一生二,二生三,三生万物,基础永远是一个计算机人的立身之本。数据结构这门课程的分析奠定了工程师对各种平台中的容器类,集合类的理解基础,正如好多人所说的,如果你对某个平台的集合类理解的不透彻,很可能,你并不是不会使用那个平台上的代码,而是数据结构没理解透彻。
Windows NT平台上,MFC, ATL提供的集合类很少,而且功能很弱,这就导致了事实上的标准成了STL,相比于.Net 和 Java平台 STL在使用上稍显逊色,但是效率上应该是更胜一筹。但是不管哪种实现,都是基于数据结构的理论基础的,本文将讨论的是Java平台的高频集合类的使用方法。
首先要讨论的是LinkedList, 当我们需要经常性的插入或者删除元素的时候,我们的选择是LinkedList,因为没有移动元素的开销,但是Java中的LinkedList有一个怪癖,大家可能需要注意一下,每当需要删除元素的时候,需要先调用一次迭代器的next(), 然后是remove(), 使用起来稍显不自然。
public class LinkedListTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
List<String> a = new LinkedList<>();
a.add("Amy");
a.add("Carl");
a.add("Erica");
List<String> b = new LinkedList<>();
b.add("Bob");
b.add("Doug");
b.add("Frances");
b.add("Gloria");
// merge the words from b into a
ListIterator<String> aIter = a.listIterator();
//Iterator<String> aIter = a.iterator();
Iterator<String> bIter = b.iterator();
while (bIter.hasNext())
{
if (aIter.hasNext()) aIter.next();
aIter.add(bIter.next());
}
System.out.println(a);
// remove every second word from b
bIter = b.iterator();
while (bIter.hasNext())
{
bIter.next(); // skip one element
if (bIter.hasNext())
{
bIter.next(); // skip next element
bIter.remove(); // remove that element
}
}
System.out.println(b);
// bulk operation: remove all words in b from a
a.removeAll(b);
System.out.println(a);
}
}
LinkedList在对数据进行查找的时候,时间复杂度是O(n)的,当对查找需求比较高的时候就需要使用更加高效率的容器,比如HashSet, 其对元素的查找可以达到线性时间复杂度。
public class SetTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Set<String> words = new HashSet<String>(); // HashSet implements Set
long totalTime = 0;
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
while (in.hasNext())
{
String word = in.next();
long callTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
words.add(word);
callTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - callTime;
totalTime += callTime;
}
Iterator<String> iter = words.iterator();
for (int i = 1; i <= 20 && iter.hasNext(); i++)
System.out.println(iter.next());
System.out.println(". . .");
System.out.println(words.size() + " distinct words. " + totalTime + " milliseconds.");
}
}
HashSet对元素的迭代访问是随机顺序的,所以如果对顺序比较敏感,可能就要考虑TreeSet,插入后的元素自动排序,输出时是有序的集合。
public class TreeSetTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SortedSet<Item> parts = new TreeSet<>();
parts.add(new Item("Toaster", 1234));
parts.add(new Item("Widget", 4562));
parts.add(new Item("Modem", 9912));
System.out.println(parts);
