标签:
全文搜索
比如,我们一个文件夹中,或者一个磁盘中有很多的文件,记事本、world、Excel、pdf,我们想根据其中的关键词搜索包含的文件。例如,我们输入Lucene,所有内容含有Lucene的文件就会被检查出来。这就是所谓的全文检索。因此,很容易的我们想到,应该建立一个关键字与文件的相关映射,盗用ppt中的一张图,很明白的解释了这种映射如何实现。
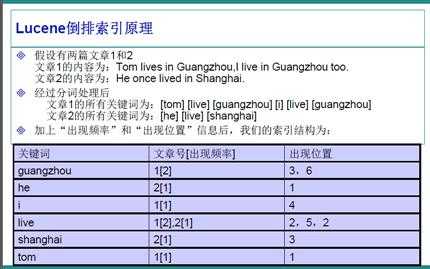
在Lucene中,就是使用这种“倒排索引”的技术,来实现相关映射。 有了这种映射关系,我们就来看看Lucene的架构设计。下面是Lucene的资料必出现的一张图,但也是其精髓的概括。
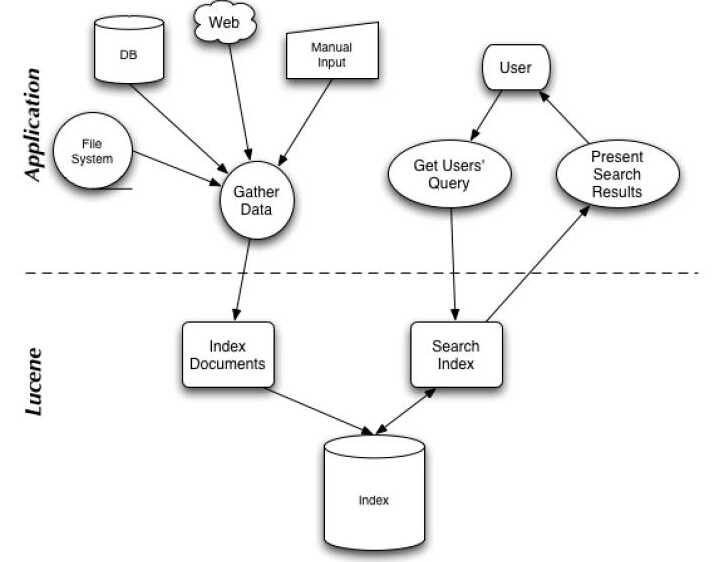
我们可以看到,Lucene的使用主要体现在两个步骤:
1 创建索引,通过IndexWriter对不同的文件进行索引的创建,并将其保存在索引相关文件存储的位置中。
2 通过索引查寻关键字相关文档。
1 Analyzer analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer(Version.LUCENE_CURRENT); 2 3 // Store the index in memory: 4 Directory directory = new RAMDirectory(); 5 // To store an index on disk, use this instead: 6 //Directory directory = FSDirectory.open("/tmp/testindex"); 7 IndexWriterConfig config = new IndexWriterConfig(Version.LUCENE_CURRENT, analyzer); 8 IndexWriter iwriter = new IndexWriter(directory, config); 9 Document doc = new Document(); 10 String text = "This is the text to be indexed."; 11 doc.add(new Field("fieldname", text, TextField.TYPE_STORED)); 12 iwriter.addDocument(doc); 13 iwriter.close(); 14 15 // Now search the index: 16 DirectoryReader ireader = DirectoryReader.open(directory); 17 IndexSearcher isearcher = new IndexSearcher(ireader); 18 // Parse a simple query that searches for "text": 19 QueryParser parser = new QueryParser(Version.LUCENE_CURRENT, "fieldname", analyzer); 20 Query query = parser.parse("text"); 21 ScoreDoc[] hits = isearcher.search(query, null, 1000).scoreDocs; 22 assertEquals(1, hits.length); 23 // Iterate through the results: 24 for (int i = 0; i < hits.length; i++) { 25 Document hitDoc = isearcher.doc(hits[i].doc); 26 assertEquals("This is the text to be indexed.", hitDoc.get("fieldname")); 27 } 28 ireader.close(); 29 directory.close();
首先,我们需要定义一个词法分析器。
比如一句话,“我爱我们的中国!”,如何对他拆分,扣掉停顿词“的”,提取关键字“我”“我们”“中国”等等。这就要借助的词法分析器Analyzer来实现,这里面使用的是标准的词法分析器,如果专门针对汉语,还可以搭配paoding,进行使用。
1 Analyzer analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer(Version.LUCENE_CURRENT);
参数中的Version.LUCENE_CURRENT,代表使用当前的Lucene版本,本文环境中也可以写成Version.LUCENE_40。
第二步,确定索引文件存储的位置,Lucene提供给我们两种方式:
1 本地文件存储
1 Directory directory = FSDirectory.open("/tmp/testindex");
2 内存存储
1 Directory directory = new RAMDirectory();
可以根据自己的需要进行设定。
第三步,创建IndexWriter,进行索引文件的写入。
1 IndexWriterConfig config = new IndexWriterConfig(Version.LUCENE_CURRENT, analyzer); 2 IndexWriter iwriter = new IndexWriter(directory, config);
这里的IndexWriterConfig,据官方文档介绍,是对indexWriter的配置,其中包含了两个参数,第一个是目前的版本,第二个是词法分析器Analyzer。
第四步,内容提取,进行索引的存储
1 Document doc = new Document(); 2 String text = "This is the text to be indexed."; 3 doc.add(new Field("fieldname", text, TextField.TYPE_STORED)); 4 iwriter.addDocument(doc); 5 iwriter.close();
第一行,申请了一个document对象,这个类似于数据库中的表中的一行。
第二行,是我们即将索引的字符串。
第三行,把字符串存储起来(因为设置了TextField.TYPE_STORED,如果不想存储,可以使用其他参数,详情参考官方文档),并存储“表明”为"fieldname".
第四行,把doc对象加入到索引创建中。
第五行,关闭IndexWriter,提交创建内容。
这就是索引创建的过程。
第一步,打开存储位置
1 DirectoryReader ireader = DirectoryReader.open(directory);
第二步,创建搜索器
1 IndexSearcher isearcher = new IndexSearcher(ireader);
第三步,类似SQL,进行关键字查询
1 QueryParser parser = new QueryParser(Version.LUCENE_CURRENT, "fieldname", analyzer); 2 Query query = parser.parse("text"); 3 ScoreDoc[] hits = isearcher.search(query, null, 1000).scoreDocs; 4 assertEquals(1, hits.length); 5 for (int i = 0; i < hits.length; i++) { 6 Document hitDoc = isearcher.doc(hits[i].doc); 7 assertEquals("This is the text to be indexed.",hitDoc.get("fieldname")); 8 }
这里,我们创建了一个查询器,并设置其词法分析器,以及查询的“表名“为”fieldname“。查询结果会返回一个集合,类似SQL的ResultSet,我们可以提取其中存储的内容。
关于各种不同的查询方式,可以参考官方手册,或者推荐的PPT
第四步,关闭查询器等。
1 ireader.close(); 2 directory.close();
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/sunfie/p/5424396.html