Spring有7种事务传播机制,本文主要用实例说明各种传播机制的事务效果,和发生异常的回滚方式。7种事务传播机制网上的资料大多都是如下的描述:
事务传播行为类型 | 说明 |
PROPAGATION_REQUIRED | 如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务,如果已经存在一个事务中,加入到这个事务中。这是最常见的选择。 |
PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS | 支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行。 |
PROPAGATION_MANDATORY | 使用当前的事务,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常。 |
PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW | 新建事务,如果当前存在事务,把当前事务挂起。 |
PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED | 以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起。 |
PROPAGATION_NEVER | 以非事务方式执行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常。 |
PROPAGATION_NESTED | 如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行。如果当前没有事务,则执行与PROPAGATION_REQUIRED类似的操作。 |
首先我们要明确几点基本知识:
①事务传播机制只适用于不同bean之间方法的调用,如果一个bean中的两个方法互相调用并不会使用到事务传播。比如,一个bean的method1的事务传播级别为Required,method2的事务传播级别为Never,我们在method1里面调用method2。首先method1会开启一个事务,而method2也没有报错并正确执行了,说明事务传播机制在一个bean自己的方法互相调用中并不起作用,只要一个方法开启了事务,那这个在方法里调用当前bean的其他方法都在这个事务中运行,而不管其他方法的事务传播机制是如何配置的。
②事务方法里如果抛RuntimeException,则会导致所有相关事务回滚,个别事务传播机制有点特殊,我们下面会讲到。
③事务方法里如果抛Throwable或者Exception,默认不会导致相关事务回滚,一般都会在出异常的地方提交,就有可能出现部分提交的问题。但可以配置rollback-for属性来控制。
本文测试基于MySQL,默认事务隔离级别为Repeatable Read,并且只讨论不同bean之间方法调用的事务传播机制。基本的测试类如下:
父事务类:
@Component
public class TransactionSuper {
@Autowired
TransactionSub transactionSub;
String insertSuperTable1 = "insert into super_table values (1, ‘super1‘)";
String insertSuperTable2 = "insert into super_table values (2, ‘super2‘)";
public void insertSuperTable(AbstractApplicationContext ctx) throws Exception{
System.out.println("========insertSuperTable start========");
JdbcTemplate jt = (JdbcTemplate)ctx.getBean("jdbcTemplate");
jt.execute(insertSuperTable1);
transactionSub.insertSubTable(ctx);
jt.execute(insertSuperTable2);
System.out.println("========insertSuperTable end========");
}
}子事务类:
@Component
public class TransactionSub {
String insertSubTable1 = "insert into sub_table values (1, ‘sub1‘)";
String insertSubTable2 = "insert into sub_table values (2, ‘sub2‘)";
public void insertSubTable(AbstractApplicationContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("========insertSubTable start========");
JdbcTemplate jt = (JdbcTemplate) ctx.getBean("jdbcTemplate");
jt.execute(insertSubTable1);
jt.execute(insertSubTable2);
System.out.println("========insertSubTable end========");
}
}异常抛出类:
public class ExceptionUtils {
public static void throwThrowable() throws Throwable{
throw new Throwable("+++++++++++MyThrowable++++++++++");
}
public static void throwException() throws Exception{
throw new Exception("+++++++++++MyException++++++++++");
}
public static void thowRuntimeException(){
throw new RuntimeException("+++++++++++MyRuntimeException++++++++++");
}
}测试类:
public class SpringTxTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
AbstractApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"com/jaeger/springtest/txtest/SpringTxTest.xml");
TransactionSuper ts = (TransactionSuper) ctx.getBean("transactionSuper");
ts.insertSuperTable(ctx);
ctx.close();
}
}Spring配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.2.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="com.jaeger.springtest.txtest"> </context:component-scan> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/java_web_core?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8" /> <property name="username" value="root" /> <property name="password" value="root" /> </bean> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <!--我们只要关注这部分配置就可以了--> <tx:attributes> <tx:method name="insertSuperTable" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="insertSubTable" propagation="NEVER"/> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <aop:config> <aop:advisor pointcut="execution(public * com.jaeger.springtest.txtest.TransactionSuper.*(..))" advice-ref="txAdvice"/> <aop:advisor pointcut="execution(public * com.jaeger.springtest.txtest.TransactionSub.*(..))" advice-ref="txAdvice"/> </aop:config> </beans>
