标签:
AMS & WMS,应该是app端打交道最多的2个framwork层的service。
ActivityManagerService 是android提供给用于管理Activity运行状态的系统进程。
本系列共分3个部分,概述,ActivityStatck & Activiy Task.
一. AMS概述
首先AMS 是一个同我们开发的service非常相似的一个service,只不过它的作用是管理activity。
所以AMS是一个进程,并且当开机以后,它就常驻在系统里面,归ServiceManager调度。
而AMS启动后,它开始有一个线程监听处理客户的需求。
一下为android5.0 的代码:
\frameworks\base\services\java\com\android\server\SystemServera.java

private void startBootstrapServices() { // Wait for installd to finish starting up so that it has a chance to // create critical directories such as /data/user with the appropriate // permissions. We need this to complete before we initialize other services. mInstaller = mSystemServiceManager.startService(Installer.class); // Activity manager runs the show. mActivityManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService( ActivityManagerService.Lifecycle.class).getService(); mActivityManagerService.setSystemServiceManager(mSystemServiceManager); // Power manager needs to be started early because other services need it. // Native daemons may be watching for it to be registered so it must be ready // to handle incoming binder calls immediately (including being able to verify // the permissions for those calls). mPowerManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(PowerManagerService.class); // Now that the power manager has been started, let the activity manager // initialize power management features. mActivityManagerService.initPowerManagement(); // Display manager is needed to provide display metrics before package manager // starts up. mDisplayManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(DisplayManagerService.class); // We need the default display before we can initialize the package manager. mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(SystemService.PHASE_WAIT_FOR_DEFAULT_DISPLAY); // Only run "core" apps if we‘re encrypting the device. String cryptState = SystemProperties.get("vold.decrypt"); if (ENCRYPTING_STATE.equals(cryptState)) { Slog.w(TAG, "Detected encryption in progress - only parsing core apps"); mOnlyCore = true; } else if (ENCRYPTED_STATE.equals(cryptState)) { Slog.w(TAG, "Device encrypted - only parsing core apps"); mOnlyCore = true; } // Start the package manager. Slog.i(TAG, "Package Manager"); mPackageManagerService = PackageManagerService.main(mSystemContext, mInstaller, mFactoryTestMode != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_OFF, mOnlyCore); mFirstBoot = mPackageManagerService.isFirstBoot(); mPackageManager = mSystemContext.getPackageManager(); Slog.i(TAG, "User Service"); ServiceManager.addService(Context.USER_SERVICE, UserManagerService.getInstance()); // Initialize attribute cache used to cache resources from packages. AttributeCache.init(mSystemContext); // Set up the Application instance for the system process and get started. mActivityManagerService.setSystemProcess(); }
可以看到AMS在这里启动。而这个函数startBootstrapServices是在run方法中运行。

public ActivityManagerService(Context systemContext) { mContext = systemContext; mFactoryTest = FactoryTest.getMode(); mSystemThread = ActivityThread.currentActivityThread(); Slog.i(TAG, "Memory class: " + ActivityManager.staticGetMemoryClass()); mHandlerThread = new ServiceThread(TAG, android.os.Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_FOREGROUND, false /*allowIo*/); mHandlerThread.start(); mHandler = new MainHandler(mHandlerThread.getLooper()); mFgBroadcastQueue = new BroadcastQueue(this, mHandler, "foreground", BROADCAST_FG_TIMEOUT, false); mBgBroadcastQueue = new BroadcastQueue(this, mHandler, "background", BROADCAST_BG_TIMEOUT, true); mBroadcastQueues[0] = mFgBroadcastQueue; mBroadcastQueues[1] = mBgBroadcastQueue; mServices = new ActiveServices(this); mProviderMap = new ProviderMap(this); // TODO: Move creation of battery stats service outside of activity manager service. File dataDir = Environment.getDataDirectory(); File systemDir = new File(dataDir, "system"); systemDir.mkdirs(); mBatteryStatsService = new BatteryStatsService(systemDir, mHandler); mBatteryStatsService.getActiveStatistics().readLocked(); mBatteryStatsService.getActiveStatistics().writeAsyncLocked(); mOnBattery = DEBUG_POWER ? true : mBatteryStatsService.getActiveStatistics().getIsOnBattery(); mBatteryStatsService.getActiveStatistics().setCallback(this); mProcessStats = new ProcessStatsService(this, new File(systemDir, "procstats")); mAppOpsService = new AppOpsService(new File(systemDir, "appops.xml"), mHandler); mGrantFile = new AtomicFile(new File(systemDir, "urigrants.xml")); // User 0 is the first and only user that runs at boot. mStartedUsers.put(0, new UserStartedState(new UserHandle(0), true)); mUserLru.add(Integer.valueOf(0)); updateStartedUserArrayLocked(); GL_ES_VERSION = SystemProperties.getInt("ro.opengles.version", ConfigurationInfo.GL_ES_VERSION_UNDEFINED); mConfiguration.setToDefaults(); mConfiguration.setLocale(Locale.getDefault()); mConfigurationSeq = mConfiguration.seq = 1; mProcessCpuTracker.init(); mCompatModePackages = new CompatModePackages(this, systemDir, mHandler); mIntentFirewall = new IntentFirewall(new IntentFirewallInterface(), mHandler); mStackSupervisor = new ActivityStackSupervisor(this); mTaskPersister = new TaskPersister(systemDir, mStackSupervisor); mProcessCpuThread = new Thread("CpuTracker") { @Override public void run() { while (true) { try { try { synchronized(this) { final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis(); long nextCpuDelay = (mLastCpuTime.get()+MONITOR_CPU_MAX_TIME)-now; long nextWriteDelay = (mLastWriteTime+BATTERY_STATS_TIME)-now; //Slog.i(TAG, "Cpu delay=" + nextCpuDelay // + ", write delay=" + nextWriteDelay); if (nextWriteDelay < nextCpuDelay) { nextCpuDelay = nextWriteDelay; } if (nextCpuDelay > 0) { mProcessCpuMutexFree.set(true); this.wait(nextCpuDelay); } } } catch (InterruptedException e) { } updateCpuStatsNow(); } catch (Exception e) { Slog.e(TAG, "Unexpected exception collecting process stats", e); } } } }; mLockToAppRequest = new LockToAppRequestDialog(mContext, this); Watchdog.getInstance().addMonitor(this); Watchdog.getInstance().addThread(mHandler); }
mStackSupervisor = new ActivityStackSupervisor(this); mTaskPersister = new TaskPersister(systemDir, mStackSupervisor);
这两句是ActivityStack & ActivityTask设置的地方。
public void setSystemProcess()就比较简单了,它不仅注册了自己一个server, 还注册了其他的server。
ServiceManager.addService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE, this, true); ServiceManager.addService(ProcessStats.SERVICE_NAME, mProcessStats); ServiceManager.addService("meminfo", new MemBinder(this)); ServiceManager.addService("gfxinfo", new GraphicsBinder(this)); ServiceManager.addService("dbinfo", new DbBinder(this)); if (MONITOR_CPU_USAGE) { ServiceManager.addService("cpuinfo", new CpuBinder(this)); } ServiceManager.addService("permission", new PermissionController(this));
二.Activit状态管理---ActivityStack
1.ActivityState
定义了如下状态:
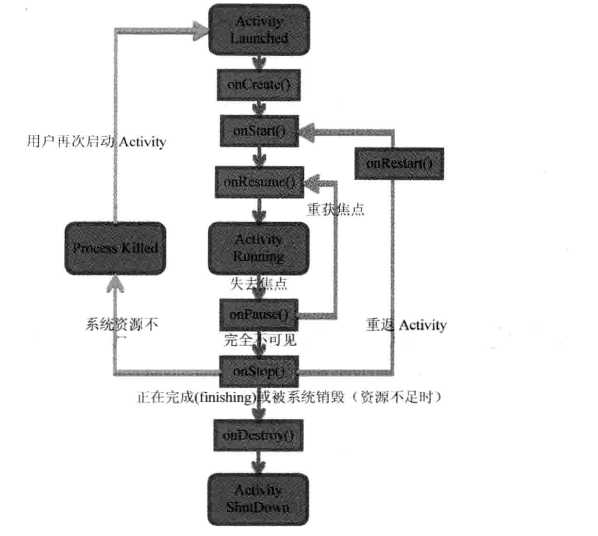
状态变化图。
三:startActivity
startActivity@ActivityManagerService.java
startActivityAsUser@ActivityManagerService.java
startActivityMayWait@ActivityStack.java
startActivityLocked@ActivityStack.java
sartActivityUncheckedLocked@ActivityStack.java
这5个函数先后关系,就是上面的顺序。
public final int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage, Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode, int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle options) { return startActivityAsUser(caller, callingPackage, intent, resolvedType, resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, startFlags, profilerInfo, options, UserHandle.getCallingUserId()); }
多了一个
UserHandle.getCallingUserId()
调用者的Userid值,通过bind机制获得的。
@Override public final int startActivityAsUser(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage, Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode, int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle options, int userId) { enforceNotIsolatedCaller("startActivity"); userId = handleIncomingUser(Binder.getCallingPid(), Binder.getCallingUid(), userId, false, ALLOW_FULL_ONLY, "startActivity", null); // TODO: Switch to user app stacks here. return mStackSupervisor.startActivityMayWait(caller, -1, callingPackage, intent, resolvedType, null, null, resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, startFlags, profilerInfo, null, null, options, false, userId, null, null); }
enforceNotIsolatedCaller 的目的是确认当前用户是否属于被隔离的对象。
接下来是 startActivityMayWait
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/deman/p/5004424.html