标签:
一、卸载掉原有mysql
[root@xiaoluo ~]# rpm -qa | grep mysql // 这个命令就会查看该操作系统上是否已经安装了mysql数据库
有的话,我们就通过 rpm -e 命令 或者 rpm -e --nodeps 命令来卸载掉
[root@xiaoluo ~]# rpm -e mysql // 普通删除模式 [root@xiaoluo ~]# rpm -e --nodeps mysql // 强力删除模式,如果使用上面命令删除时,提示有依赖的其它文件,则用该命令可以对其进行强力删除
在删除完以后我们可以通过 rpm -qa | grep mysql 命令来查看mysql是否已经卸载成功!!
三、通过yum来进行mysql的安装
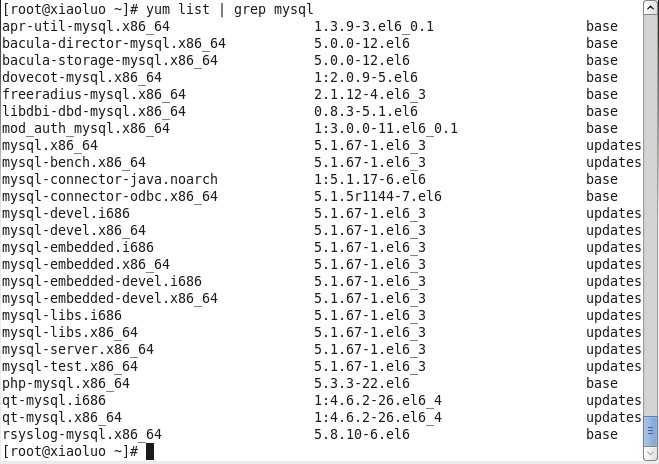
我是通过yum的方式来进行mysql的数据库安装,首先我们可以输入 yum list | grep mysql 命令来查看yum上提供的mysql数据库可下载的版本:
[root@xiaoluo ~]# yum list | grep mysql
就可以得到yum服务器上mysql数据库的可下载版本信息:
然后我们可以通过输入 yum install -y mysql-server mysql mysql-devel 命令将mysql mysql-server mysql-devel都安装好(注意:安装mysql时我们并不是安装了mysql客户端就相当于安装好了mysql数据库了,我们还需要安装mysql-server服务端才行)
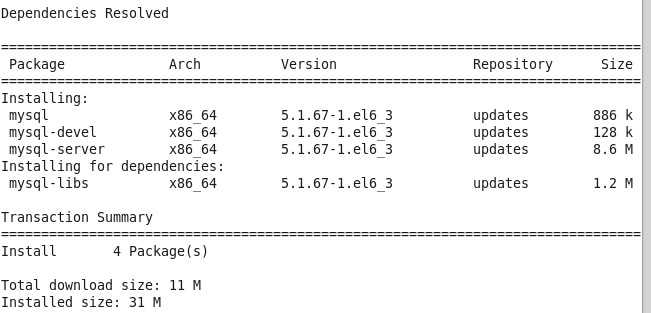
[root@xiaoluo ~]# yum install -y mysql-server mysql mysql-deve
在等待了一番时间后,yum会帮我们选择好安装mysql数据库所需要的软件以及其它附属的一些软件
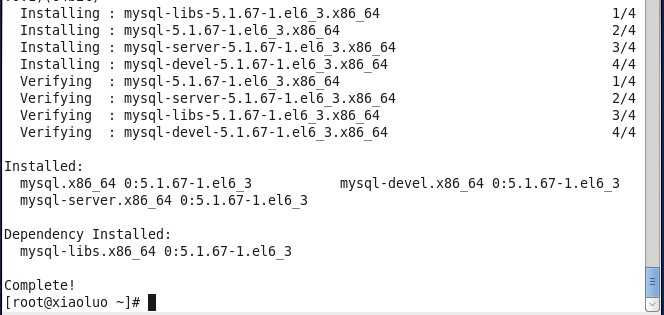
我们发现,通过yum方式安装mysql数据库省去了很多没必要的麻烦,当出现下面的结果时,就代表mysql数据库安装成功了
此时我们可以通过如下命令,查看刚安装好的mysql-server的版本
[root@xiaoluo ~]# rpm -qi mysql-server
我们安装的mysql-server并不是最新版本,如果你想尝试最新版本,那就去mysql官网下载rpm包安装就行了,至此我们的mysql数据库已经安装完成了。
四、mysql数据库的初始化及相关配置
我们在安装完mysql数据库以后,会发现会多出一个mysqld的服务,这个就是咱们的数据库服务,我们通过输入service mysqld start 命令就可以启动我们的mysql服务。
注意:如果我们是第一次启动mysql服务,mysql服务器首先会进行初始化的配置,如:
[root@xiaoluo ~]# service mysqld start 初始化 MySQL 数据库: WARNING: The host ‘xiaoluo‘ could not be looked up with resolveip. This probably means that your libc libraries are not 100 % compatible with this binary MySQL version. The MySQL daemon, mysqld, should work normally with the exception that host name resolving will not work. This means that you should use IP addresses instead of hostnames when specifying MySQL privileges ! Installing MySQL system tables... OK Filling help tables... OK To start mysqld at boot time you have to copy support-files/mysql.server to the right place for your system PLEASE REMEMBER TO SET A PASSWORD FOR THE MySQL root USER ! To do so, start the server, then issue the following commands: /usr/bin/mysqladmin -u root