标签:
http://fabiensanglard.net/bumpMapping/index.php
March 19th, 2009
BumpMapping with GLSL
 When I got started learning bump mapping and parallax mapping, I found a lot of tutorial involving a simple rectangle but nothing close to real life usage:
When I got started learning bump mapping and parallax mapping, I found a lot of tutorial involving a simple rectangle but nothing close to real life usage:
This is my attemps to fill the gap.
Concept
BumpMapping allows designers to express their creativity through a
100,000+ polygons creature. Once art is done, a low poly model (5000
polygons) is automatically generated along with a normal map.

At runtime, details are added back by combining the low model with the normal map.
Illumination model.
Details are added back to the low poly via surface reaction to the light. The illumination equation is Blinn-Phong where:
pixelColor= Ambient + (Diffuse + Specular) * Shadow ( but let‘s forget about shadow).
Ambient = ambientMaterial * ambientLight
Diffuse = diffuseMaterial * diffuseLight * lamberFactor
lamberFactor = max (dot (lightVec, normal), 0.0)
Specular = specularMaterial * specularLight * speculatCoef
speculatCoef = pow (max (dot (halfVec, normal), 0.0), shininess)
Details:
- Ambient is pretty much a constant.
- Diffuse depends on the angle between the light vector and the surface normal vector.
- Specular depends on the angle between the eye vector and the surface normal vector.
Note: As we deal with normal vectors, a cosinus can be obtained with a simple dot product.
Usually, every calculations are done in eye space, but in bump
mapping the normal vector from the normal map are expressed in Tangent
space.
We hence need to transform all of the vectors requiered . In order
to do this, we use a matrix: Eye space -> Tangent space.
Tangent space maths.
The matrix for each vertex is as follow:
[ Normal.x Normal.y Normal.z ]
[ BiNormal.x BiNormal.y BiNormal.z ]
[ Tangent.x Tangent.y Tangent.z ]
Normal is easy to calculate. A simple cross-product per face. The normal for a vertex is equal to the sum of normals (all faces related to this vertex), normalized at the end.
for each faces in model
{
generate the face‘s normal via cross product
fore each vertex in the face, add the normal vector
}
for each vertices in model
normalize normal vector
For the tangent and binormal, you can find the solution in any good math book ( I highly recommend Mathematics for 3D Game Programming ). Here is a code sample:
generateNormalAndTangent(float3 v1, float3 v2, text2 st1, text2 st2)
{
float3 normal = v1.crossProduct(v2);
float coef = 1/ (st1.u * st2.v - st2.u * st1.v);
float3 tangent;
tangent.x = coef * ((v1.x * st2.v) + (v2.x * -st1.v));
tangent.y = coef * ((v1.y * st2.v) + (v2.y * -st1.v));
tangent.z = coef * ((v1.z * st2.v) + (v2.z * -st1.v));
float3 binormal = normal.crossProduct(tangent);
}
Just like normals: tangents and binormals are accumulated for each
faces connected to this vertex and then averaged via normalization.
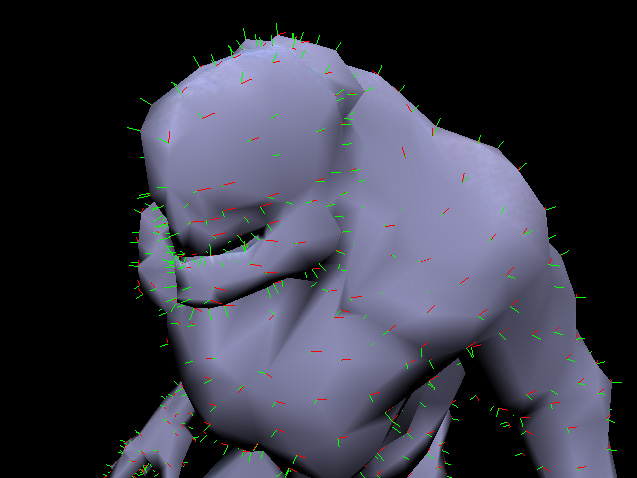
In your implementation, try to visualize the vectors you generate,
they need to be consistant because they will be interpolated by the GPU.

