标签:
Hibernate的所有session都是由sessionFactory来生成的,那么,sessionFactory是怎么得来的呢?它与我们配置的xxx.cfg.xml文件以及xxx.hbm.xml文件之间又有着怎么样的联系呢?
先看一小段生成sessionFactory的代码:
code_1:
public class HibernateTest { @Test public void test() { System.out.println("test..."); //1. 创建一个 SessionFactory 对象 SessionFactory sessionFactory = null; //1). 创建 Configuration 对象: 对应 hibernate 的基本配置信息和 对象关系映射信息 Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure(); //4.0 之前这样创建 //sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory(); //2). 创建一个 ServiceRegistry 对象: hibernate 4.x 新添加的对象 //hibernate 的任何配置和服务都需要在该对象中注册后才能有效. ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry = new ServiceRegistryBuilder().applySettings(configuration.getProperties()) .buildServiceRegistry(); //3). 利用serviceRegistry来创建sessionFactory实例 sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory(serviceRegistry); //2. 创建一个 Session 对象 Session session = sessionFactory.openSession(); //3. 开启事务 Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction(); //4. 执行保存操作 News news = new News("Java12345", "ATGUIGU", new Date(new java.util.Date().getTime())); session.save(news); //5. 提交事务 transaction.commit(); //6. 关闭 Session session.close(); //7. 关闭 SessionFactory 对象 sessionFactory.close(); } }
从上面的代码很清晰的可以看见,这一切的源头都在 Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure() 这条语句上:创建ServiceRegistry 需要用到configuration,生成sessionFactory同样需要用到configuration。
Configuration的生成过程
从源代码中可以看到,Configuration的configure()方法共有5中重载方式:
code_2:
public Configuration configure(); //无参 public Configuration configure(String resource) public Configuration configure(URL url) public Configuration configure(File configFile) public Configuration configure(org.w3c.dom.Document document)
现在从无参的configure()方法开始分析,它代表了一种默认的行为,默认读取类路径下的hibernate.cfg.xml文件作为hibernate的配置文件:
code_3:
public Configuration configure() throws HibernateException { configure( "/hibernate.cfg.xml" ); //默认读取classpath路径下的hibernate.cfg.xml文件 return this; }
继续追踪configure( "/hibernate.cfg.xml" )方法:
code_4:
1 public Configuration configure(String resource) throws HibernateException { 2 InputStream stream = getConfigurationInputStream( resource ); //通过传入的资源路径获取一个输入流 3 return doConfigure( stream, resource ); //这个方法会完成解析的第一步:将输入流转换成Document对象 4 }
继续追踪 return doConfigure( stream, resource ) 语句,可以发现底层会通过SAX解析工具将输入流转换成Document对象。然后调用然后调用doConfigure(Document doc)来继续解析这个文档:
code_5:
1 protected Configuration doConfigure(InputStream stream, String resourceName) throws HibernateException { 2 3 ErrorLogger errorLogger = new ErrorLogger( resourceName ); //将输入流转换成Document对象 5 Document document = xmlHelper.createSAXReader( errorLogger, entityResolver ) 6 .read( new InputSource( stream ) ); 7 //具体解析document树,并将结果以键值对的形式存放到properties中 8 doConfigure( document ); 9 10 return this; 11 }
doConfigure(Document doc)是实际解析文档的方法,前面configure()的5种重载方法最后都要调用这个方法来完成实际的解析。我们看看它的解析思路:
code_6:
