标签:
上一篇在这 C++混合编程之idlcpp教程Lua篇(6)
第一篇在这 C++混合编程之idlcpp教程(一)
与LuaTutorial4工程相似,工程LuaTutorial5中,同样加入了四个文件:LuaTutorial5.cpp, Tutorial5.cpp, Tutorial5.i, tutorial5.lua。其中LuaTutorial5.cpp的内容基本和LuaTutorial4.cpp雷同,不再赘述。
首先看一下Tutorial5.i的内容:
#import "../../paf/src/pafcore/Reference.i"
$$#include <vector>
namespace tutorial
{
struct Point
{
float x;
float y;
Point();
Point(float a, float b);
meta:
Point(const Point ref pt);
};
export class Shape : Reference
{
export abstract float getArea();
$$ virtual ~Shape() {}
};
class ShapeManager(value_object)
{
void addShape(Shape ptr shape);
float getTotalArea();
static ShapeManager ptr GetInstance();
$*
~ShapeManager();
private:
std::vector<Shape*> m_shapes;
*$
};
class Triangle : Shape
{
Point m_vertices[$3];
meta:
Triangle();
$$virtual float getArea();
};
}
与Tutorial4.i相比,大部分内容是一样的,不同之处在于类型Shape的声明以及其下的纯虚函数getArea;
export class Shape : Reference
export abstract float getArea();
在这两处声明的最前面都多了一个关键字export。这个关键字和C++中的export意义完全不一样,只是想在C++中找一个现成的关键字直接使用而已,其实这个也不太合适,暂时先用着。此处的写法意味着可以在脚本代码中写一个类型,让它“派生”自Shape,并且能够“覆盖”虚函数getArea。当然实际上是通过idlcpp生成的一个派生类配合脚本插件代码来完成类似的任务。
通过在类型的声明class 前加上关键字export 表示此类型可以被脚本“派生”,在虚函数声明的关键字virtual 或 abstract前加上关键字export 表示此虚函数可以被脚本“覆盖”。
在宿主语言和脚本的混合使用中,一个常见的用法是在宿主语言中根据一定的条件向外发出事件,而用脚本语言来编写事件处理代码,例如在WOW中用一个XML文件描述GUI界面,同时注明事件处理函数对应的Lua函数名。idlcpp提供的脚本继承C++类然后重写虚函数的功能可以很好的实现类似的需求。
编译后生成的Tutorial5.h的内容如下:
//DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE, it is generated by idlcpp
//http://www.idlcpp.org
#pragma once
#include "./Tutorial5.h"
#include "../../paf/src/pafcore/Reference.h"
namespace tutorial{ class ShapeManager; }
namespace tutorial{ class Triangle; }
#include <vector>
namespace tutorial
{
struct Point
{
public:
float x;
float y;
Point();
Point(float a,float b);
public:
static Point* New();
static Point* New(float a,float b);
static Point* NewArray(unsigned int count);
static Point* Clone(const Point& pt);
};
class Shape : public ::pafcore::Reference
{
public:
virtual ::pafcore::Type* getType();
virtual float getArea() = 0 ;
virtual ~Shape() {}
};
class ShapeManager
{
public:
void addShape(Shape* shape);
float getTotalArea();
static ShapeManager* GetInstance();
~ShapeManager();
private:
std::vector<Shape*> m_shapes;
};
class Triangle : public Shape
{
public:
virtual ::pafcore::Type* getType();
Point m_vertices[3];
public:
static Triangle* New();
static Triangle* NewARC();
static Triangle* NewArray(unsigned int count);
static Triangle* NewArrayARC(unsigned int count);
virtual float getArea();
};
}
这里生成的代码和Tutorial4.h基本一致。
最后看一下Tutorial5.lua的内容
Circle = {}
Circle.__index = Circle;
function Circle.New()
circle= {radius = 1.0}
setmetatable(circle, Circle);
circle.shape = paf.tutorial.Shape._Derive_(circle);
return circle;
end
function Circle:getArea()
return self.radius * self.radius * 3.1415926;
end
circle = Circle.New();
circle.radius = 2.0;
shapeManager = paf.tutorial.ShapeManager.GetInstance();
shapeManager:addShape(circle.shape);
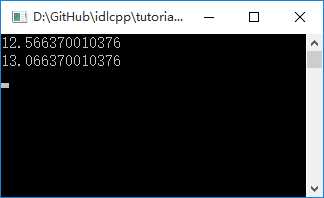
print(shapeManager:getTotalArea()._);
triangle = paf.tutorial.Triangle();
triangle.m_vertices[0] = paf.tutorial.Point(0,0);
triangle.m_vertices[1] = paf.tutorial.Point(0,1);
triangle.m_vertices[2] = paf.tutorial.Point(1,1);
shapeManager:addShape(triangle);
print(shapeManager:getTotalArea()._);
在上面的代码中,写了一个类型Circle。在函数Circle.New 通过下面这一行
circle.shape = paf.tutorial.Shape._Derive_(circle);
来模拟继承,语法:C++类型._Derive_(脚本对象) 用于完成模拟继承的行为。实际上circle.shape才是C++类型Shape的派生类实例的引用,在C++中需要用到Shape类型的地方,将circle.shape传递过去即可,如下面的使用方式。
shapeManager:addShape(circle.shape);
然后在类型Circle中提供一个与C++基类同名的函数getArea用来计数圆的面积即可,最终使用时脚本插件会找到对应函数进行调用。
编译执行,结果如下图:
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/fdyjfd/p/5402962.html