CPU side
On the openGL side, a few things have to be done:
- Bind the vertex array
- Bind the normal array
- Bind the texture coordinate array
- Bind the elements index array
- Bind the tangent array to the shader
- Bind the color texture
- Bind the normalmap texture (bump mapping)
- Bind the heightmap texture (parallax mapping)
// The vertex VBO is updated every frame for animation purpose
glBindBufferARB(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER_ARB,vboVertexId);
glVertexPointer (3, GL_FLOAT, 0, 0);
// Same as vertex VBO: updated every frames
glBindBufferARB(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER_ARB,vboNormalId);
glNormalPointer(GL_FLOAT,0, 0);
// VBO, created and populated once, texture coordinate never change
glBindBufferARB(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER_ARB,vboTexturId);
glTexCoordPointer(2,GL_FLOAT,0,0);
// Tangent generated previously, no need to pass the binormal, a cross product will generate it
glVertexAttribPointerARB(tangentLoc, 3, GL_FLOAT,GL_FALSE, 0, tangentArraySkinPointer);
// VBO, created and populated once, elements to draw never change
glBindBufferARB(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER_ARB,vboElementsId);
glDrawElements (GL_TRIANGLES, meshes[i].facesCount * 3 , GL_UNSIGNED_INT, 0);
glActiveTextureARB(GL_TEXTURE0);
glBindTexture(diffuseTextureId);
glUniform1iARB(diffuseTextureUniform,0);
glActiveTextureARB(GL_TEXTURE1);
glBindTexture(normalTextureId);
glUniform1iARB(normalTextureUniform,0);
glActiveTextureARB(GL_TEXTURE2);
glBindTexture(heightTextureId);
glUniform1iARB(heightTextureUniform,0);
GPU side
The role of the vertex shader is to build the matrix and rotate vectors used in Blinn-Phong model, hence:
- Generate the bi-tangent with a cross-product from normal and tangent.
- Assemble the three vectors to form a rotation matrix, from camera space to tangent space.
- Rotate light and camera vectors.
In the fragment shader:
- Retrieve the normal coordinate from the normal map texture.
- Convert value from [-1,1] to [0,1].
- Calculate angles, generate ambiant, diffuse and specular.
- Add ambiant, diffuse and specular component.
Vertex shader
attribute vec3 tangent;
varying vec3 lightVec;
varying vec3 halfVec;
varying vec3 eyeVec;
void main()
{
gl_TexCoord[0] = gl_MultiTexCoord0;
// Building the matrix Eye Space -> Tangent Space
vec3 n = normalize (gl_NormalMatrix * gl_Normal);
vec3 t = normalize (gl_NormalMatrix * tangent);
vec3 b = cross (n, t);
vec3 vertexPosition = vec3(gl_ModelViewMatrix * gl_Vertex);
vec3 lightDir = normalize(gl_LightSource[0].position.xyz - vertexPosition);
// transform light and half angle vectors by tangent basis
vec3 v;
v.x = dot (lightDir, t);
v.y = dot (lightDir, b);
v.z = dot (lightDir, n);
lightVec = normalize (v);
v.x = dot (vertexPosition, t);
v.y = dot (vertexPosition, b);
v.z = dot (vertexPosition, n);
eyeVec = normalize (v);
vertexPosition = normalize(vertexPosition);
/* Normalize the halfVector to pass it to the fragment shader */
// No need to divide by two, the result is normalized anyway.
// vec3 halfVector = normalize((vertexPosition + lightDir) / 2.0);
vec3 halfVector = normalize(vertexPosition + lightDir);
v.x = dot (halfVector, t);
v.y = dot (halfVector, b);
v.z = dot (halfVector, n);
// No need to normalize, t,b,n and halfVector are normal vectors.
//normalize (v);
halfVec = v ;
gl_Position = ftransform();
}
Fragment shader
uniform sampler2D diffuseTexture;
uniform sampler2D normalTexture;
// New bumpmapping
varying vec3 lightVec;
varying vec3 halfVec;
varying vec3 eyeVec;
void main()
{
// lookup normal from normal map, move from [0,1] to [-1, 1] range, normalize
vec3 normal = 2.0 * texture2D (normalTexture, gl_TexCoord[0].st).rgb - 1.0;
normal = normalize (normal);
// compute diffuse lighting
float lamberFactor= max (dot (lightVec, normal), 0.0) ;
vec4 diffuseMaterial = 0.0;
vec4 diffuseLight = 0.0;
// compute specular lighting
vec4 specularMaterial ;
vec4 specularLight ;
float shininess ;
// compute ambient
vec4 ambientLight = gl_LightSource[0].ambient;
if (lamberFactor > 0.0)
{
diffuseMaterial = texture2D (diffuseTexture, gl_TexCoord[0].st);
diffuseLight = gl_LightSource[0].diffuse;
// In doom3, specular value comes from a texture
specularMaterial = vec4(1.0) ;
specularLight = gl_LightSource[0].specular;
shininess = pow (max (dot (halfVec, normal), 0.0), 2.0) ;
gl_FragColor = diffuseMaterial * diffuseLight * lamberFactor ;
gl_FragColor += specularMaterial * specularLight * shininess ;
}
gl_FragColor += ambientLight;
}
Results




Note: The shadow component is not in the shader snippet but you can find it in the downloaded code.
Video
The video shows a 2000 polygons Hellknight:
- Raw model.
- Model with 512x512 bump mapping.
- Model with 512x512 bump mapping and diffuse/specular mapping.
- Model with 512x512 bump mapping and diffuse/specular mapping and shadow.
The code features a C++ md5 model viewer, you can configure a lot
via config.cfg and define the scene in scene.cfg. I included the
hellknight md5 so anybody can run the demo, I hope this will be
tolerated as a matter of educationnal purpose.
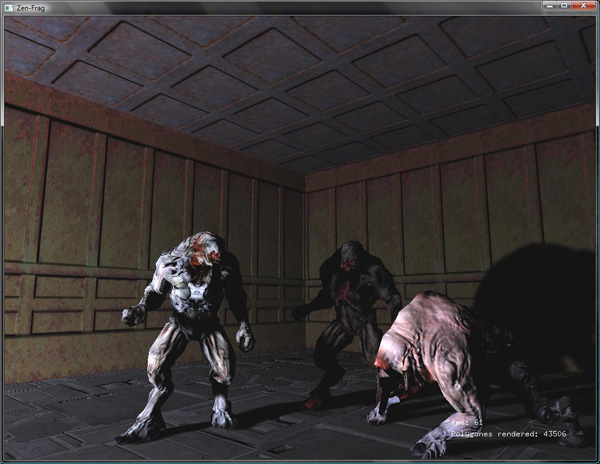