1 protected Configuration doConfigure(Document doc) throws HibernateException { 2 Element sfNode = doc.getRootElement().element( "session-factory" ); 3 String name = sfNode.attributeValue( "name" ); 4 if ( name != null ) { //session-factory根节点是可以有name属性值的 5 properties.setProperty( Environment.SESSION_FACTORY_NAME, name ); 6 } 7 //遍历文档中所有的property节点,读取器name属性值以及节点的文本, 8 //以name-value的形式放入到properties中 9 addProperties( sfNode ); 10 //解析除了property之外的节点:mapping、class-cache、collection-cache 11 parseSessionFactory( sfNode, name ); 12 13 Element secNode = doc.getRootElement().element( "security" ); 14 if ( secNode != null ) { 15 parseSecurity( secNode ); 16 } 17 18 LOG.configuredSessionFactory( name ); 19 LOG.debugf( "Properties: %s", properties ); 20 21 return this; 22 }
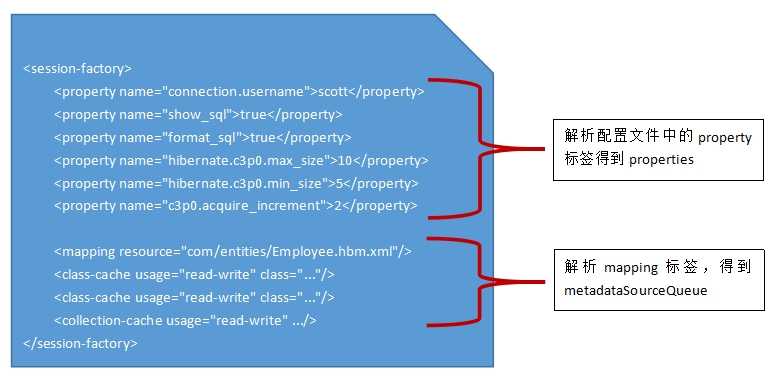
doConfigure(Document doc)方法中对Document的解析主要分为两个步骤进行:①解析xxx.cfg.xml配置文档中所有的property节点;②解析xxx.cfg.xml配置文档中除了property节点之外的其它5种节点。
先来看看第①步,它在addProperties(...)方法中完成(code_6代码段的第9行)思路很清晰,用一个迭代器来遍历文档中所有的property节点,并将name-value存放到Configuration的properties属性中:
code_7:
1 private void addProperties(Element parent) { 2 //指定,只会遍历property节点 3 Iterator itr = parent.elementIterator( "property" ); 4 while ( itr.hasNext() ) {//循环遍历 5 Element node = (Element) itr.next(); 6 //读取节点的name属性值 7 String name = node.attributeValue( "name" ); 8 //读取节点的文本值 9 String value = node.getText().trim(); 10 LOG.debugf( "%s=%s", name, value ); 11 //将name-value值存放如properties中 12 properties.setProperty( name, value ); 13 //待研究... 14 if ( !name.startsWith( "hibernate" ) ) { 15 properties.setProperty( "hibernate." + name, value ); 16 } 17 } 18 Environment.verifyProperties( properties ); 19 }
再来看看第②步,它在parseSessionFactory( ...)方法中进行(code_6代码段的第10行),它主要解析3类标签:mapping、class-cache、collection-cache:
code_8:
1 private void parseSessionFactory(Element sfNode, String name) { 2 Iterator elements = sfNode.elementIterator(); 3 while ( elements.hasNext() ) { 4 Element subelement = (Element) elements.next(); 5 String subelementName = subelement.getName(); 6 //解析mapping节点,mapping可以指定hibernate的映射文件位置 7 if ( "mapping".equals( subelementName ) ) { 8 //具体解析mapping节点 9 parseMappingElement( subelement, name ); 10 } 11 //下面两个是和hibernate的二级缓存相关的配置,不做深入探讨 12 else if ( "class-cache".equals( subelementName ) ) { 13 String className = subelement.attributeValue( "class" ); 14 Attribute regionNode = subelement.attribute( "region" ); 15 final String region = ( regionNode == null ) ? className : regionNode.getValue(); 16 boolean includeLazy = !"non-lazy".equals( subelement.attributeValue( "include" ) ); 17 setCacheConcurrencyStrategy( className, subelement.attributeValue( "usage" ), region, includeLazy ); 18 } 19 else if ( "collection-cache".equals( subelementName ) ) { 20 String role = subelement.attributeValue( "collection" ); 21 Attribute regionNode = subelement.attribute( "region" ); 22 final String region = ( regionNode == null ) ? role : regionNode.getValue(); 23 setCollectionCacheConcurrencyStrategy( role, subelement.attributeValue( "usage" ), region ); 24 } 25 } 26 }
后面两个标签class-cache和collection-cache是和hibernate的二级缓存相关,不作深入探讨。主要看看解析mapping的方法:
code_9:
