标签:
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html> 3 <head lang="en"> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title></title> 6 7 <script type="application/javascript"> 8 9 //基于伪装的继承 10 /** 11 * call方法: 12 语法:call([thisObj[,arg1[, arg2[, [,.argN]]]]]) 13 定义:调用一个对象的一个方法,以另一个对象替换当前对象。 14 说明: 15 call 方法可以用来代替另一个对象调用一个方法。call 方法可将一个函数的对象上下文从初始的上下文改变为由 thisObj 指定的新对象。 16 如果没有提供 thisObj 参数,那么 Global 对象被用作 thisObj。 17 */ 18 function Parent(){ 19 this.color = ["red","blue"]; 20 this.name = "Leon"; 21 } 22 23 function Child(){ 24 //在Child中的this明显应该是指向Child的对象 25 //当调用Parent方法的时候,而且this有时指向了Child 26 //此时就等于在这里完成this.color = ["red","blue"] 27 //也就是等于在Child中有了this.color的属性,这样也就变相的完成了集成 28 29 Parent.call(this); 30 31 //这种调用方式,Parent的上下文是Parent对象,根本无法实现继承 32 //Parent(); 33 } 34 35 var c1 = new Child(); 36 c1.color.push("green"); 37 console.info(c1.color); //["red", "blue", "green"] 38 var c2 = new Child(); 39 console.info(c2.color); //["red", "blue"] 40 console.info(c2.name); //Leon 41 42 43 function Parent2(name){ 44 this.color = ["red","blue"]; 45 this.name = name; 46 } 47 48 function Child2(name , age){ 49 //在Child中的this明显应该是指向Child的对象 50 //当调用Parent方法的时候,而且this有时指向了Child 51 //此时就等于在这里完成this.color = ["red","blue"] 52 //也就是等于在Child中有了this.color的属性,这样也就变相的完成了集成 53 54 this.age = age; 55 Parent2.call(this , name); 56 57 //这种调用方式,Parent的上下文是Parent对象,根本无法实现继承 58 //Parent(); 59 } 60 61 var c3 = new Child2("Leon" , 12); 62 c3.color.push("green"); 63 console.info(c3.color); //["red", "blue", "green"] 64 console.info(c3.name + " " + c3.age); //Leon 12 65 var c4 = new Child2("Ada" , 22); 66 console.info(c4.color); //["red", "blue"] 67 console.info(c4.name + " " + c4.age); //Ada 22 68 69 //这个例子中的意思就是用 add 来替换 sub,add.call(sub,3,1) == add(3,1) ,所以运行结果为:alert(4); 70 // 注意:js 中的函数其实是对象,函数名是对 Function 对象的引用。 71 function add(a,b){ 72 console.info(a+b); 73 } 74 function sub(a,b){ 75 console.info(a-b); 76 } 77 78 add.call(sub,3,1); //4 79 80 81 82 //call 的意思是把 animal 的方法放到cat上执行,原来cat是没有showName() 方法,现在是把animal 的showName()方法放到 cat上来执行,所以this.name 应该是 Cat 83 function Animal(){ 84 this.name = "Animal"; 85 this.showName = function(){ 86 console.info(this.name); 87 } 88 } 89 90 function Cat(){ 91 this.name = "Cat"; 92 } 93 94 var animal = new Animal(); 95 var cat = new Cat(); 96 97 //通过call或apply方法,将原本属于Animal对象的showName()方法交给对象cat来使用了。 98 //输入结果为"Cat" 99 animal.showName.call(cat,","); //Cat 100 animal.showName.apply(cat,[]);//Cat 101 102 103 104 105 // Animal.call(this) 的意思就是使用 Animal对象代替this对象,那么 Cat中不就有Animal的所有属性和方法了吗,Cat对象就能够直接调用Animal的方法以及属性了. 106 function Animal2(name){ 107 this.name = name; 108 this.showName = function(){ 109 console.info(this.name); 110 } 111 } 112 113 function Cat2(name){ 114 Animal2.call(this, name); 115 } 116 117 var cat2 = new Cat2("Black Cat"); 118 cat2.showName();//Black Cat 119 120 121 122 // 123 //实现多继承 124 // 很简单,使用两个 call 就实现多重继承了 125 // 当然,js的继承还有其他方法,例如使用原型链,这个不属于本文的范畴,只是在此说明call 的用法。 