标签:
机器学习可分为监督学习和无监督学习。有监督学习就是有具体的分类信息,比如用来判定输入的是输入[a,b,c]中的一类;无监督学习就是不清楚最后的分类情况,也不会给目标值。
K-近邻算法属于一种监督学习分类算法,该方法的思路是:如果一个样本在特征空间中的k个最相似(即特征空间中最邻近)的样本中的大多数属于某一个类别,则该样本也属于这个类别。
需要进行分类,分类的依据是什么呢,每个物体都有它的特征点,这个就是分类的依据,特征点可以是很多,越多分类就越精确。
机器学习就是从样本中学习分类的方式,那么就需要输入我们的样本,也就是已经分好类的样本,比如特征点是A , B2个特征,输入的样本甲乙丙丁,分别为[[1.0, 1.1], [1.0, 1.0], [0., 0.], [0.0, 0.1]]。 那么就开始输入目标值,当然也要给特征了,最终的目标就是看特征接近A的多还是B的多,如果把这些当做坐标,几个特征点就是几纬坐标,那么就是坐标之间的距离。那么问题来了,要怎么看接近A的多还是B的多。
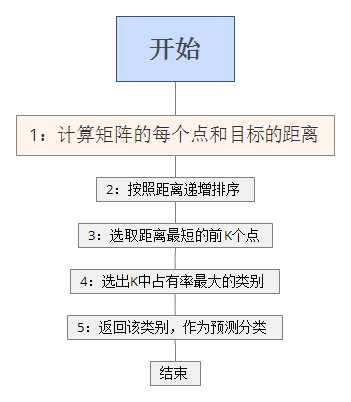
我就直接贴代码了,基于python,首先输入特征量labels和样本group。
一开始需要导入的模块
1 #coding=utf-8 2 3 #科学计算包 4 #from numpy import * 5 import numpy 6 #运算符模块 7 import operator
数据样本和分类模拟
1 #手动建立一个数据源矩阵group,和数据源的分类结果labels 2 def createDataSet(): 3 group = numpy.array([[1.0, 1.1], [1.0, 1.0], [5., 2.], [5.0, 0.1]]) 4 labels = [‘A‘, ‘A‘, ‘B‘, ‘B‘] 5 return group, labels
然后进行KNN算法。
1 # newInput为输入的目标,dataset是样本的矩阵,label是分类,k是需要取的个数 2 def kNNClassify(newInput, dataSet, labels, k): 3 #读取矩阵的行数,也就是样本数量 4 numSamples = dataSet.shape[0] 5 print ‘numSamples: ‘ ,numSamples 6 7 #变成和dataSet一样的行数,行数=原来*numSamples,列数=原来*1 ,然后每个特征点和样本的点进行相减 8 diff = numpy.tile(newInput, (numSamples, 1)) - dataSet 9 print ‘diff: ‘,diff 10 11 #平方 12 squaredDiff = diff ** 2 13 print "squaredDiff: ",squaredDiff 14 15 #axis=0 按列求和,1为按行求和 16 squaredDist = numpy.sum(squaredDiff, axis = 1) 17 print "squaredDist: ",squaredDist 18 19 #开根号,距离就出来了 20 distance = squaredDist ** 0.5 21 print "distance: ",distance 22 23 #按大小逆序排列 24 sortedDistIndices = numpy.argsort(distance) 25 print "sortedDistIndices: ",sortedDistIndices 26 27 classCount = {} 28 for i in range(k): 29 #返回距离(key)对应类别(value) 30 voteLabel = labels[sortedDistIndices[i]] 31 print "voteLabel: " ,voteLabel 32 33 # 取前几个K值,但是K前几个值的大小没有去比较,都是等效的 34 classCount[voteLabel] = classCount.get(voteLabel, 0) + 1 35 print "classCount: " ,classCount 36 maxCount = 0 37 #返回占有率最大的 38 sortedClassCount=sorted(classCount.iteritems(),key=operator.itemgetter(1),reverse=True) 39 40 return sortedClassCount[0][0]
最后进行测试
1 dataSet, labels = createDataSet() 2 3 testX = numpy.array([0, 0]) 4 k = 3 5 outputLabel = kNNClassify(testX, dataSet, labels, k) 6 print "Your input is:", testX, "and classified to class: ", outputLabel
可以发现输出
1 numSamples: 4 2 diff: [[-1. -1.1] 3 [-1. -1. ] 4 [-5. -2. ] 5 [-5. -0.1]] 6 squaredDiff: [[ 1.00000000e+00 1.21000000e+00] 7 [ 1.00000000e+00 1.00000000e+00] 8 [ 2.50000000e+01 4.00000000e+00] 9 [ 2.50000000e+01 1.00000000e-02]] 10 squaredDist: [ 2.21 2. 29. 25.01] 11 distance: [ 1.48660687 1.41421356 5.38516481 5.0009999 ] 12 sortedDistIndices: [1 0 3 2] 13 voteLabel: A 14 voteLabel: A 15 voteLabel: B 16 classCount: {‘A‘: 2, ‘B‘: 1} 17 Your input is: [0 0] and classified to class: A
这里我之前一直有个疑问,关于K的取值,结果也许跟K的取值产生变化,只要在K的取值范围内们所有特征点距离远近也就没有关系了。所以才叫K近邻分类算法
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/ssss429170331/p/5353416.html