核层
2. Hardware Abstraction Layer 硬件抽象层
3. Libraries and Runtime 系统运行库层
4. Application Framework 应用程序框架层
5. Application 应用程序层
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/wwwsealss/p/5231813.html