126 // 说了call ,当然还有 apply,这两个方法基本上是一个意思,区别在于 call 的第二个参数可以是任意类型,而apply的第二个参数必须是数组,也可以是arguments 127 // 还有 callee,caller.. 128 function Class10(){ 129 this.showSub = function(a,b){ 130 console.info(a-b); 131 } 132 } 133 134 function Class11() { 135 this.showAdd = function(a,b){ 136 console.info(a+b); 137 } 138 } 139 140 function Class2(){ 141 Class10.call(this); 142 Class11.call(this); 143 } 144 145 var c2 = new Class2(); 146 c2.showSub(1,2); 147 c2.showAdd(1,2); 148 149 </script> 150 151 </head> 152 <body> 153 154 </body> 155 </html>
基于伪造继承问题:
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html> 3 <head lang="en"> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title></title> 6 7 <script type="application/javascript"> 8 9 //基于伪造的继承存在问题: 10 11 12 function Parent2(name){ 13 this.color = ["red","blue"]; 14 this.name = name; 15 } 16 17 //由于使用伪造的方式,不会完成Child的原形指向Parent,所以say方法不存在, 18 //解决方法:将该say方法放入到Parent2中使用this来创建, 19 // 但是又有新问题:每个对象中又存在say方法,这样空间占用太大,所有也不会单独的方式实现 20 Parent2.prototype.say = function(){ 21 console.info(this.name); 22 } 23 24 25 function Child2(name , age){ 26 //在Child中的this明显应该是指向Child的对象 27 //当调用Parent方法的时候,而且this有时指向了Child 28 //此时就等于在这里完成this.color = ["red","blue"] 29 //也就是等于在Child中有了this.color的属性,这样也就变相的完成了集成 30 31 this.age = age; 32 /* 33 * 使用伪造的方式就可以吧自雷的构造函数参数传递到父类中 34 */ 35 Parent2.call(this , name); 36 37 //这种调用方式,Parent的上下文是Parent对象,根本无法实现继承 38 //Parent(); 39 } 40 41 var c3 = new Child2("Leon" , 12); 42 c3.color.push("green"); 43 console.info(c3.color); //["red", "blue", "green"] 44 console.info(c3.name + " " + c3.age); //Leon 12 45 c3.say(); //异常: Uncaught TypeError: c3.say is not a function 46 var c4 = new Child2("Ada" , 22); 47 console.info(c4.color); //["red", "blue"] 48 console.info(c4.name + " " + c4.age); //Ada 22 49 50 51 </script> 52 53 </head> 54 <body> 55 56 </body> 57 </html>
解决伪造继承的问题;
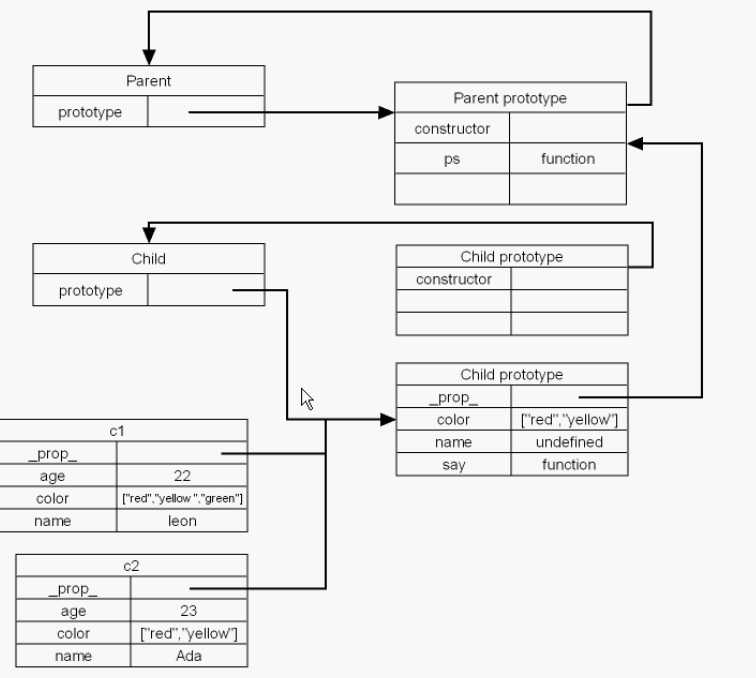
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html> 3 <head lang="en"> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title></title> 6 7 <script type="application/javascript"> 8 9 10 /** 11 * 组合的实现方式是属性通过伪造的方法实现,方法通过原形连的方式实现 12 * 13 */ 14 15 function Parent(name){ 16 this.color = ["red","blue"]; 17 this.name = name; 18 } 19 20 Parent.prototype.ps = function(){ 21 console.info(this.name + "[ " + this.color + "]"); 22 } 23 24 25 function Child(name , age){ 26 Parent.call(this,name); 27 this.age = age; 28 } 29 30 31 Child.prototype = new Parent(); 32 Child.prototype.say = function(){ 33 console.info(this.name + " " + this.age + " " + this.color); 34 } 35 36 var c1 = new Child("Leon" , 22) ; 37 c1.color.push("green"); 38 c1.say(); //Leon 22 red,blue,green 39 c1.ps(); //Leon[ red,blue,green] 40 var c2 = new Child("Ada" , 23) ; 41 c2.say(); //Ada 23 red,blue 42 </script> 43 44 </head> 45 <body> 46 47 </body> 48 </html>
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/a757956132/p/5454121.html