标签:
上个文章分享了一些多线程的一些基础的知识,今天我们继续学习。
努力学习,成为最好的自己。
上次我们说了线程池,线程池的QueueUserWorkItem()方法发起一次异步的线程执行很简单
但是该方法最大的问题是没有一个内建的机制让你知道操作什么时候完成,有没有一个内建的机制在操作完成后获得一个返回值。为此,可以使用System.Threading.Tasks中的Task类。
简单代码实现:

using System; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Threading { class Program { public static Int32 ThreadSum(Int32 n) { Int32 sum = 0; for (; n > 0; --n) sum += n; return sum; } static void Main(string[] args) { var t = new Task<Int32>(n => ThreadSum((Int32)n), 100); t.Start(); var cwt = t.ContinueWith(task => Console.WriteLine("The result is {0}", t.Result)); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
委托的异步执行代码:BeginInvoke() 和 EndInvoke()

using System; namespace Threading { public delegate string MyDelegate(object data); class Program { public static string Thread1(object data) { return data.ToString(); } public static void ThreadCallback(IAsyncResult data) { Console.WriteLine("ThreadCallback = > " + data.AsyncState); } static void Main(string[] args) { var mydelegate = new MyDelegate(Thread1); IAsyncResult result = mydelegate.BeginInvoke("Thread1 Para", ThreadCallback, "Callback Para"); //异步执行完成 var resultstr = mydelegate.EndInvoke(result); Console.WriteLine(resultstr); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
1、互斥锁lock()语句
同步访问共享资源的首选技术是C#的 lock 关键字,lock 允许定义一段线程同步的代码语句,它需要定义一个标记(即一个对象引用),线程在进入锁定范围的时候必须获得这个标记,在退出锁定范围时需要释放锁。当试图锁定的是一个实例级的私有方法时,使用方法本身所在对象的引用就可以了。然而,如需锁定公共成员中的一段代码,比较安全的做法是声明私有的object成员作为锁标识。
public class DemoClass { private readonly object threadLock = new object(); public void Method() { // 使用锁标识 lock (threadLock) { //…… } } }
2、Monitor实现线程同步
通过Monitor.Enter() 和 Monitor.Exit()实现排它锁的获取和释放,获取之后独占资源,不允许其他线程访问。
还有一个TryEnter方法,请求不到资源时不会阻塞等待,可以设置超时时间,获取不到直接返回false。
public class DemoClass { private readonly object threadLock = new object(); public void Method() { Monitor.Enter(threadLock); try { //…… } finally { Monitor.Exit(threadLock); } } }
3、维护自由锁(System.Threading.Interlocked)实现线程同步,Interlocked允许我们对数据进行一些原子操作:CompareExchange(), Decrement(), Exchange(), Increment()。这些静态方法需要以引用方式传入变量。如:注意newVal 和 intVal 的值都是递增之后的值。
4、[Synchronization]特性可以有效地使对象的所以实例的成员都保持线程安全。当CLR分配带[Synchronization]特性的对象时,它会把这个对象放在同步上下文中。这是编写线程安全代码的一种偷懒方式,因为它不需要我们实际深入线程控制敏感数据的细节,但这种方式对性能有影响,因为即使一个方法没有使用共享资源,CLR仍然会锁定对该方法的调用。
5、系统内置对象
互斥(Mutex), 信号量(Semaphore), 事件(AutoResetEvent/ManualResetEvent),线程池
系统会为每一个线程分配一个优先级别。.NET线程优先级,是指定一个线程的相对于其他线程的相对优先级,它规定了线程的执行顺序,对于在CLR中创建的线程,其优先级别默认为Normal,而在CLR之外创建的线程进入CLR时,将会保留其先前的优先级,可以通过访问线程的Priority属性来获取或设置线程的优先级别。
