标签:
一、第一句Python代码
[root@localhost ~]# vim first.py print("Hello World!") [root@localhost ~]# python first.py Hello World!
python内部执行过程如下:
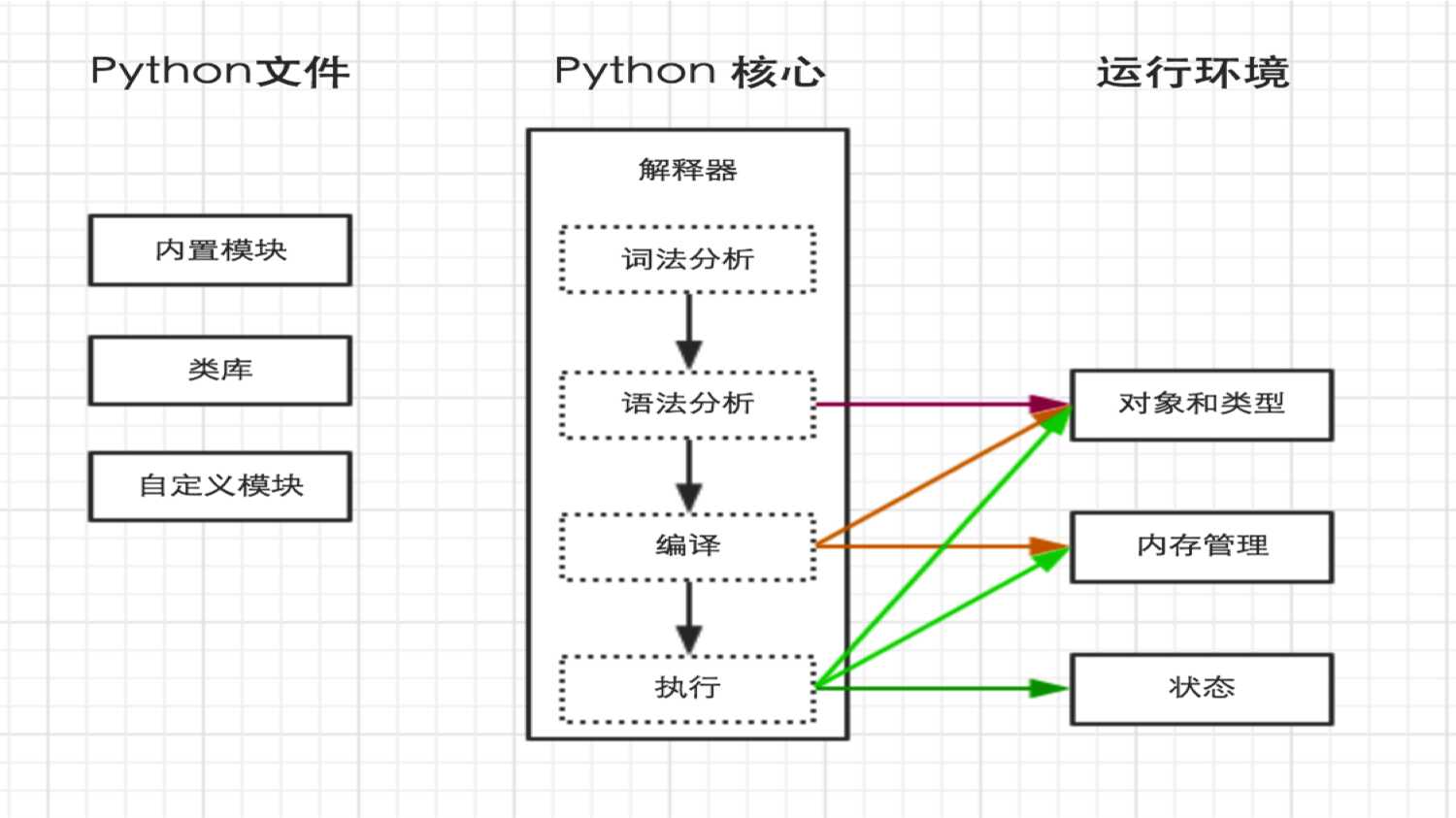
二、注释
单行注释:#被注释内容
多行注释:"""被注释内容"""
三、脚本传参
Python有大量的模块,从而使得开发Python程序非常简洁。类库有包括三中:
Python内部提供一个 sys 的模块,其中的 sys.argv 用来捕获执行执行python脚本时传入的参数,argv类型为列表。
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 4 import sys 5 6 print sys.argv
[root@KVMserver ~]# python argv.py
[‘argv.py‘]
[root@KVMserver ~]# python argv.py 8080
[‘argv.py‘, ‘8080‘]
四、变量
1 name = "flash" 2 print(name) #打印变量的值 3 4 r=r‘\n‘ # 输出时原型打印 5 u=u‘中文‘ # 定义为unicode编码 6 global x # 全局变量 7 a = 0 or 2 or 1 # 布尔运算赋值,a值为True既不处理后面,a值为2. None、字符串‘‘、空元组()、空列表[],空字典{}、0、空字符串都是false 8 name = raw_input("input:").strip() # 输入字符串变量 9 num = int(raw_input("input:").strip()) # 输入字符串str转为int型 10 locals() # 所有局部变量组成的字典 11 locals().values() # 所有局部变量值的列表 12 os.popen("date -d @{0} +‘%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S‘".format(12)).read() # 特殊情况引用变量 {0} 代表第一个参数
打印
1 # 字符串 %s 整数 %d 浮点 %f 原样打印 %r 2 print ‘字符串: %s 整数: %d 浮点: %f 原样打印: %r‘ % (‘aa‘,2,1.0,‘r‘) 3 print ‘abc‘, # 有逗号,代表不换行打印,在次打印会接着本行打印
列表
2 shoplist = [‘apple‘, ‘mango‘, ‘carrot‘, ‘banana‘] 3 shoplist[2] = ‘aa‘ 4 del shoplist[0] 5 shoplist.insert(‘4‘,‘www‘) 6 shoplist.append(‘aaa‘) 7 shoplist[::-1] # 倒着打印 对字符翻转串有效 8 shoplist[2::3] # 从第二个开始每隔三个打印 9 ‘\t‘.join(li) # 将列表转换成字符串 10 list(set([‘qwe‘, ‘as‘, ‘123‘, ‘123‘])) # 将列表通过集合去重复
元组