SortedSet<Item> sortByDescription = new TreeSet<>(new
Comparator<Item>()
{
public int compare(Item a, Item b)
{
String descrA = a.getDescription();
String descrB = b.getDescription();
return descrA.compareTo(descrB);
}
});
sortByDescription.addAll(parts);
System.out.println(sortByDescription);
}
}
还记得数据结构中的小根堆吧?Java中也有相应的实现,他的名字是priorityQueue, 这个小根堆本身的迭代是无序的,但是小根堆保证每次删除的元素都是集合中最小的一个,也就是根。
public class PriorityQueueTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
PriorityQueue<GregorianCalendar> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.add(new GregorianCalendar(1906, Calendar.DECEMBER, 9)); // G. Hopper
pq.add(new GregorianCalendar(1815, Calendar.DECEMBER, 10)); // A. Lovelace
pq.add(new GregorianCalendar(1903, Calendar.DECEMBER, 3)); // J. von Neumann
pq.add(new GregorianCalendar(1910, Calendar.JUNE, 22)); // K. Zuse
System.out.println("Iterating over elements...");
for (GregorianCalendar date : pq)
System.out.println(date.get(Calendar.YEAR));
System.out.println("Removing elements...");
while (!pq.isEmpty())
System.out.println(pq.remove().get(Calendar.YEAR));
}
}
大家在使用Set类集合的时候有个不方便的地方就是,如果我需要查找一个元素,我得先知道这个元素的详细信息,所有的信息,而不能通过关键字查找,Map的出现解决了这个问题, Map本身是一个键值对,可以通过键来取值,这就大大方便了查找,但是付出的代价是多存储了一个键。
public class MapTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Map<String, Employee> staff = new HashMap<>();
staff.put("144-25-5464", new Employee("Amy Lee"));
staff.put("567-24-2546", new Employee("Harry Hacker"));
staff.put("157-62-7935", new Employee("Gary Cooper"));
staff.put("456-62-5527", new Employee("Francesca Cruz"));
// print all entries
System.out.println(staff);
// remove an entry
staff.remove("567-24-2546");
// replace an entry
staff.put("456-62-5527", new Employee("Francesca Miller"));
// look up a value
System.out.println(staff.get("157-62-7935"));
// iterate through all entries
for (Map.Entry<String, Employee> entry : staff.entrySet())
{
String key = entry.getKey();
Employee value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println("key=" + key + ", value=" + value);
}
}
}
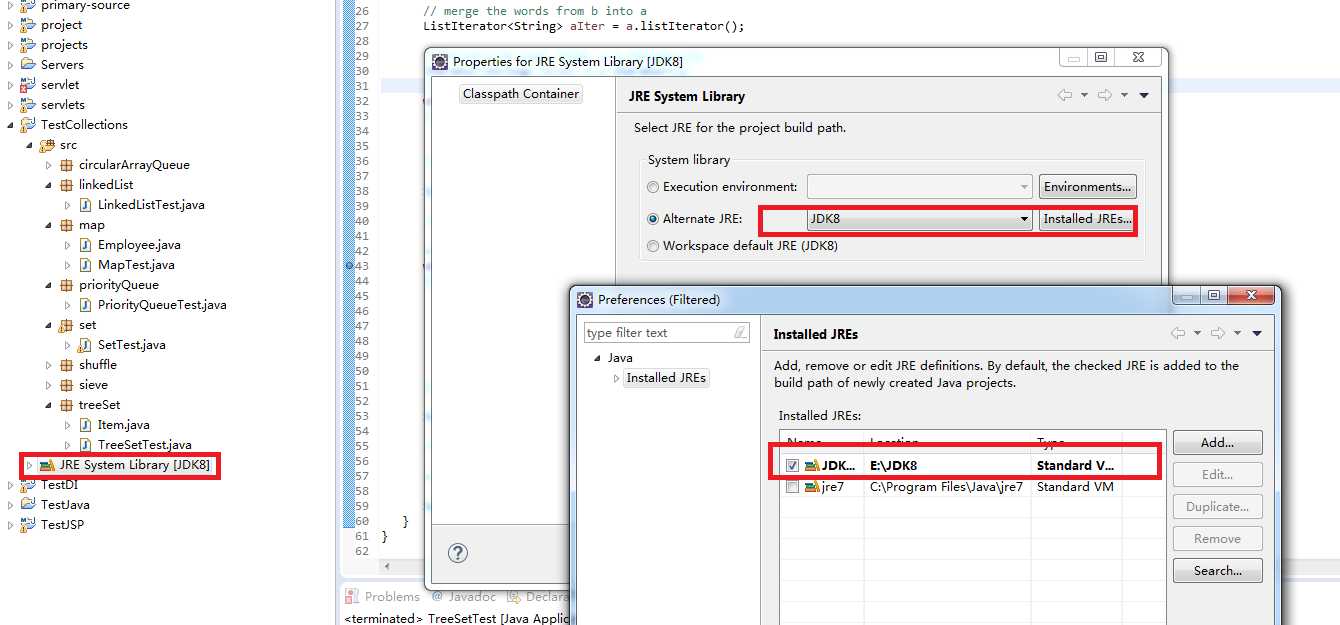
另外,Java语言本身是开源的,所有这些集合类的实现也是开源的,如果我们能够学习和调试这些大师们写的代码,无疑会使我们的学习事半功倍,那么怎么进行设置才能调试这些平台源码呢?
1. 必须安装JDK, JRE是不行的
2. 在配置项目的时候选择JDK下的JRE
3. 在你想研究的类或者函数上按键F3, 更多快捷键请参考下文, 具体设置请参看下图。
JAVA - Collections用法总结
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/crazyacking/p/crazyacking.html