1 private void parseMappingElement(Element mappingElement, String name) { 2 //从源代码可以看出,mapping节点支持的属性值有5个 3 final Attribute resourceAttribute = mappingElement.attribute( "resource" ); 4 final Attribute fileAttribute = mappingElement.attribute( "file" ); 5 final Attribute jarAttribute = mappingElement.attribute( "jar" ); 6 final Attribute packageAttribute = mappingElement.attribute( "package" ); 7 final Attribute classAttribute = mappingElement.attribute( "class" ); 8 9 if ( resourceAttribute != null ) { 10 final String resourceName = resourceAttribute.getValue(); 11 LOG.debugf( "Session-factory config [%s] named resource [%s] for mapping", name, resourceName ); 12 //将hibernate的映射文件作进一步的解析 13 addResource( resourceName ); 14 } 15 else if ( fileAttribute != null ) { 16 final String fileName = fileAttribute.getValue(); 17 LOG.debugf( "Session-factory config [%s] named file [%s] for mapping", name, fileName ); 18 addFile( fileName ); 19 } 20 else if ( jarAttribute != null ) { 21 final String jarFileName = jarAttribute.getValue(); 22 LOG.debugf( "Session-factory config [%s] named jar file [%s] for mapping", name, jarFileName ); 23 addJar( new File( jarFileName ) ); 24 } 25 else if ( packageAttribute != null ) { 26 final String packageName = packageAttribute.getValue(); 27 LOG.debugf( "Session-factory config [%s] named package [%s] for mapping", name, packageName ); 28 addPackage( packageName ); 29 } 30 else if ( classAttribute != null ) { 31 final String className = classAttribute.getValue(); 32 LOG.debugf( "Session-factory config [%s] named class [%s] for mapping", name, className ); 33 try { 34 addAnnotatedClass( ReflectHelper.classForName( className ) ); 35 } 36 catch ( Exception e ) { 37 throw new MappingException( 38 "Unable to load class [ " + className + "] declared in Hibernate configuration <mapping/> entry", 39 e 40 ); 41 } 42 } 43 else { 44 throw new MappingException( "<mapping> element in configuration specifies no known attributes" ); 45 } 46 }
addResource( resourceName )是如何解析的呢?那么它是如何工作的呢?这里不再一步一步追踪源代码,因为嵌套太深,直接给出一个感性的认识即可:
在Configuration中定义了一个名为MetadataSourceQueue的内部内,同时Configuration中还有一个该队列的属性值:metadataSourceQueue。
addResource( resourceName )方法嵌套到最后会调用metadataSourceQueue.add(...)方法来将映射的元数据存储到metadataSourceQueue队列中。要使用的时候,从该队列中取就可以了。
metadataSourceQueue的底层存储是一个Map类型...
到现在为止,Configuration对象就得到了,总结一下,其重要的几个点:
1、configure()方法默认读取/hibernate.cfg.xml作为hibernate的配置文件。当然,configure()方法还有其它重载形式可用。
2、doConfigure(Document document)方法会调用两个重要的方法:addProperties( sfNode )和parseSessionFactory( sfNode, name );
3、addProperties( sfNode )方法会解析配置文件中的property节点,并将解析到的name-value放入到properties中
4、parseSessionFactory( sfNode, name )方法会解析配置文件中除了property节点外的其它3个类型的节点(4.2版本):mapping、class-cache和collection-cache
5、mapping配置是和映射相关的,class-cache和collection-cache是与二级缓存相关的。
6、mapping解析的结果会存放到metadataSourceQueue对象中。
7、所以,整个过程得到Configuration中两个重要的属性值:properties和metadataSourceQueue。
1、Hibernate之生成SessionFactory源码追踪
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/lj95801/p/5396736.html