System.Threading命名空间中的ThreadPriority枚举定义了一组线程优先级的所有可能值,我这里按级别由高到低排列出来常用的,具体的说明就不在这里解释。
Highest , AboveNormal , Normal , BelowNormal , Lowest
除了这些还有Realtime,但Realtime优先级尽量避免,他的优先级相当高,甚至会干扰操作系统的任务,比如阻碍一些必要的磁盘I/O和网络传输。也可能会造成不及时处理键盘和鼠标的输入,导致用户会感觉死机了。
代码示例:
using System; using System.Threading; namespace Threading { class Program { public static void Thread1() { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Console.Write("1 "); } } public static void Thread2() { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Console.Write("2 "); } } public static void Thread3() { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Console.Write("3 "); } } public static void Thread4() { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Console.Write("4 "); } } public static void Thread5() { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Console.Write("5 "); } } static void Main(string[] args) { var t1 = new Thread(Thread1); var t2 = new Thread(Thread2); var t3 = new Thread(Thread3); var t4 = new Thread(Thread4); var t5 = new Thread(Thread5); t1.Priority = ThreadPriority.Highest; t2.Priority = ThreadPriority.AboveNormal; t3.Priority = ThreadPriority.Normal; t4.Priority = ThreadPriority.BelowNormal; t5.Priority = ThreadPriority.Lowest; t1.Start(); t2.Start(); t3.Start(); t4.Start(); t5.Start(); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
运行结果:
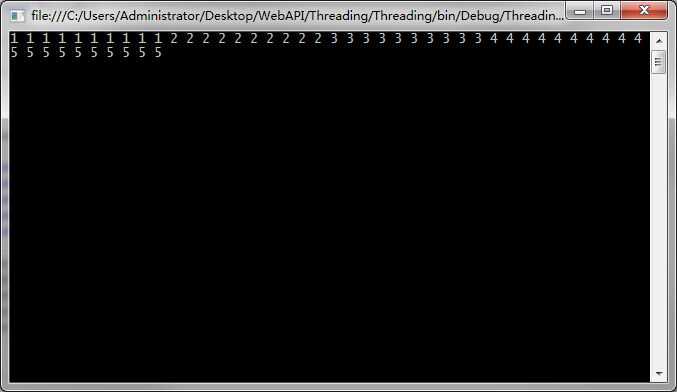
很明显,根据线程的优先级高低顺序执行的。
Join阻塞调用线程,直到该线程终止。
using System; using System.Threading; namespace Threading { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { var threadStartA = new ThreadStart(delegate() { for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) { if (i % 10000 == 0) Console.Write("A"); } }); var threadA = new Thread(threadStartA); var threadStartB = new ThreadStart(delegate() { for (int i = 0; i < 500000; i++) { if (i % 10000 == 0) Console.Write("B"); } threadA.Join(); //阻塞线程threadB,插入threadA进行执行 for (int i = 0; i < 500000; i++) { if (i % 10000 == 0) Console.Write("B1"); } }); var threadB = new Thread(threadStartB); //启动线程 threadA.Start(); threadB.Start(); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
运行结果:
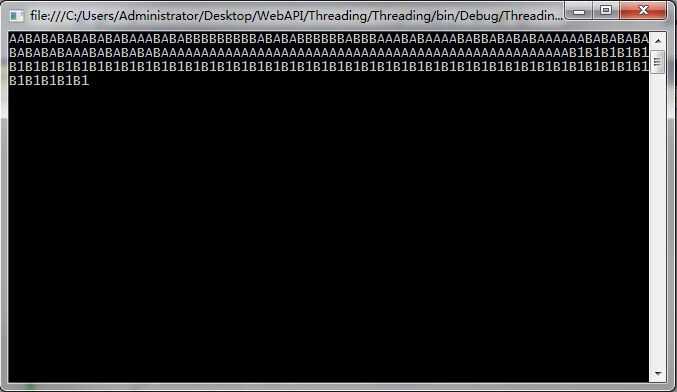
从运行结果可以看出:一开始,ThreadA和ThreadB交替执行,当ThreadB执行到ThreadA.Join()方法时,ThreadB被阻塞,ThreadA插入进来单独执行,当ThreadA执行完毕以后,ThreadB继续执行。
除了ThreadA和ThreadB外,程序中还有一个主线程(Main Thread)。现在我们在主线程中添加一些输出代码,看看主线程和工作线程A、B是如何并发运行的。
如果本文对你有帮助,请点击右下角【好文要顶】和【关注我】
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinrq/p/5413317.html