1 # 列表元素的个数最多 536870912 2 shoplist = [‘apple‘, ‘mango‘, ‘carrot‘, ‘banana‘] 3 shoplist[2] = ‘aa‘ 4 del shoplist[0] 5 shoplist.insert(‘4‘,‘www‘) 6 shoplist.append(‘aaa‘) 7 shoplist[::-1] # 倒着打印 对字符翻转串有效 8 shoplist[2::3] # 从第二个开始每隔三个打印 9 ‘\t‘.join(li) # 将列表转换成字符串 10 list(set([‘qwe‘, ‘as‘, ‘123‘, ‘123‘])) # 将列表通过集合去重复
字典
1 ab = { ‘Swaroop‘ : ‘swaroopch@byteofpython.info‘, 2 ‘Larry‘ : ‘larry@wall.org‘, 3 } 4 ab[‘c‘] = 80 # 添加字典元素 5 del ab[‘Larry‘] # 删除字典元素 6 ab.keys() # 查看所有键值 7 ab.values() # 打印所有值 8 ab.has_key(‘a‘) # 查看键值是否存在 9 ab.items() # 返回整个字典列表
流程结构
1 if判断 2 3 # 布尔值操作符 and or not 实现多重判断 4 if a == b: 5 print ‘==‘ 6 elif a < b: 7 print b 8 else: 9 print a 10 fi 11 12 while循环 13 14 while True: 15 if a == b: 16 print "==" 17 break 18 print "!=" 19 else: 20 print ‘over‘ 21 22 count=0 23 while(count<9): 24 print count 25 count += 1 26 27 for循环 28 29 sorted() # 返回一个序列(列表) 30 zip() # 返回一个序列(列表) 31 enumerate() # 返回迭代器(类似序列) 32 reversed() # 反序迭代器对象 33 dict.iterkeys() # 通过键迭代 34 dict.itervalues() # 通过值迭代 35 dict.iteritems() # 通过键-值对迭代 36 randline() # 文件迭代 37 iter(obj) # 得到obj迭代器 检查obj是不是一个序列 38 iter(a,b) # 重复调用a,直到迭代器的下一个值等于b 39 for i in range(1, 5): 40 print i 41 else: 42 print ‘over‘ 43 44 list = [‘a‘,‘b‘,‘c‘,‘b‘] 45 for i in range(len(list)): 46 print list[i] 47 for x, Lee in enumerate(list): 48 print "%d %s Lee" % (x+1,Lee) 49 50 流程结构简写 51 52 [ i * 2 for i in [8,-2,5]] 53 [16,-4,10] 54 [ i for i in range(8) if i %2 == 0 ] 55 [0,2,4,6]
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/Rambotien/p/5371233.html