password ‘new-password‘ /usr/bin/mysqladmin -u root -h xiaoluo password ‘new-password‘ Alternatively you can run: /usr/bin/mysql_secure_installation which will also give you the option of removing the test databases and anonymous user created by default. This is strongly recommended for production servers. See the manual for more instructions. You can start the MySQL daemon with: cd /usr ; /usr/bin/mysqld_safe & You can test the MySQL daemon with mysql-test-run.pl cd /usr/mysql-test ; perl mysql-test-run.pl Please report any problems with the /usr/bin/mysqlbug script! [确定] 正在启动 mysqld: [确定]
这时我们会看到第一次启动mysql服务器以后会提示非常多的信息,目的就是对mysql数据库进行初始化操作,当我们再次重新启动mysql服务时,就不会提示这么多信息了,如:
[root@xiaoluo ~]# service mysqld restart
停止 mysqld: [确定]
正在启动 mysqld: [确定]
我们在使用mysql数据库时,都得首先启动mysqld服务,我们可以 通过 chkconfig --list | grep mysqld 命令来查看mysql服务是不是开机自动启动,如:
[root@xiaoluo ~]# chkconfig --list | grep mysqld mysqld 0:关闭 1:关闭 2:关闭 3:关闭 4:关闭 5:关闭 6:关闭
我们发现mysqld服务并没有开机自动启动,我们当然可以通过 chkconfig mysqld on 命令来将其设置成开机启动,这样就不用每次都去手动启动了
[root@xiaoluo ~]# chkconfig mysqld on [root@xiaoluo ~]# chkconfig --list | grep mysql mysqld 0:关闭 1:关闭 2:启用 3:启用 4:启用 5:启用 6:关闭
mysql数据库安装完以后只会有一个root管理员账号,但是此时的root账号还并没有为其设置密码,在第一次启动mysql服务时,会进行数据库的一些初始化工作,在输出的一大串信息中,我们看到有这样一行信息 :
/usr/bin/mysqladmin -u root password ‘new-password‘ // 为root账号设置密码
所以我们可以通过 该命令来给我们的root账号设置密码(注意:这个root账号是mysql的root账号,非Linux的root账号)
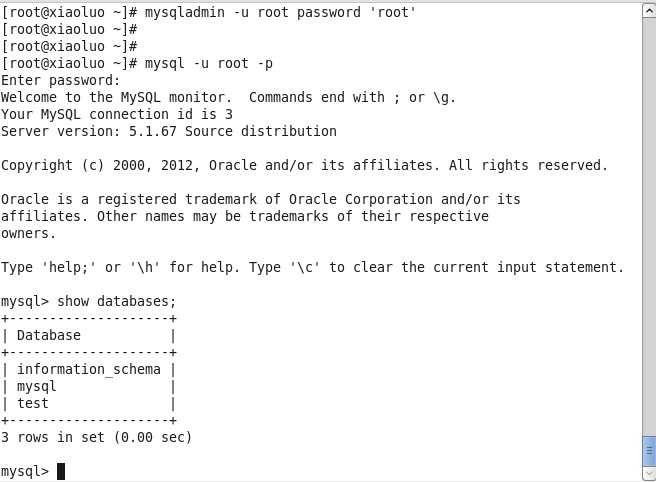
[root@xiaoluo ~]# mysqladmin -u root password ‘root‘ // 通过该命令给root账号设置密码为 root
此时我们就可以通过 mysql -u root -p 命令来登录我们的mysql数据库了
二,远程访问设置
[root@localhost mysql]# mysql -u root mysql
mysql> use mysql;
mysql> desc user;
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO root@"%" IDENTIFIED BY "root"; //为root添加远程连接的能力
mysql> update user set Password = password(‘123456‘) where User=‘root‘; //设置root用户密码
mysql> select Host,User,Password from user where User=‘root‘;
mysql> flush privileges;
mysql> exit
标签:
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/u012592062/article/details/51188503