super_table表:
sub_table表:
1. NEVER
我们先从比较简单的NEVER开始,被该属性标注的方法,就说明该方法不能运行在任何事务中。如果有事务存在则报错,并且让所有事务回滚。我们直接运行上面的测试方法,日志如下:
2. MANDATORY
被该属性标注的方法,就说明该方法必须运行在事务中,如果没有事务则报错。我们更改上面的配置文件为:
<tx:attributes> <!-- <tx:method name="insertSuperTable" propagation="REQUIRED"/> --> <tx:method name="insertSubTable" propagation="MANDATORY"/> </tx:attributes>
运行测试方法,得到如下日志,可以明显看出因为没有父事务所以子事务报错了。但插入了super1,因为insertSuperTable方法没有事务,所以也不会回滚。
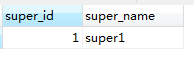
我们把上面的配置文件还原,给insertSuperTable方法加上事务。
<tx:attributes> <tx:method name="insertSuperTable" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="insertSubTable" propagation="MANDATORY"/> </tx:attributes>
再次运行测试方法,插入成功:
从上面可以看出MANDATORY是以和父事务共用connection的方式加入父事务,所以父事务对数据库的修改对子事务是可见的,因为他们本来就是一个事务。如果中间出现异常,它会怎么处理呢,我们下面就来看看。
①RuntimeException
修改父子事务类的方法如下,我们先让insertSubTable方法抛出一个RuntimeException:
父事务类:
@Component
public class TransactionSuper {
@Autowired
TransactionSub transactionSub;
String insertSuperTable1 = "insert into super_table values (1, ‘super1‘)";
String insertSuperTable2 = "insert into super_table values (2, ‘super2‘)";
public void insertSuperTable(AbstractApplicationContext ctx) throws Exception{
System.out.println("========insertSuperTable start========");
JdbcTemplate jt = (JdbcTemplate)ctx.getBean("jdbcTemplate");
jt.execute(insertSuperTable1);
transactionSub.insertSubTable(ctx);
jt.execute(insertSuperTable2);
System.out.println("========insertSuperTable end========");
}
}子事务类:
@Component
public class TransactionSub {
String insertSubTable1 = "insert into sub_table values (1, ‘sub1‘)";
String insertSubTable2 = "insert into sub_table values (2, ‘sub2‘)";
public void insertSubTable(AbstractApplicationContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("========insertSubTable start========");
JdbcTemplate jt = (JdbcTemplate) ctx.getBean("jdbcTemplate");
jt.execute(insertSubTable1);
ExceptionUtils.thowRuntimeException(); //这里抛出RuntimeException
jt.execute(insertSubTable2);
System.out.println("========insertSubTable end========");
}
}执行测试方法:
②Throwable和Exception
让insertSubTable方法抛出一个Exception,因为抛出Throwable和Exception效果都一样,Spring都当是非运行时异常,所以后面我们都以Exception为例。
子事务类:
@Component
public class TransactionSub {
String insertSubTable1 = "insert into sub_table values (1, ‘sub1‘)";
String insertSubTable2 = "insert into sub_table values (2, ‘sub2‘)";
public void insertSubTable(AbstractApplicationContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("========insertSubTable start========");
JdbcTemplate jt = (JdbcTemplate) ctx.getBean("jdbcTemplate");
jt.execute(insertSubTable1);
ExceptionUtils.throwException();;、 //这里抛出Exception
jt.execute(insertSubTable2);
System.out.println("========insertSubTable end========");
}
}执行测试方法:
可以看出上面出现了部分提交的现象,这并不是我们想要看到的,但我们可以用rollback-for属性来控制。注意rollback-for属性只针对Exception和Throwable,对RuntimeException没有作用,因为发生RuntimeException事务一定会回滚。下面我们修改下配置文件:
<tx:attributes> <tx:method name="insertSuperTable" propagation="REQUIRED"/> <tx:method name="insertSubTable" propagation="MANDATORY" rollback-for="Exception"/> </tx:attributes>
执行测试方法:
rollback-for属性只要发生指定异常类或者其子类异常都会回滚,所以这里我们用rollback-for="Throwable"也可以让Exception回滚。
本文出自 “銅鑼衛門” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://jaeger.blog.51cto.com/11064196/1761660
原文地址:http://jaeger.blog.51cto.com/11064196/1761660