An example of configuration for ZenFrag engine.
Downloads
April, 5 2010 : It seems the binary distribution doesn‘t work with Windows 7. I‘ll have to take a look at this as soon as I have some time.
Recommended reading
A few books to learn more about bump mapping and parallax mapping.
Doom3 is a great ressource to learn as well, every models are easily
accessible and in plain text.



-
SomeGuy • 5 years ago
Hi,
Thanks for the useful tutorial. I am trying to work with shaders in Android (OpenGL ES 2.0) and thought I might implement Bump mapping as an example. I‘m a tad confused about generating the tangents for each vertex.
I‘m exporting OBJ files with vertex positions, normals and texture coordinates and then reading them in my program. I‘m just wondering why I need two texture coordinates to generate the tangent? Shouldn‘t one set of texture coordinates be enough?
Thanks.
-
Fabien Sanglard • 5 years ago
SomeGuy,
You need two texture coordinates and two points so all tangents will be consistent with each other (and SO interpolation on the varying will work !!).
Fabien
-
cvk • 4 years ago
Hi there. Question about your shaders there.
I noticed that you go to some lengths to compute eyeVec in the vertex shader, but it‘s not actually used in the fragment shader. What‘s that vector useful for?
Cheers!
-
Fabien Sanglard • 4 years ago
@cvk:
It is a debug artefact. Nice catch.
Fab
-
Dawid • 4 years ago
Hi, I am writing my first shader, I do it in Stage3D so openGL is not exactly my thing but I do get around it. Anyway I have a question about Tangent vectors calculation. In your text above you are saying that it is done in the game program before sending it to the GPU.
I am just trying to visualize what happens when mesh gets deformed and some vertices change their positions, then this Tangent vector array will need to be recalculated again. But I would say only when deformation happens, with the translation, rotation and scaling there would be no need to do so.
Am I right here?
-
Jorro • 4 years ago
Hi Fabien,
why "vec3 lightdir" is
gl_LightSource[0].position.xyz - vertexPosition
instead of
vertexPosition - gl_LightSource[0].position.xyz ?
I
understand that you want the vector from lightposition to the vertex,
and as far as I understand the vector subtraction operation A - B is a
vector from "BHead" to "AHead", right? I know you‘re correct, and I‘ve
seen the same equation in other resources, but I just don‘t get it. I
hope you can make this concept clearer. thanks
-
Matti
•
4 years ago
Hmm.. how would you handle models with precalculated normals and no shared vertices? What I‘m trying is
-
calculate the Tangent vector for the triangle; since the normal has
already been "smoothed" by the modeling software (and not calculated
here), the vectors are not perpendicular (90deg angle), so:
--> Adjust the Tangent for each of the triangle‘s vertices via Binormal as such:
B = N x T, T‘ = N x B --> This way TNB form a proper orthogonal base --> save this base for each vertex
..yet this is not quite working properly.
-
Laetitia
•
3 years ago
Hi,
Many thanks for this nice tutorial. I would like to ask you
something. You were talking about ‘Automatically generated low poly
model with 5000 polygons‘. How do you do that? Is there a program for
that?
Thank you :)
-
Fei
•
3 years ago
I don‘t understand, how do you configure the mapper to create scenes like the one in your example screenshot?
In other words, how do you put two hell knights in the scene and use wall, ceiling and floor textures?
-
Fei
•
3 years ago
In the Mac OS X release, where are the other md5anim and monster data files???
The only monster is Hell Knight, but the config.txt mentions pinky, zfat, zombies and imp, which I guess are other monsters.
For
the Hell Knight, there is only the idle2 md5anim. However, in the
config.txt, it mentions md5anim‘s including roar1, walk7, stand and
turret_attack.
Why?!?!
-
Jedd Haberstro
•
2 years ago
Noticed a small typo:
"Convert value from [-1,1] to [0,1]."
should read as:
"Convert value from [0,1] to [-1,1]."
Otherwise, thanks for the write up!
-
sakrist
•
a year ago
How about add checks for NaN in generateNormalAndTangent?
Because after this line, could be NaN
float coef = 1/ (st1.u * st2.v - st2.u * st1.v);
-
uk superior papers review
•
a month ago
This information looks pretty helpful to learn for those people who
love to do such kind of work. They can surely gain a lot of skills on
how are they going to do such kind of thing that will help them with
their studies and with their work. It would also be a good thing for
them that would totally help them to succeed.
BumpMapping [转]
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/mazhenyu/p/5331744.html











